Understanding The Neutron Number: Determining Neutron Count In Neon-20

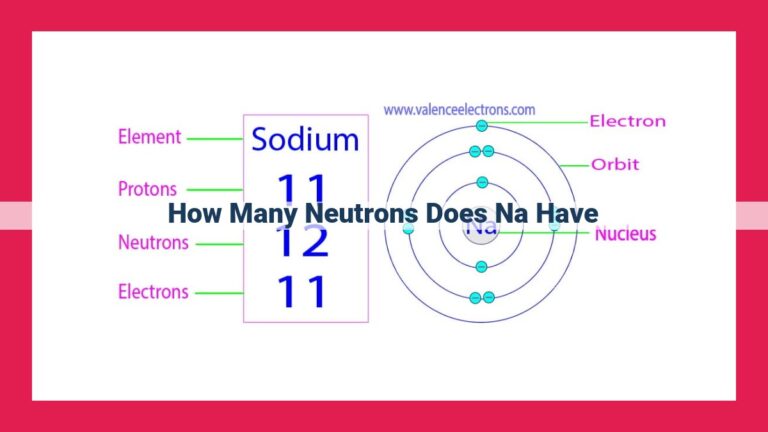
Neon, an element with atomic number 10, has a most common isotope, Neon-20. To determine the number of neutrons in Neon, we calculate the neutron number using the formula: Neutron number = Mass number – Atomic number. Substituting the mass number (20) and atomic number (10) of Neon-20, we get 10 neutrons. The neutron number plays a crucial role in determining the stability and properties of atomic nuclei.
How Many Neutrons are in Neon?
In the vast expanse of the atomic realm, neutrons play an enigmatic yet crucial role in shaping the structure and properties of elements. Neon, an abundant gas renowned for its vibrant glow, is no exception to this atomic dance. With 10 protons swirling around its nucleus, Neon’s atomic identity is firmly established. But what about its enigmatic neutron companions? Let’s embark on a neutron-hunting expedition to unravel this atomic mystery.
Understanding the Neutron Number
Neutrons, the silent partners of atomic nuclei, lurk within the heart of atoms, nestled alongside their positively charged counterparts, protons. The neutron number of an atom, a fundamental property, represents the count of these enigmatic particles residing in its nucleus. This number holds immense significance, influencing the stability and behavior of atomic nuclei.
Exploring Neon’s Atomic Landscape
Neon, with 10 protons dancing within its nucleus, is an element of particular interest. Its atomic number, a unique fingerprint for each element, determines Neon’s position on the periodic table and defines its chemical characteristics. Understanding Neon’s atomic number is a crucial step in our neutron-counting journey.
Unveiling the Mass Number
The mass number of an atom, a hefty sum, encompasses both protons and neutrons nestled within its nucleus. This number provides a glimpse into the atom’s overall mass and its location on the mass spectrum. For Neon, its most prevalent isotope, Neon-20, boasts a mass number of 20.
Calculating the Neutron Number
With Neon’s atomic number (10) and mass number (20) at our disposal, we can now unveil the elusive neutron number. By employing the formula Neutron number = Mass number – Atomic number, we embark on a mathematical expedition:
Neutron number = 20 (Mass number) - 10 (Atomic number)
Neutron number = 10
Eureka! Neon-20, the most abundant isotope of Neon, harbors 10 neutrons within its nucleus.
Our neutron-counting adventure has led us to the conclusion that Neon-20, the most common isotope of Neon, proudly boasts 10 neutrons within its nucleus. This neutron number plays a pivotal role in determining the stability and properties of Neon, shaping its atomic destiny.
Unraveling the Mystery of Neutrons in Neon
Understanding Neutron Number
In the heart of every atom lies a tiny nucleus, a microscopic realm where protons and neutrons reside. Neutrons, the uncharged companions of protons, play a pivotal role in shaping the structure and stability of atomic nuclei. Neutron number, aptly named, refers to the number of neutrons harbored within the nucleus of a particular atom.
Closely related to neutron number are other fundamental concepts in nuclear physics. Nucleon number encompasses the total number of both protons and neutrons, while atomic mass represents the combined weight of all these particles.
The formula for calculating neutron number is straightforward: Neutron number = Mass number – Atomic number. The mass number signifies the total number of protons and neutrons, while the atomic number indicates the number of protons alone.
The Significance of Neutron Number
Neutron number holds immense significance in determining the properties and behavior of atomic nuclei. It influences the stability of an atom, dictating whether it will decay or remain intact. Moreover, neutron number plays a crucial role in determining the elemental identity of an atom, as it helps distinguish between isotopes of the same element.
Calculating Neutron Number in Neon
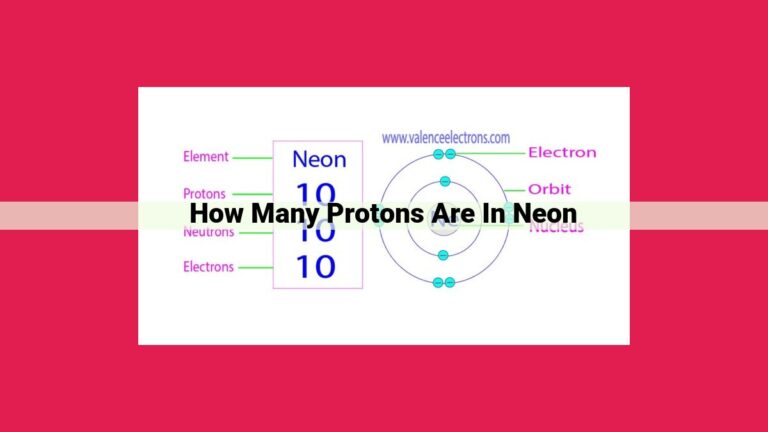
Neon, a noble gas with the symbol Ne, holds an atomic number of 10, indicating that its nucleus harbors 10 protons. The most common isotope of neon, known as Neon-20, possesses a mass number of 20. Using the formula for neutron number, we can unravel the mystery:
- Neutron number = Mass number – Atomic number
- Neutron number = 20 – 10
- Neutron number = 10
Therefore, Neon-20 possesses 10 neutrons within its nucleus. This information enriches our understanding of neon’s atomic structure and its behavior in various chemical reactions.
