Understanding Tendons And Ligaments: Their Role In Movement, Stability, And Health
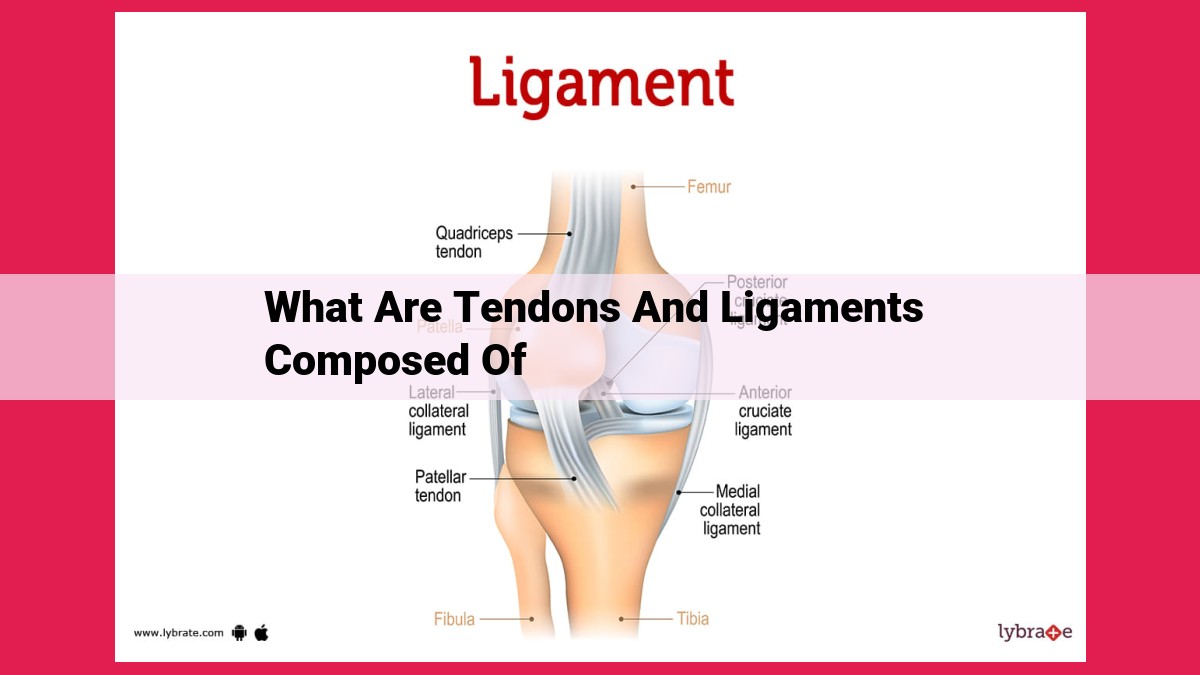
Tendons and ligaments are connective tissues that facilitate movement by bridging muscles to bones (tendons) and uniting bones to bones (ligaments). Both structures comprise collagen, elastin, and ground substance, with collagen providing strength, elastin offering flexibility, and ground substance providing lubrication and support. This shared composition underpins the essential roles of tendons and ligaments in ensuring mobility, stability, and overall movement.
Tendons: The Unsung Heroes of Movement
In the symphony of our bodies, tendons play an unassuming yet crucial role. These fibrous cords act as the essential bridge between muscles and bones, orchestrating our every movement with precision.
Definition and Function of Tendons
Simply put, tendons are tough, rope-like tissues that anchor muscles to bones. They are composed primarily of collagen, a protein that provides exceptional strength and resistance. When muscles contract, they pull on tendons, which in turn transmit that force to bones, enabling us to move.
Tendons are not merely passive conduits. They also play a role in energy storage and release. When muscles stretch, tendons store energy like a rubber band. When the muscles relax, the tendons recoil, releasing that energy to assist in movement. This elastic recoil contributes to our ability to jump, run, and perform other dynamic activities.
Structure of Tendons: The Resilient Connective Tissue
Tendons, the unsung heroes of our musculoskeletal system, play a crucial role in transmitting force from muscles to bones. Their intricate structure enables them to withstand the rigors of movement and maintain the integrity of our joints.
At the core of tendons lies collagen, a fibrous protein that arranges itself in parallel bundles, providing tendons with their remarkable strength. Collagen fibers are like tiny cables, efficiently transferring the contractile forces of muscles to bones.
Interwoven with the collagen fibers is elastin, another protein that imparts elasticity to tendons. Elastin allows tendons to stretch slightly under load and then snap back to their original length, facilitating smooth and effortless movement.
The spaces between collagen and elastin fibers are filled with ground substance, a viscous fluid-like matrix that provides cushioning and lubrication. The ground substance contains proteoglycans and glycosaminoglycans, which attract and hold water, giving tendons their resilient and slightly compressible nature.
