Understanding Precipitating Factors: Essential For Effective Medical Condition Management
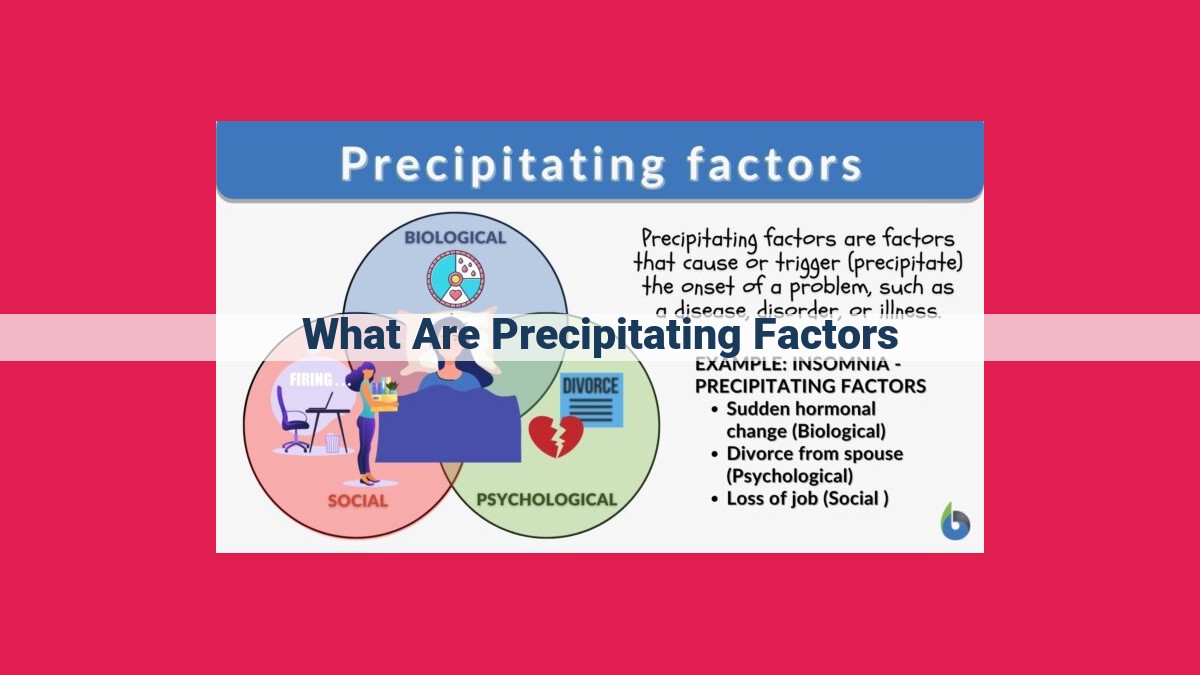
Precipitating factors are triggers that initiate or worsen medical conditions. They can include stress, sleep deprivation, hormonal changes, allergens, infections, medications, environmental factors, trauma, and substance abuse. These factors impact various physiological processes, hormonal balance, immune function, and neurotransmitter levels, leading to the onset or exacerbation of symptoms. Understanding precipitating factors is crucial for effective management of medical conditions by identifying and addressing potential triggers.
Unraveling the Enigmatic World of Precipitating Factors
In the intricate tapestry of human health, there lies a hidden force capable of weaving a tangled web of challenges: precipitating factors. These are the enigmatic triggers that lurk in the shadows, waiting to ignite or exacerbate medical ailments.
The Role of Stress, the Silent Saboteur
Like a relentless storm, stress can wreak havoc on our well-being. Whether it strikes as a sudden surge or an enduring torment, stress has the power to unleash a torrent of physiological changes that can fuel conditions like mood disorders, irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), and incessant headaches. It plays a manipulative game, altering hormonal balances, disrupting sleep, and weakening our immune defenses.
Sleep Deprivation: A Gateway to Misery
When the gentle embrace of slumber eludes us, our bodies and minds embark on a treacherous journey. _Sleep deprivation casts a sinister shadow, robbing us of vitality and clouding our cognitive abilities. It orchestrates a symphony of hormonal imbalances, elevates stress hormone levels, and leaves our immune system vulnerable to attack.
