Understanding Neon: Atomic Number And Its Significance For Element Identification
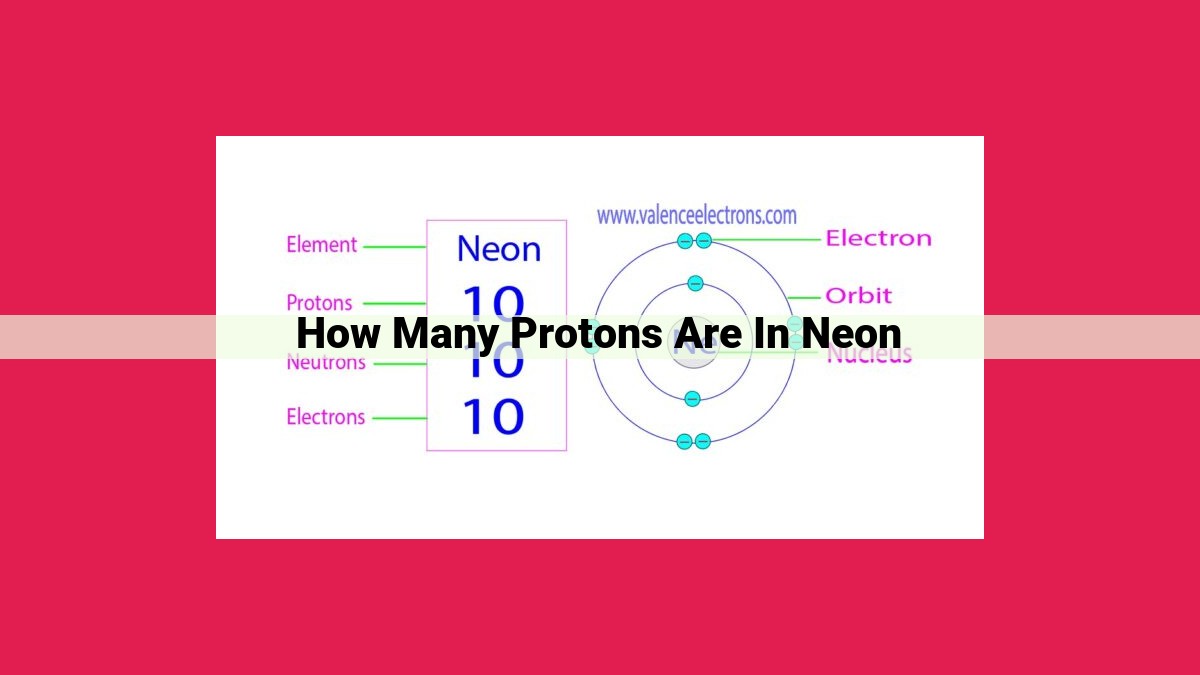
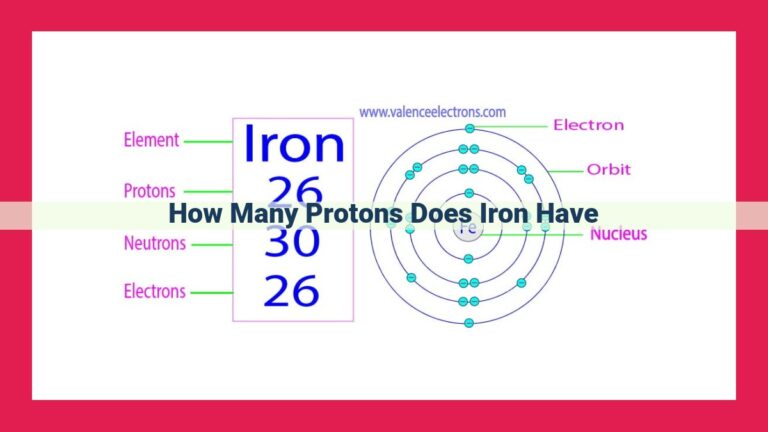
Neon, with an atomic number of 10, possesses 10 protons in its nucleus, as atomic number represents the number of protons in an element. These protons, carrying a positive charge of +1, contribute to an atom’s overall electrical charge. The atomic number also determines an element’s identity, making it crucial for distinguishing neon from other elements.
Understanding the Atomic Number: Neon’s Identity Card
In the vast realm of chemistry, knowing the identity of each element is crucial. And one key piece of information that helps us distinguish one element from another is the atomic number. It’s like each element’s unique ID card, telling us the number of protons, those positively charged particles, residing in its atomic nucleus.
