Understanding Combustion Products: Impact On Environment And Health
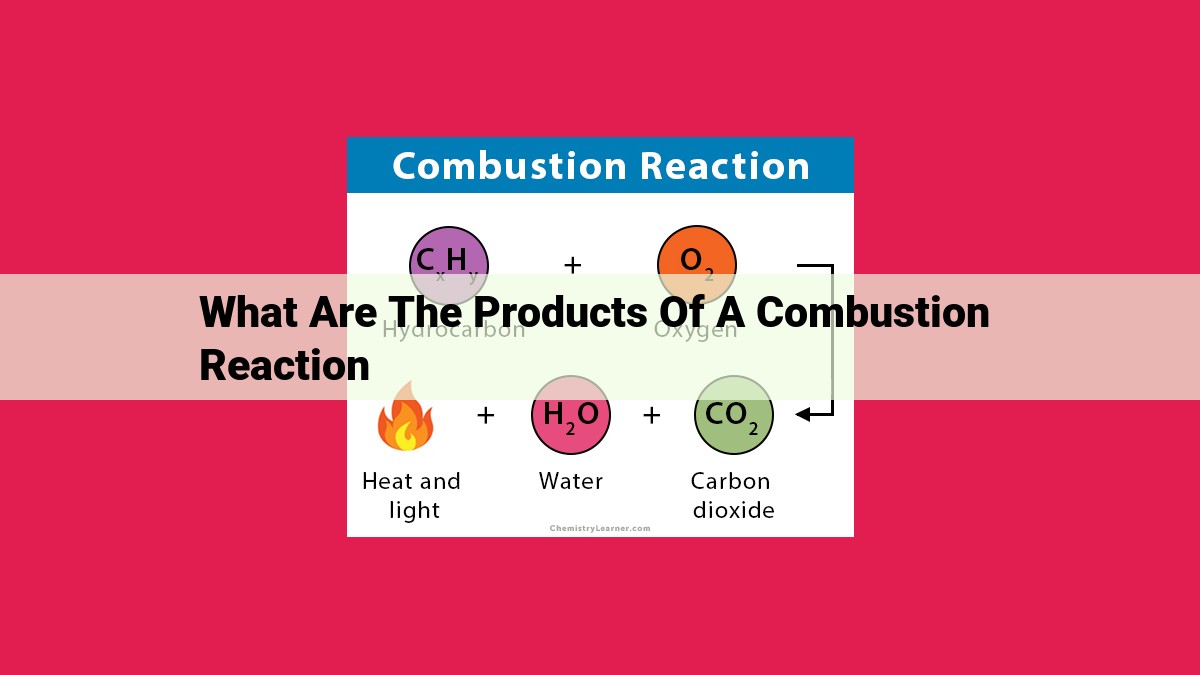
Combustion reactions yield an array of products, including carbon dioxide, water, nitrogen oxides, sulfur oxides, and particulate matter. Carbon dioxide contributes to climate change, while water sustains life and forms part of the Earth’s water cycle. Nitrogen oxides and sulfur oxides impair air quality and lead to environmental issues like smog and acid rain, respectively. Particulate matter, composed of tiny particles, poses health hazards by damaging respiratory and cardiovascular systems. Understanding the products of combustion is crucial for developing responsible combustion practices and mitigating their environmental impacts.
- Briefly explain the concept of combustion reactions and their importance.
Combustion Reactions: The Science Behind Fire and Its Impact on Our Planet
In the tapestry of nature’s processes, combustion reactions play a pivotal role, shaping our planet and our daily lives. These reactions, characterized by the rapid exothermic union of a substance with oxygen, release energy in the form of heat and light.
Combustion reactions are the driving force behind wildfires, the flames that flicker in our fireplaces, and the engines that power our vehicles. They provide us with warmth, energy, and a myriad of products that we rely on. Yet, these same reactions can have profound implications for our environment and our health.
The Products of Combustion: A Mixed Blessing
As combustion reactions unfold, a range of products are formed, each with its own unique characteristics and environmental impact.
Carbon Dioxide: The Invisible Culprit of Climate Change
Carbon dioxide (CO2), a colorless and odorless gas, is an inevitable byproduct of most combustion reactions. It is a potent greenhouse gas, trapping heat in the Earth’s atmosphere and contributing to global warming. The burning of fossil fuels, such as coal, oil, and natural gas, is a major source of carbon dioxide emissions.
Water: The Elixir of Life
Water (H2O), surprisingly, is also a product of combustion. As hydrocarbons burn, they combine with oxygen to form both carbon dioxide and water vapor. This water vapor plays a crucial role in the Earth’s water cycle, replenishing our lakes, rivers, and oceans.