Hormonal Fluctuations: A Dance of Extremes
Hormones, the messengers of our bodies, can become unruly dance partners, swaying in unpredictable rhythms. _Hormonal changes associated with menstruation, menopause, and pregnancy can trigger mood swings, PMS, hot flashes, and a profound sense of fatigue. They hold sway over neurotransmitter levels in the brain, dictating our emotional landscape.
Allergens: Invisible Agents of Discomfort
_Allergens, like mischievous sprites, float in the air, waiting to pounce on unsuspecting victims. Pollen, dust mites, and pet dander are just a few of their cunning disguises. Once they infiltrate our bodies, they trigger a chain reaction, summoning the immune system to mount an inflammatory offensive, leaving us with a symphony of sneezes, watery eyes, and congested breathing.
Infections: Battles Fought Within
_Infections, both viral and bacterial, are relentless adversaries that wage war against our bodies. Respiratory illnesses, gastrointestinal disorders, and urinary tract infections (UTIs) are just a few of the battlegrounds where they wreak havoc. As they ravage our systems, they evoke a thunderous immune response, igniting inflammation and a myriad of uncomfortable symptoms.
Medications: A Double-Edged Sword
While medications can be lifelines in the battle against disease, they can also play the role of treacherous allies, morphing into precipitating factors. _Adverse drug reactions, drug interactions, and medication side effects can disrupt body chemistry, interfering with normal physiological processes and causing a range of unexpected consequences.
Stress: A Hidden Precipitator of Health Concerns
In the tapestry of our health, precipitating factors play a pivotal role, often lurking in the shadows, ready to trigger or exacerbate medical conditions. Among these, stress stands out as a potent force, shaping our physical and mental well-being.
Acute and Chronic Stress: A Double-Edged Sword
Stress, in its fleeting or persistent forms, exerts a profound impact on our bodies. Acute stress, like a sudden shock, can trigger a cascade of physiological responses, preparing us for immediate threats. However, chronic stress, a persistent burden, can wreak havoc on our health.
Mood Disorders: Stress as a Shadowed Catalyst
Stress can cast a dark shadow over our emotional landscape, triggering mood disorders such as depression and anxiety. It disrupts the delicate balance of neurotransmitters, the chemical messengers in our brains, leading to a cascade of negative emotions.
IBS and Headaches: Stress as an Unwelcome Guest
Stress doesn’t just affect our minds; it also wreaks havoc on our bodies. Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) and headaches are common ailments that can be ignited or worsened by stress. It disrupts the delicate functioning of our digestive system and nervous system, causing discomfort and pain.
The Stress-Sleep-Stress Cycle: A Vicious Dance
Sleep, our body’s sanctuary, is often disrupted by stress. It alters our sleep-wake cycle, making it difficult to fall or stay asleep. This sleep deprivation, in turn, intensifies stress levels, creating a vicious cycle that can wreak havoc on our well-being.
Immune System: Under Stress, Under Attack
Stress doesn’t spare our immune system, our body’s defense mechanism. It suppresses the immune response, making us more vulnerable to infections and compromising our ability to fight off illness.
Breaking the Cycle: Stress Management for a Healthier You
While stress is an inevitable part of life, managing its impact is crucial. Effective stress management techniques, such as exercise, mindfulness, and spending time in nature, can help mitigate its harmful effects and promote overall well-being.
Remember, understanding and addressing precipitating factors like stress is essential for maintaining optimal health. By recognizing its influence and implementing strategies to manage it, we can cultivate a life of resilience and well-being.
Sleep Deprivation: A Precipitating Factor for Health Woes
Imagine sacrificing a night’s slumber for a pressing deadline or indulging in late-night escapades. While this may seem harmless, chronic sleep deprivation can trigger a cascade of health concerns that linger beyond momentary fatigue. This blog delves into the profound impact of sleep deprivation on our well-being and explores how it can pave the way for various medical conditions.
Fatigue and Cognitive Decline
Sleep deprivation’s most evident effect is unrelenting fatigue, which saps our energy and impairs our daily functioning. It’s like carrying a heavy weight on our shoulders, making even simple tasks feel like an uphill battle. Moreover, our cognitive abilities suffer, leading to difficulty concentrating, reduced focus, and impaired decision-making.
Compromised Immune Function
Sleep is crucial for our immune system to recharge and bolster its defenses. When we’re sleep-deprived, our body’s ability to fight off infections is weakened. This leaves us more susceptible to colds, flu, and other illnesses. Studies have even linked chronic sleep deprivation to an increased risk of chronic diseases like heart disease and diabetes.