Unveiling the Secrets of Neon: A Journey into the Heart of Atoms
In the vast realm of atoms, understanding the intricacies of their building blocks is paramount. Among these fundamental components, neutrons hold a unique significance, influencing the stability and properties of atomic nuclei. In this blog, we embark on an enlightening journey to uncover the fascinating world of neutrons, with a particular focus on the element Neon.
Defining Atomic Number: The Identity Card of Elements
Every atom possesses a unique identity determined by its atomic number. This number represents the count of protons residing within its nucleus. Protons, along with electrons, define an element’s chemical behavior and distinguish it from all other elements.
Neon’s Atomic Number: Unveiling its Essence
In the periodic table, Neon proudly occupies position number 10. This number signifies that each Neon atom contains 10 protons within its nucleus, establishing its singular identity as the Neon element.
Understanding the Significance of Atomic Number
The atomic number not only defines an element’s identity but also plays a pivotal role in shaping its chemical properties. Elements with similar atomic numbers tend to exhibit similar chemical behavior, forming the basis of the periodic table’s organization.
Atomic Number and Neon’s Chemical Nature
Neon’s atomic number of 10 positions it within the noble gases group. Noble gases, known for their exceptional stability and low reactivity, share the common trait of having a full outermost electron shell. This configuration explains Neon’s reluctance to form chemical bonds, contributing to its inert nature.
In summary, the atomic number serves as a crucial identifier for elements, determining their unique properties and chemical behavior. Neon, with an atomic number of 10, proudly stands among the noble gases, showcasing its distinctive characteristics.
Mass Number: Unveiling the Heart of an Atom
In our exploration of the atomic realm, we encounter a fundamental concept that defines the physical essence of each element: the mass number. It represents the total number of protons and neutrons nestled within an atom’s nucleus, the very core of its existence. The mass number not only quantifies the atomic weight but also sheds light on the stability and properties of different isotopes within an element.
A Symphony of Nucleons: Mass Number and Its Companions
The mass number forms an intricate dance with various nuclear components. It shares a close relationship with the nucleon number, which encapsulates the combined count of protons and neutrons. This total serves as a unique identifier for each isotope, a variation of the same element with differing neutron content. The mass number also influences the atomic weight, a weighted average that considers the abundance of various isotopes within an element.
Neon-20: A Neon Isotope in the Spotlight
Among the myriad of Neon isotopes, Neon-20 holds a prominent position as the most prevalent form. Its mass number, as its name suggests, stands at 20. This pivotal number reflects the sum of its 10 protons and 10 neutrons. With this configuration, Neon-20 embodies the quintessence of atomic stability, boasting an exceptionally stable nucleus.
By unraveling the mass number of Neon-20, we uncover a crucial aspect of its atomic identity. It not only distinguishes Neon-20 from other isotopes but also hints at its unique physical and chemical properties. This, in turn, shapes the behavior and applications of Neon-20 in scientific and industrial realms.
How Many Neutrons Are in Neon: Delving into the Atomic Structure
Navigating the Realm of Neutrons
In the captivating world of atoms, neutrons stand as silent guardians, their presence shaping the very heart of these tiny building blocks. Neutron number, a crucial concept in nuclear physics, unveils the number of neutrons residing within an atom’s nucleus. Side by side with protons and electrons, neutrons play a pivotal role in determining an element’s stability and its position on the periodic table.
Neon’s Atomic Identity
Neon, a noble gas renowned for its radiant glow, holds an atomic number of 10. This number signifies the presence of 10 protons in Neon’s nucleus, the fundamental particles that lend each element its unique identity and chemical characteristics.
Uncovering the Mass Number
Mass number embodies the combined count of protons and neutrons dwelling in an atom’s nucleus. It holds a deep connection to an element’s atomic weight, a crucial parameter in myriad scientific endeavors. For the most prevalent Neon isotope, known as Neon-20, the mass number ascends to 20.
Calculating the Neutron Number: A Journey into Neon’s Core
With the atomic number and mass number of Neon-20 in hand, we embark on a quest to uncover the number of neutrons concealed within its nucleus. A simple yet potent formula guides our path:
Neutron number = Mass number – Atomic number
Substituting Neon-20’s atomic number (10) and mass number (20) into this equation, we arrive at:
Neutron number = 20 – 10 = 10
Unveiling the Answer: Neon’s Neutron Count
Lo and behold, our meticulous calculations reveal that Neon-20 possesses 10 neutrons. These neutrons, in concert with the 10 protons, form the very core of Neon’s atoms, endowing them with their distinctive properties and shaping their behavior in the enchanting realm of chemistry.
Our journey into the atomic nucleus of Neon has led us to the profound understanding that Neon-20, the most abundant Neon isotope, harbors 10 neutrons. This knowledge deepens our comprehension of Neon’s atomic structure, paving the way for further exploration into the fascinating world of nuclear physics and the intricate tapestry of elements that make up our universe.