Unlocking Synergistic Muscles: The Key To Enhanced Movement And Efficiency
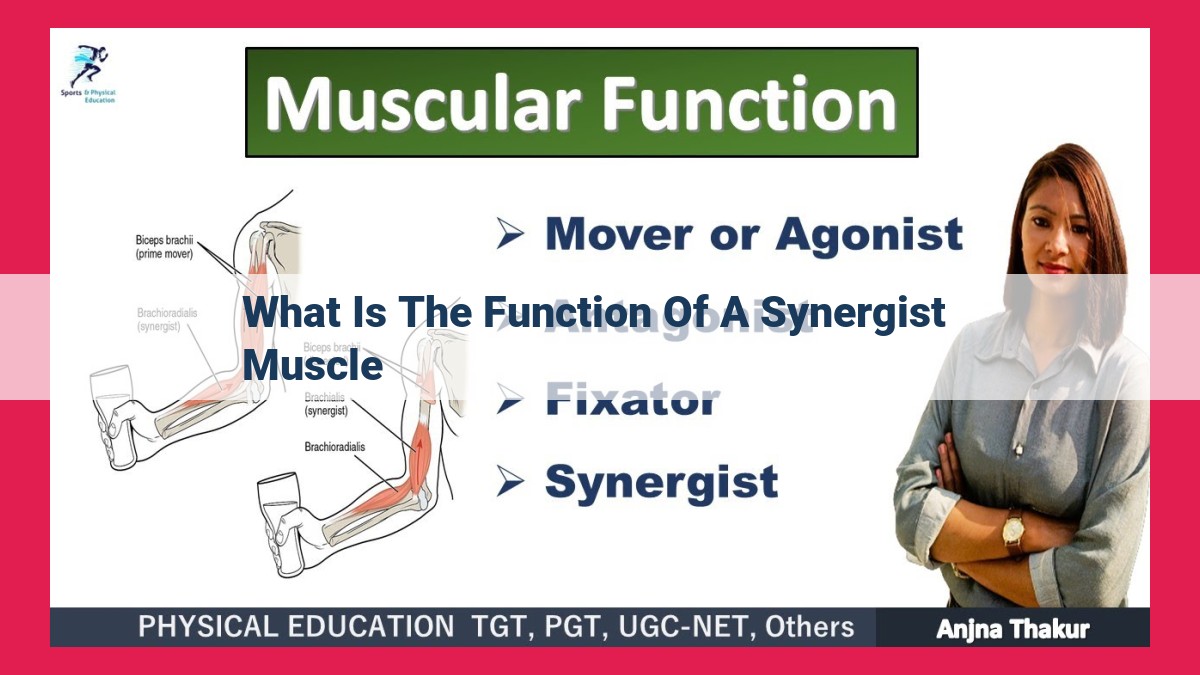
Synergist muscles are those that contract simultaneously with the prime mover muscle to aid in producing a specific movement. They assist the prime mover by enhancing its action, increasing the range of motion, and providing additional force. For instance, when the biceps brachii (prime mover) flexes the elbow, the brachioradialis (synergist) contracts to assist in the movement. By working together, synergist muscles enable coordinated and efficient body movements.
- Define synergist muscles and their role in coordinated muscle actions.
- Explain how synergist muscles work with prime movers and secondary movers.
In the intricate tapestry of our bodies, every muscle plays a vital role, harmoniously working together to execute the symphony of movement. Among these unsung heroes are the synergist muscles, like supporting actors who enhance the performance of the lead roles.
Defining Synergist Muscles and Their Role
Synergist muscles are those that assist the prime mover, the primary muscle responsible for initiating a movement. By working in synergy, they augment the force and range of motion achieved. For instance, in raising your arm, the deltoid muscle acts as the prime mover, while the supraspinatus and infraspinatus muscles act as synergists, stabilizing the shoulder.
The Interplay of Prime Movers, Secondary Movers, and Synergists
In the hierarchy of muscle movement, we have three primary roles:
- Prime Mover: The star of the show, directly responsible for executing the movement.
- Secondary Mover: Provides additional power or assists in controlling the movement.
- Synergists: Enhance the prime mover’s efficiency by stabilizing the joint, reducing friction, and fine-tuning movement trajectory.
Functions of Synergist Muscles
Synergist muscles play crucial roles in coordinating movements within the body. They work harmoniously with prime movers and secondary movers to ensure efficient and smooth muscle actions.
Role in Prime Mover Function
Prime movers are the primary muscles responsible for a specific movement, such as the biceps muscle in flexing the elbow. Synergist muscles assist the prime mover by reducing resistance and stabilizing the joint. For instance, the brachioradialis muscle helps the biceps flex the elbow by counteracting opposing forces.
Role in Secondary Mover Function
Secondary movers support prime movers by providing additional force or assisting with a different aspect of the movement. Synergist muscles enhance the movement produced by secondary movers. In the case of elbow flexion, the supinator muscle rotates the forearm, which allows the biceps to focus solely on flexing the elbow.
By working together, synergist muscles create a synergistic effect that improves the overall efficiency of muscle contraction. They help in:
- Reducing joint friction: By stabilizing the joint, synergist muscles decrease resistance, making movement smoother.
- Ensuring smooth transitions: Synergist muscles help coordinate transitions between different muscle actions, preventing abrupt changes in movement patterns.
- Maintaining joint stability: Synergist muscles stabilize joints, providing support and preventing excessive movement.
- Enhancing force production: Synergist muscles can contribute additional force to assist prime movers in generating more power during movements.
Related Concepts
Synergist muscles play a crucial role in coordinating muscle actions and influencing the overall movement of joints. Let’s delve into how they interact with other concepts:
Range of Motion
Synergist muscles work in harmony with antagonist muscles to determine the range of motion of a joint. While antagonist muscles contract to oppose the direction of movement, synergist muscles assist in the same direction, extending the range of motion beyond what the prime mover alone can achieve.
Joint Action
Synergist muscles contribute significantly to the complex movements of joints. For instance, in arm flexion, the biceps brachii acts as the prime mover. However, the brachioradialis and brachialis, as synergist muscles, enhance the flexion by stabilizing and aiding in the concentric contraction of the biceps.
Muscle Contraction and Relaxation
Coordinating muscle actions require precise contraction and relaxation of muscles. Synergist muscles contract simultaneously with the prime mover, enhancing its force and efficiency. Simultaneously, antagonist muscles relax to allow the desired movement to occur. This coordinated interplay of muscle activity is essential for smooth and controlled movements.
Importance of Synergist Muscles
Functions of Synergist Muscles
Synergist muscles play a crucial role in the efficient execution of body movements. They work in synergy with prime movers to enhance the primary movement. For instance, when the biceps brachii muscle (prime mover) flexes the elbow joint, the brachialis muscle (synergist) contracts to assist this motion. This coordination ensures a smooth and powerful movement.
Coordinated Muscle Contractions
Synergist muscles are essential for coordinated muscle contractions. They work in harmony with other muscle groups to control and stabilize movements. In the case of walking, the quadriceps muscles (prime movers) extend the knee joint, while the hamstrings muscles (synergists) contract to limit excessive knee extension. This coordinated effort creates a balanced and efficient gait.
Key Takeaways
- Synergist muscles work together with prime movers to enhance and refine body movements.
- They assist in the execution of coordinated muscle contractions, ensuring smooth and controlled motions.
- Synergist muscles are vital for efficient and coordinated body functions, such as walking, running, and manipulating objects.