Hormonal Imbalance and Stress
Sleep deprivation disrupts the delicate balance of our hormones. The hormone leptin, responsible for suppressing appetite, decreases, while ghrelin, which stimulates hunger, increases. This hormonal fluctuation can lead to weight gain and increased cravings. Sleep deprivation also elevates levels of stress hormones, such as cortisol and adrenaline, which can exacerbate symptoms of anxiety and depression.
By understanding the precipitating role of sleep deprivation in various health conditions, we can prioritize our slumber and safeguard our well-being. Make a conscious effort to establish regular sleep-wake cycles, create a conducive sleep environment, and seek professional help if persistent sleep problems arise. Rest assured, the benefits of restful nights far outweigh the temporary pleasures of sacrificing sleep.
Hormonal Changes: A Hidden Trigger for Health Disruptions
Hormones, the chemical messengers that regulate our bodies, play a crucial role in our overall health and well-being. However, hormonal fluctuations can also act as precipitating factors, triggering or worsening a wide range of medical conditions.
Menstrual Cycle and PMS
Throughout the menstrual cycle, women experience fluctuating levels of estrogen and progesterone. These changes can lead to a variety of symptoms, including mood swings, irritability, bloating, and breast tenderness. Some women may experience more severe symptoms known as premenstrual syndrome (PMS).
Menopause
As women approach menopause, their estrogen levels decline, triggering a cascade of physical and emotional changes. Common symptoms include hot flashes, night sweats, mood swings, and vaginal dryness. These symptoms can significantly impact a woman’s quality of life.
Pregnancy
Pregnancy is a time of significant hormonal upheaval. Estrogen and progesterone levels soar, creating a supportive environment for the developing baby. However, these hormonal changes can also lead to nausea, vomiting, mood swings, and fatigue.
The Hormone-Neurotransmitter Connection
Hormonal fluctuations don’t just affect physical symptoms; they also have a profound impact on the brain. Hormones interact with neurotransmitters, the chemicals that transmit signals between neurons. By altering neurotransmitter levels, hormonal changes can influence our mood, sleep, and overall well-being.
For example, a decline in estrogen levels during menopause can lead to a decrease in serotonin, a neurotransmitter linked to mood regulation. This drop in serotonin can contribute to mood swings and depression.
Managing Hormonal Triggers
Understanding the role of hormonal changes as precipitating factors is crucial for managing health conditions related to them. Lifestyle modifications, such as regular exercise, a healthy diet, and stress reduction techniques, can help regulate hormones and reduce the severity of symptoms. In some cases, hormonal therapy or other medical interventions may be necessary to address hormonal imbalances.
Hormonal changes are a natural part of life. However, by being aware of their potential to act as precipitating factors, we can take steps to manage their effects and maintain our health and well-being. By recognizing and addressing hormonal triggers, we can unlock a more harmonious and fulfilling life.
Allergens: Unseen Triggers Unleashing Inflammatory Storms
In the intricate symphony of our bodies, allergens play a discordant melody, acting as concealed conductors that orchestrate unpleasant symptoms. These stealthy invaders can lurk in various forms, such as pollen, dust mites, and pet dander, each carrying the potential to trigger a cascade of reactions within our immune system.
Upon exposure to these insidious foes, our body’s defense mechanism goes into overdrive, recognizing them as foreign invaders. This immune overture triggers the release of histamine and other inflammatory mediators, leading to a symphony of symptoms that can range from sneezing, runny nose, and itchy eyes to wheezing, shortness of breath, and even anaphylaxis.
The inflammatory surge caused by allergens can affect various tissues and organs, including the respiratory system, skin, and gastrointestinal tract. This inflammatory response can manifest as hay fever, asthma, eczema, and food allergies, among other conditions.
Understanding the role of allergens as precipitating factors is crucial for effectively managing their impact. By identifying the specific allergens that trigger symptoms, individuals can take steps to avoid exposure or minimize their presence in their environment.
Infections: The Hidden Culprit in Health Issues
Understanding the Role of Infections as Precipitating Factors
Illness strikes when we least expect it. But what if certain events or conditions could trigger or worsen these ailments? These triggers are known as precipitating factors, and infections are one of them. Let’s explore how infections can play a significant role in our health.