Nitrogen Oxides: The Bane of Air Pollution
Nitrogen oxides (NOx), produced when combustion occurs at high temperatures, are major contributors to air pollution. These gases react with other pollutants in the atmosphere to form smog, which can cause respiratory problems and visibility reduction. NOx also contribute to the formation of acid rain, which can damage forests, lakes, and buildings.
Sulfur Oxides: The Sour Source of Acid Rain
Sulfur oxides (SOx) are released into the atmosphere during the combustion of sulfur-containing fuels, such as coal and oil. These gases combine with water vapor to form sulfuric acid, which falls to Earth as acid rain. Acid rain damages forests, lakes, and human health.
Particulate Matter: A Health Hazard in the Air
Particulate matter (PM) consists of tiny particles of soot, dust, and other materials released during combustion. These particles can penetrate deep into the lungs, causing respiratory and cardiovascular problems. Long-term exposure to PM has been linked to an increased risk of chronic diseases such as asthma, bronchitis, and lung cancer.
The Environmental Impact of Combustion: A Call to Action
The products of combustion have profound implications for our environment and our health. The release of carbon dioxide contributes to climate change, while air pollution from nitrogen oxides and sulfur oxides damages ecosystems and human health. Particulate matter poses a significant health risk, particularly in urban areas.
Recognizing the importance of combustion reactions and their environmental consequences is the first step towards mitigating their impact. By adopting responsible combustion practices and investing in technological advancements, we can harness the benefits of fire while safeguarding our planet for future generations.
Carbon Dioxide: A Key Greenhouse Gas
Understanding Combustion and Carbon Dioxide Formation
Combustion reactions, such as the burning of fossil fuels, play a crucial role in our daily lives, providing us with energy for transportation, heating, and electricity. However, these reactions release a range of products that can have significant environmental consequences, including carbon dioxide (CO2).
CO2 is a colorless, odorless gas that is naturally present in the Earth’s atmosphere. It forms when carbon-containing fuels, such as coal, oil, and natural gas, burn in the presence of oxygen. During combustion, carbon atoms in the fuel combine with oxygen atoms from the air, forming CO2 molecules.
The Role of Carbon Dioxide in Climate Change
CO2 is a potent greenhouse gas, meaning it absorbs and traps heat in the Earth’s atmosphere. As the concentration of CO2 in the atmosphere increases, more heat is retained, leading to an increase in global temperatures. This phenomenon is known as climate change.
The burning of fossil fuels is a major contributor to the rise in CO2 levels in the atmosphere. Over the past century, human activities have significantly increased CO2 emissions, leading to unprecedented levels of atmospheric CO2.
The consequences of climate change are far-reaching, including more frequent and intense heat waves, rising sea levels, changes in weather patterns, and the loss of biodiversity. These changes have profound impacts on human health, ecosystems, and the global economy.
Mitigating Carbon Dioxide Emissions
Recognizing the urgent need to address climate change, governments and industries worldwide are implementing measures to reduce CO2 emissions. These efforts include:
- Switching to renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind power
- Increasing energy efficiency in buildings, transportation, and industry
- Capturing and storing carbon dioxide from power plants and industrial processes
- Promoting sustainable land use practices to enhance carbon sequestration by forests and soils
By taking these steps, we can collectively mitigate the impacts of carbon dioxide emissions on our planet and secure a more sustainable future for generations to come.
Water: The Life-Sustaining Byproduct of Combustion
Amidst the myriad of products that emerge from the fiery dance of combustion reactions, water stands as an unsung hero, a testament to nature’s intricate balance. While often overlooked, this humble molecule plays a pivotal role in our planet’s life-sustaining systems.
When fuels burn, a chemical reaction occurs, transforming their molecular structure into simpler compounds. One of the most prevalent byproducts of this process is water vapor. As the flames flicker and dance, releasing energy into the atmosphere, they also contribute to the replenishment of our Earth’s water cycle.
The water vapor released during combustion rises into the atmosphere, where it forms clouds. These celestial reservoirs hold the potential for rain, snow, and fog, enriching the Earth’s surface with life-giving moisture. The water that eventually falls back to the ground seeps into the soil, replenishing aquifers and providing sustenance for plant life. It also flows into rivers and lakes, creating diverse ecosystems that support countless species.
The significance of combustion-produced water extends beyond its role in the water cycle. It also contributes to maintaining the Earth’s temperature. As water vapor rises into the atmosphere, it traps heat, acting as a natural blanket that prevents the planet from becoming too cold. This phenomenon, known as the greenhouse effect, plays a crucial role in regulating our climate, making Earth a habitable realm.
In essence, combustion reactions, despite their association with environmental concerns, also contribute to the sustenance of life on our planet. Water, the humble byproduct of these reactions, is a testament to the interconnectedness of natural processes, reminding us that even in the midst of change, life-sustaining forces persist.
