The Vital Element Iodine: Unraveling The Role Of Isotopes In Its Stability, Properties, And Applications
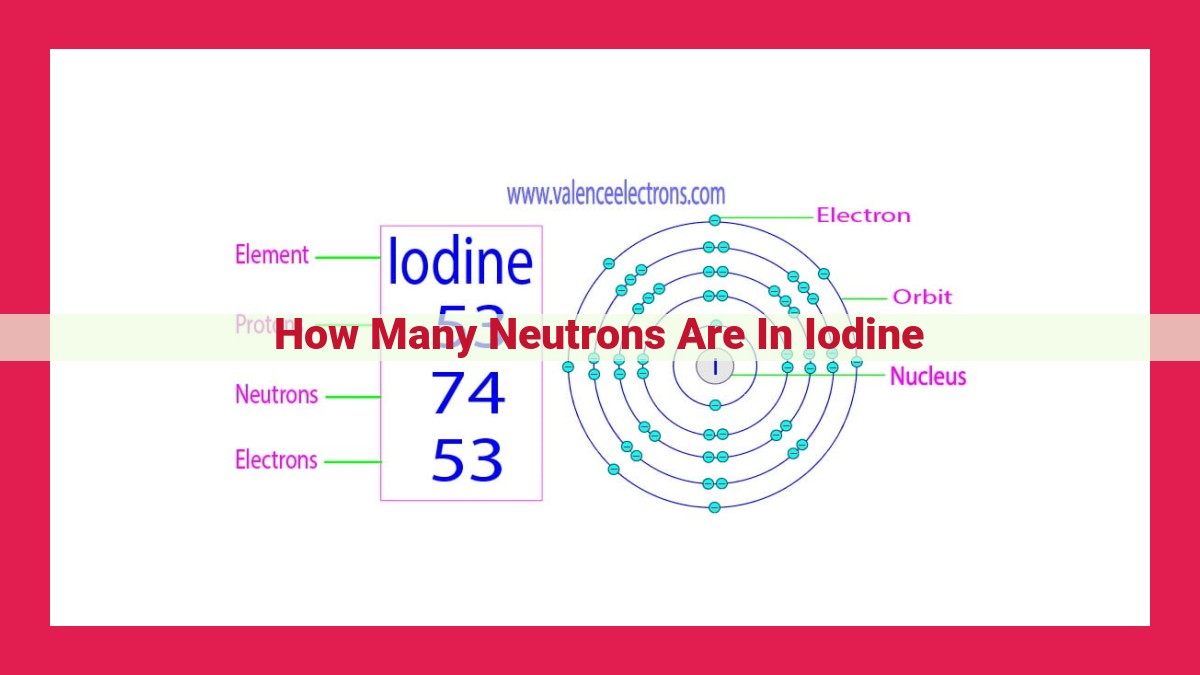
Iodine is a crucial element with naturally occurring isotopes. The stable isotope iodine-127 contains 74 neutrons, while the radioactive iodine-129 has 76 neutrons, and iodine-131, used in medicine, possesses 78 neutrons. These neutron counts determine the stability, properties, and applications of each isotope, highlighting the significance of nuclear structure in shaping the element’s behavior.
The Intriguing World of Iodine: Unveiling the Secrets of Its Isotopes
Embark on a captivating journey into the realm of iodine, an essential element that plays a pivotal role in human health and various scientific applications. In this blog, we will delve into the fascinating world of iodine isotopes, exploring their unique properties and applications.
Iodine: A Crucial Element
Iodine, a non-metallic element found in various forms throughout nature, holds immense importance in our lives. It is primarily known for its vital role in regulating thyroid function, influencing our metabolism and overall well-being. Its deficiency can lead to health issues like goiter and hypothyroidism.
Isotopes: The Multifaceted Forms of Elements
Isotopes are variants of the same element that share the same number of protons but differ in the number of neutrons in their atomic nuclei. This variation in neutron count imparts unique properties to each isotope, influencing their stability, reactivity, and applications.
Navigating the Intricacies of Iodine Isotopes
In the upcoming sections, we will explore three key iodine isotopes: iodine-127, iodine-129, and iodine-131. Each isotope has its own distinct characteristics and applications. By understanding their neutron counts and properties, we gain valuable insights into the diverse applications of iodine in various fields. Stay tuned as we unravel the intriguing world of iodine isotopes!
Unveiling the Neutron Secrets of Iodine-127: A Journey into the Heart of an Atom
In the vast expanse of chemistry, iodine stands out as an element of immense significance. Its presence in the human body makes it an essential nutrient, while its versatility extends to a wide range of industrial applications. However, beyond the realm of its chemical properties lies a fascinating world of nuclear particles, where the mysteries of iodine-127 unfold.