Respiratory Illnesses: Cough, Cold, and Beyond
Respiratory infections, caused by viruses or bacteria, are common precipitating factors for conditions like the common cold, flu, pneumonia, and bronchitis. These infections invade the airways, causing inflammation and irritation. The body’s immune response triggers symptoms such as coughing, runny nose, and fever. In severe cases, infections can spread to the lungs and other respiratory organs, leading to more serious complications.
Gastrointestinal Disorders: From Diarrhea to Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS)
Infections can also disrupt the digestive system. Viral or bacterial infections can cause gastroenteritis, resulting in symptoms like diarrhea, vomiting, and abdominal pain. In some individuals, infections can trigger or worsen irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), a chronic condition characterized by abdominal pain, bloating, and alternating diarrhea and constipation.
Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs): A Painful Surprise
Urinary tract infections (UTIs) are caused by bacteria that enter the urinary tract. They can range from mild to severe, causing symptoms like burning during urination, increased frequency, and lower abdominal pain. If left untreated, UTIs can ascend to the kidneys, leading to more serious complications.
How Infections Trigger Symptoms
Infections trigger the body’s immune response. The immune system sends white blood cells to fight the infection, releasing inflammatory chemicals that lead to symptoms. These chemicals can cause fever, pain, and swelling. In the case of respiratory infections, inflammation can block airways, causing coughing and shortness of breath. In gastrointestinal infections, inflammation can irritate the digestive tract, leading to diarrhea and vomiting.
Infections can act as precipitating factors, triggering or worsening various health conditions. By understanding the role of infections, we can be more aware of the risks and take preventive measures. Proper hygiene, vaccination, and prompt medical attention for infections are crucial steps in maintaining good health.
Medications as Precipitating Factors
Medications play a critical role in managing various health conditions. However, they can also act as precipitating factors, triggering or worsening existing conditions. Understanding the potential for adverse drug reactions, drug interactions, and medication side effects is essential for both patients and healthcare providers.
Adverse Drug Reactions
Adverse drug reactions occur when a medication produces an unexpected and harmful response in the body. These reactions can range from mild (e.g., nausea, rash) to life-threatening (e.g., allergic reactions, organ failure). Factors such as individual susceptibility, dosage, and duration of treatment can influence the risk of an adverse drug reaction.
Drug Interactions
When multiple medications are taken simultaneously, they can interact with each other, leading to unexpected effects. These interactions can either enhance or diminish the therapeutic effects of the medications or cause new side effects. Understanding potential drug interactions is crucial to optimize treatment and minimize risks.
Medication Side Effects
All medications have the potential to cause side effects, which are unwanted responses to the medication that are typically predictable and dose-dependent. While most side effects are mild, some can be severe and require medical intervention. It is essential to weigh the potential benefits of medication against the potential risks of side effects when making treatment decisions.
Altered Body Chemistry and Physiological Processes
Medications can alter body chemistry and interfere with normal physiological processes. For example, antibiotics can disrupt the balance of gut bacteria, leading to digestive issues. Pain relievers can interfere with **blood clotting, increasing the risk of bleeding. It is important for patients to be aware of the potential impact of medications on their bodies and to report any unusual symptoms to their healthcare provider.
Medications can be powerful tools for managing health conditions, but it is essential to be aware of their potential to act as precipitating factors. Understanding adverse drug reactions, drug interactions, and medication side effects is crucial for ensuring safe and effective treatment. Patients should work closely with their healthcare providers to identify and manage potential risks associated with medication use.
Environmental Factors: Precipitating Forces Shaping Our Health
The intricate tapestry of our health is woven not only by our genes but also by external factors that can act as triggers, exacerbating or initiating a cascade of medical conditions. Among these external precipitating forces, environmental factors play a significant role.
Extreme Temperatures
Imagine stepping out into a sweltering desert, where the blistering sun beats relentlessly upon your skin. The heat stress on your body triggers a series of physiological responses. Your blood vessels dilate, increasing blood flow to the skin’s surface in an attempt to cool down. This diversion of blood causes fatigue, headaches, and dizziness. Prolonged exposure to extreme heat can lead to heat exhaustion and, in severe cases, heat stroke.