Nitrogen Oxides: Air Pollution Contributors
Combustion reactions, such as those that occur in power plants, vehicles, and industrial processes, produce a range of gases and particles. Among these products are nitrogen oxides, which play a significant role in air pollution and its associated environmental issues.
Nitrogen oxides, commonly referred to as NOx, are formed when nitrogen and oxygen react at high temperatures, such as those encountered in combustion processes. These reactions occur primarily in the combustion engines of vehicles or in industrial boilers. NOx emissions contribute to air pollution in various ways.
One primary concern is the formation of smog, a hazy brown cloud that often blankets urban areas. Smog is primarily caused by the reaction of NOx with volatile organic compounds (VOCs) in the presence of sunlight. This reaction creates a complex mixture of pollutants, including ozone and particulate matter, which can cause respiratory problems, eye irritation, and other health issues.
Additionally, NOx emissions contribute to acid rain. When NOx is released into the atmosphere, it can react with water vapor to form nitric acid. This nitric acid condenses into rain or snow, resulting in acid rain. Acid rain can damage forests, lakes, and other ecosystems, as well as infrastructure such as buildings and bridges. It can also have negative effects on human health, including respiratory issues and skin irritation.
To mitigate the environmental impacts of nitrogen oxide emissions, it is crucial to implement control measures. These measures include using clean combustion technologies, such as catalytic converters in vehicles and low-NOx burners in industrial processes. Additionally, promoting the use of renewable energy sources and improving energy efficiency can help reduce the reliance on fossil fuels, thereby reducing NOx emissions.
Sulfur Oxides: The Invisible Culprits of Acid Rain
In the realm of combustion, sulfur oxides emerge as sinister agents, contributing to a silent threat that looms over our environment. As fuels rich in sulfur, such as coal and oil, burn, they release these gaseous compounds into the atmosphere.
These sulfur oxides, primarily sulfur dioxide (SO2), are the unsung villains behind acid rain. When they ascend into the sky, they undergo a transformation, reacting with oxygen and water molecules to form sulfuric acid (H2SO4). This acidic concoction then descends upon our world in the form of rain, snow, or fog.
The consequences of acid rain are far-reaching and devastating. It corrodes buildings and infrastructure, eroding the very foundations of our society. Aquatic ecosystems suffer, as lakes and rivers become acidic, suffocating marine life and disrupting the delicate balance of nature.
Human health is also at risk. Acid rain can aggravate respiratory conditions such as asthma and bronchitis. It can damage crops, diminishing food security, and even contribute to the formation of smog, a hazardous cocktail of pollutants that hangs heavy in the air.
The insidious nature of sulfur oxides lies in their stealthy release. Unlike other combustion byproducts like carbon dioxide, they are odorless and colorless, leaving us unaware of their presence. It is only when the damage becomes evident, such as the yellowing of leaves or the erosion of marble statues, that we realize the extent of their impact.
Mitigating the effects of sulfur oxides requires collective action. Advanced combustion technologies, such as flue gas desulfurization systems, can capture and remove these harmful gases before they escape into the atmosphere. Renewable energy sources, like solar and wind power, offer a cleaner alternative to fossil fuels, reducing our reliance on sulfur-emitting energy sources.
As responsible citizens of our planet, it is essential to be aware of the perils of sulfur oxides. Together, we can demand cleaner combustion practices and support sustainable energy solutions. Only then can we break the cycle of acid rain and safeguard the health of our environment and ourselves.
Particulate Matter: A Stealthy Health Hazard
In the realm of combustion reactions, one of the most insidious byproducts is particulate matter. These tiny particles, often invisible to the naked eye, are released into the atmosphere during the burning of fossil fuels and biomass.
Particulate matter is not a monolithic entity. It comes in a wide array of shapes, sizes, and compositions. Some particles are small enough to penetrate deep into the lungs, while others are larger and can be trapped in the upper respiratory tract.
Regardless of their size, particulate matter can have a profound impact on our health. It has been linked to a range of respiratory ailments, including asthma, bronchitis, and emphysema. Even short-term exposure can trigger irritation, wheezing, and coughing.
Particulate matter can also wreak havoc on the cardiovascular system. Tiny particles can damage the lining of blood vessels, increasing the risk of heart disease and stroke. Studies have shown that prolonged exposure to particulate matter can even increase mortality rates.
The detrimental effects of particulate matter are not limited to humans. Animals, plants, and ecosystems can also suffer the consequences. Particulate matter can damage crops, harm wildlife, and contribute to smog and acid rain.
It’s clear that particulate matter is a serious threat to our health and environment. As we continue to rely heavily on combustion processes, it’s crucial that we take steps to mitigate the release of these harmful pollutants. Technological advancements and responsible combustion practices can help reduce our exposure to particulate matter and protect our well-being.