Iodine-127: A Unique Isotope
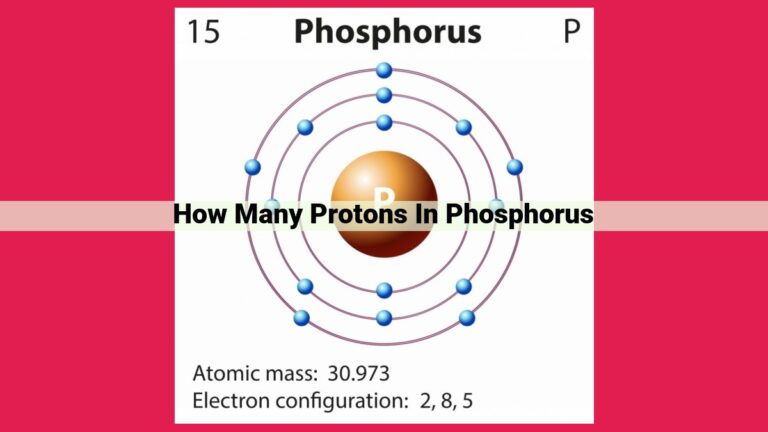
Every element exists in various forms called isotopes, which differ in the number of neutrons in their nuclei. Iodine-127 is one such isotope, boasting a distinctive atomic structure. The nucleus of iodine-127 comprises 53 protons, giving it an atomic number of 53. What sets it apart, however, is the presence of 74 neutrons, making its total number of nucleons (protons + neutrons) equal to 127.
Determining the Neutron Count
Delving into the depths of an iodine-127 atom, we encounter a harmonious balance of subatomic particles. The number of protons is conveniently revealed by the element’s atomic number. Determining the neutron count requires a slightly different approach.
Scientists rely on mass spectrometry to uncover this elusive information. This powerful technique separates isotopes based on their mass-to-charge ratio. By meticulously measuring the mass of iodine-127 ions, researchers can deduce the number of neutrons. The difference between the atomic mass and the atomic number yields the number of neutrons, which in the case of iodine-127 is 74.
Applications of Iodine-127
The stable nature of iodine-127 makes it a valuable tool in diverse fields:
-
Nuclear medicine: Iodine-127 is used in thyroid function tests, providing insights into the health of this essential gland.
-
Industrial applications: Iodine-127 serves as a contrast agent in x-ray imaging, enhancing the visibility of structures such as blood vessels.
-
Scientific research: Iodine-127 isotopes are employed in various experiments, including studies of nuclear reactions and radioactive decay.
Understanding the Number of Neutrons in Iodine-129
Iodine is an essential trace element with a fascinating story to tell. It has several isotopes, including iodine-129, each with its own unique characteristics. In this blog post, we’ll delve into the world of iodine-129, exploring its definition, neutron count, and how it compares to other iodine isotopes.
Defining Iodine-129
Iodine-129 is an isotope of iodine with an atomic number of 53 and a mass number of 129. This means it has 53 protons and 76 neutrons in its nucleus. The symbol for iodine-129 is written as ¹²⁹I.
Determining the Neutron Count
The number of neutrons in an atom’s nucleus can be calculated by subtracting the atomic number from the mass number. For iodine-129, this calculation is as follows:
Neutron count = Mass number - Atomic number
Neutron count = 129 - 53
Neutron count = 76
Comparison with Iodine-127
Iodine-129 is one of the two stable isotopes of iodine, along with iodine-127. Both isotopes have similar chemical properties, but they differ in their neutron count. Iodine-127 has 74 neutrons, while iodine-129 has 76. This difference in neutron count affects the isotopes’ stability and applications.
Stability and Uses of Iodine-129
Iodine-129 has a very long half-life of 15.7 million years, making it a stable isotope. This stability makes iodine-129 suitable for use in geological studies and as a tracer in environmental monitoring. It can also be used in medical applications, such as diagnostic imaging and radiotherapy.
Iodine-129 is an important isotope with a range of applications. Its 76 neutrons contribute to its stability and usefulness in various fields. Understanding the number of neutrons in iodine-129 provides valuable insights into the behavior and applications of this essential element.
Iodine-131: A Radioactive Isotope with Medical and Industrial Significance
In the realm of nuclear physics, the element iodine plays a pivotal role, particularly its radioactive isotope, iodine-131. With 78 neutrons nestled within its atomic nucleus, iodine-131 stands out as a unique and versatile isotope. Let’s delve into its definition, radioactive nature, and its indispensable applications in medicine and industry.
Definition and Neutron Count
Iodine-131, denoted as ¹³¹I, is an isotope of iodine with an atomic number of 53 and a mass number of 131. Its原子核contains 53 protons and 78 neutrons, giving it a total of 131 nucleons. This neutron count is significantly higher than the stable isotope, iodine-127, which possesses only 74 neutrons.
Radioactive Properties
¹³¹I is an unstable isotope, emitting beta particles (electrons) as it decays into the stable isotope xenon-131. Its half-life, the time it takes for half of the radioactive atoms in a sample to decay, is approximately 8 days. This inherent radioactivity makes iodine-131 a valuable tool in various fields.
Medical Applications
In the medical realm, ¹³¹I has gained prominence as a diagnostic and therapeutic agent. By administering small amounts of the isotope, physicians can image the thyroid gland’s function and detect thyroid disorders. Its use in thyroid cancer treatment is also noteworthy, as it selectively targets and destroys thyroid cancer cells, sparing healthy tissues.
Industrial Applications
Beyond medicine, ¹³¹I finds employment in industrial settings. One notable application is in smoke detectors, where it plays a crucial role in detecting fires. When radioactive particles emitted by ¹³¹I encounter smoke, they are absorbed or scattered, triggering an alarm. This sensitive detection makes it an essential component in safeguarding lives and property.
Iodine-131, with its unique neutron count of 78 and inherent radioactivity, has emerged as a cornerstone in both medical and industrial fields. Its versatility, ranging from medical imaging and therapy to fire detection, underscores its significance in our modern world. As research continues in nuclear physics, we can anticipate further advancements and applications of this fascinating isotope, shaping the future of healthcare and technology alike.