Conversely, exposure to extreme cold poses its own set of challenges. Your body instinctively shivers to generate heat, consuming precious calories and increasing your risk of hypothermia. Cold temperatures can also constrict blood vessels, making it harder for blood to reach your extremities and causing numbness, tingling, and even frostbite.
Noise Pollution
Modern society’s relentless hum can become an insidious threat to our well-being. Excessive noise can disrupt our sleep, leading to fatigue, irritability, and difficulty concentrating. It can also increase stress hormone levels, contributing to conditions such as high blood pressure and heart disease.
Air Pollution
The air we breathe can be laden with harmful pollutants, including particulate matter, ozone, and nitrogen dioxide. These pollutants can penetrate deep into our lungs, triggering inflammation and respiratory problems. They can also increase our risk of asthma, chronic bronchitis, and other cardiovascular diseases.
While we cannot always control our environment, understanding the precipitating role that certain environmental factors play is essential for maintaining our health. By reducing our exposure to extreme temperatures, noise pollution, and air pollution, we can mitigate their detrimental effects and create a more conducive environment for our physical and mental well-being.
Trauma as a Precipitating Factor in Mental Health Conditions
Trauma’s Impact on Mental Health
Experiencing trauma can significantly impact an individual’s mental well-being. Trauma encompasses both physical and emotional experiences that are overwhelming and can disrupt brain functioning. These experiences often trigger intense stress responses that can lead to the development of Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD), anxiety disorders, and depressive disorders.
Overwhelming Stress Responses
Trauma exposes an individual to extreme stress, which activates the body’s fight-or-flight response. This response is a natural survival mechanism designed to prepare the body to respond to danger. However, in the case of trauma, this response can become chronic and lead to a heightened state of arousal, anxiety, and fear.
Brain Function and Trauma
The constant stress response triggered by trauma can disrupt brain functioning. The brain’s amygdala, responsible for processing emotions, especially fear, becomes overactive, while the hippocampus, involved in memory formation, is impaired. This disruption causes difficulty in regulating emotions, forming new memories, and concentration problems.
Types of Trauma
Trauma can manifest in various forms, including:
- Physical abuse
- Emotional abuse
- Sexual abuse
- Natural disasters
- Accidents
- War
Trauma has far-reaching effects on mental health, potentially triggering PTSD, anxiety disorders, and depressive disorders. Understanding the role of trauma in mental health conditions can help individuals seek appropriate support and develop coping mechanisms to manage the impact of these traumatic experiences.
Substance Abuse as a Precipitating Factor in Illnesses
Substance abuse, whether it is alcohol, drugs, or nicotine, can significantly impact our physical and mental well-being. Its detrimental effects go beyond addiction and can act as a precipitating factor for various illnesses, triggering or worsening their symptoms.
Overdose and Associated Risks:
Excessive consumption of substances like alcohol and drugs can lead to overdoses, which can be life-threatening. When taken in high doses, these substances impair the brain’s vital functions, including breathing and heart rate, increasing the risk of organ damage and death.
Addiction and Its Consequences:
Substance abuse can lead to addiction, characterized by compulsive use and an inability to control substance intake. This addiction not only affects the individual’s physical and mental health but also impacts their relationships, work, and overall quality of life.
Mental Health Disorders:
Substance abuse can also trigger or worsen mental health disorders such as anxiety, depression, and psychosis. Alcohol and drugs alter brain chemistry, disrupting the balance of neurotransmitters that regulate mood, behavior, and cognition.
Physiological Disruptions:
Substance abuse can disrupt various bodily systems. Excessive alcohol consumption can damage the liver, kidneys, and heart. Drug abuse can impair immune function, increasing the risk of infections and other health complications. Nicotine addiction can constrict blood vessels, leading to heart problems and reduced oxygen flow throughout the body.
Understanding the Mechanisms:
Substance abuse alters brain chemistry by mimicking or blocking the effects of natural neurotransmitters. It can impair the brain’s reward system, leading to increased cravings and compulsive use. Additionally, substances can affect the production of hormones, disrupt sleep-wake cycles, and damage brain cells.
Seeking Help and Breaking the Cycle:
If you or someone you know is struggling with substance abuse, it is crucial to seek professional help. Treatment programs can provide support, guidance, and evidence-based interventions to overcome addiction and address its underlying causes. Breaking the cycle of substance abuse not only improves physical and mental health but also enhances overall well-being and quality of life.