Let’s take neon as an example. Its atomic number is 10, meaning every neon atom has 10 protons snugly packed in their nuclei. This number is what makes neon … well, neon. If it had 9 protons, it would be fluorine. With 11 protons, it would transform into sodium.
So, how does this atomic number help us? Well, since protons carry a positive charge, the number of protons present determines the overall electrical charge of an atom. In the case of neon, with its 10 protons, it has an equal number of electrons, making it electrically neutral. Just like a perfect balance of charges!
Proton Number and Proton Mass: A Matter of Weight
In the vast realm of atomic structure, the atomic number plays a crucial role in defining the identity of an element. It represents the number of protons, the positively charged particles, residing in the atom’s nucleus. Each element on the periodic table possesses a unique atomic number, distinguishing it from all others.
Protons and their number hold significant implications for an atom’s mass and charge. The proton number is identical to the atomic number, as each proton contributes a single positive charge to the nucleus. This fundamental relationship establishes the foundational identity of every element.
Moreover, protons possess a substantial mass, approximately 1 atomic mass unit (amu). This weight, far exceeding that of electrons, constitutes the predominant mass of an atom. In contrast, electrons, with their negligible mass, orbit the nucleus at astonishing speeds, contributing minimally to the atom’s overall mass.
The interplay between proton number and proton mass underscores the fundamental properties that shape the elements. The number of protons determines the element’s atomic number and its position on the periodic table, while the mass of protons governs the atom’s overall weight. Understanding these concepts unravels the building blocks of matter and the intricate tapestry of the atomic world.
Proton Charge: A Force of Nature
In the heart of every atom lies a bustling metropolis of subatomic particles. Among these tiny inhabitants, protons stand out as the nucleus’s heavyweights, carrying an intrinsic positive charge that shapes the very essence of matter.
Each proton, an indispensable building block of the universe, bears a positive charge equal to +1. This fundamental property plays a pivotal role in determining the overall electrical charge of an atom. Typically, atoms strive to maintain a delicate balance, with an equal number of positively charged protons and negatively charged electrons, resulting in an overall neutral state.
Consider the enigmatic element neon, with an atomic number of 10. This number, a unique identifier for each element, reveals that neon’s nucleus harbors a retinue of 10 protons. These protons, unrelenting in their positive charge, contribute a total charge of +10 to the neon atom.
The harmonious interplay between protons and electrons governs the electrical landscape of an atom. The positive charge of protons attracts electrons, forming the foundation for chemical bonding and the intricate interplay of chemical reactions. Without this electrostatic dance, the universe as we know it would dissolve into a chaotic soup of unbound particles.
So, as we delve into the depths of matter, let us remember the significance of protons and their unwavering positive charge. These tiny powerhouses, the cornerstone of atomic identity, shape the very fabric of our world, influencing everything from the properties of elements to the bonds that hold us together.
Calculating the Number of Protons in Neon: A Breeze
In the realm of chemistry, understanding the fundamental building blocks of matter is essential. Protons, the positively charged particles residing in an atom’s nucleus, play a crucial role in defining an element’s identity. Let’s embark on a journey to calculate the number of protons in neon, a noble gas with unique properties.
Unveiling the Atomic Number
Every element in the periodic table possesses a unique atomic number, which represents the number of protons in its nucleus. This number not only identifies the element but also serves as a blueprint for its chemical behavior. In the case of neon, an element renowned for its inert nature, the atomic number is 10. This means that every neon atom contains 10 protons.
Proton Mass and Charge
Protons, along with neutrons, constitute the mass of an atom. Each proton carries a mass of approximately 1 atomic mass unit (amu), which is significantly heavier than the electron, another fundamental particle with a nearly negligible mass. The positive charge carried by protons, equal to +1, balances the negative charge carried by electrons to maintain electrical neutrality in atoms.
Determining Neon’s Proton Count
Given the atomic number of neon as 10, we can confidently conclude that each neon atom harbors 10 protons within its nucleus. This number serves as the foundation for the element’s unique chemical properties, contributing to its stability and reluctance to participate in chemical reactions.
Making Chemistry Accessible
Understanding the fundamental concepts of chemistry can sometimes feel daunting, but it doesn’t have to be that way. By adopting a storytelling approach and breaking down complex ideas into relatable terms, we can make chemistry more approachable and enjoyable. Remember, every element, like neon, has a fascinating story to tell, and unraveling these tales can ignite a passion for science in anyone willing to explore.