Together, collagen, elastin, and ground substance form a complex and dynamic structure that endows tendons with their unique properties. These essential tissues ensure that our every move is effortless, graceful, and pain-free.
Definition and Function of Ligaments
Ligaments, the unsung heroes of our musculoskeletal system, are the tough, fibrous tissues that connect bones to bones. They serve as sturdy bridges, ensuring that our joints remain stable and move smoothly. Unlike tendons, which link muscles to bones, ligaments prevent excessive movement and provide structural support for our bodies.
Imagine a symphony orchestra where each instrument plays a crucial role in creating harmony. Ligaments act as the sheet music, guiding our bones into a delicate dance of movement. They reinforce our joints, granting us the freedom to twist, bend, and explore the world around us. Without these vital connective tissues, our bodies would be like puppets with loose strings, unable to perform even the simplest of actions.
In essence, ligaments are the silent guardians of our mobility, enabling us to navigate our environment with grace and agility. By understanding their vital role, we can appreciate the importance of maintaining healthy ligaments for a lifetime of movement.
Ligaments: The Unsung Heroes of Skeletal Connectivity
Ligaments, the unsung heroes of our skeletal system, play a crucial role in maintaining the integrity of our joints. These fibrous bands of connective tissue bridge the gap between bones, ensuring stability, strength, and proper alignment.
Beneath the Microscope
Delving into the microscopic realm reveals the complex structure of ligaments. Collagen, a protein renowned for its exceptional strength and rigidity, forms the backbone of these tissues. Interwoven with collagen fibers are elastin fibers, which impart elasticity and flexibility to ligaments.
Completing the ligamentous trio is ground substance, a gel-like matrix that cushions and lubricates the fibers. This vital component ensures smooth gliding of bones during movement, protecting them from wear and tear.
The Interplay of Components
Collagen, elastin, and ground substance cooperate to create a dynamic tissue that can withstand the rigors of everyday activities. Collagen provides tenacity, elastin confers adaptability, while ground substance facilitates movement and protects against damage.
The result is a resilient connective tissue that safeguards our joints, stabilizes our body, and enables seamless motion.
Tendons and Ligaments: The Unsung Heroes of Movement
Beneath our skin, hidden from plain sight, two remarkable tissues play a vital role in our ability to move with ease: tendons and ligaments. These connective tissues serve as bridges between muscles and bones, allowing us to perform countless actions, from walking and jumping to grasping and writing.
Tendons: The Bridges of Strength
Tendons are the fibrous cords that connect muscles to bones. Imagine them as reinforced ropes, with tough strands of a protein called collagen running parallel to each other, giving them incredible tensile strength. This strength allows tendons to transmit the force generated by muscles to bones, enabling us to move our limbs and joints.
Ligaments: The Bonds of Stability
Ligaments, on the other hand, are the tough bands of tissue that connect one bone to another. Unlike tendons, ligaments are less mobile and serve primarily to stabilize and prevent excessive movement at joints. They also contain collagen as their primary structural component, but in a different arrangement than tendons, allowing them to resist shearing forces and prevent dislocation.
The Shared Secret: Structural Synergy
The strength and flexibility of both tendons and ligaments stem from their shared structural components. In addition to collagen, they both contain a protein called elastin, which provides elasticity and allows them to stretch and recoil as we move. Embedded within this collagen-elastin network is a gel-like substance called ground substance, which provides lubrication and cushioning, reducing friction and protecting these tissues from wear and tear.
The Vital Role of Ground Substance in Tendons and Ligaments: A Story of Support and Resilience
Beneath the surface of our skin, a vast network of fascinating tissues silently orchestrates our every movement. Among these unsung heroes are tendons and ligaments, the flexible bridges that connect our muscles to bones and bones to bones. These resilient tissues work tirelessly to ensure the smooth and painless execution of our daily activities, from lifting objects to walking and even breathing.
The Secret Ingredient: Ground Substance
Supporting the delicate structures of tendons and ligaments is a remarkable substance known as ground substance. This viscous gel-like matrix acts as a shock absorber, cushioning the tissues from the forces of movement and preventing painful friction. It also provides essential nourishment to the surrounding cells, ensuring their optimal health and function.
Ground Substance’s Composition
Ground substance is composed primarily of water, along with a complex mix of proteins, proteoglycans, and glycosaminoglycans. These components work together to form a dynamic network that supports, nourishes, and protects the collagen and elastin fibers that make up tendons and ligaments.
The Strength and Elasticity of Collagen and Elastin
Collagen fibers provide strength and resistance to tendons and ligaments, while elastin fibers contribute elasticity and flexibility. These properties allow tendons to transmit the force of muscle contractions to bones without tearing, while ligaments provide stability to joints by preventing excessive movement.
Ground Substance’s Role in Flexibility
In addition to its cushioning and lubricating properties, ground substance also plays a crucial role in maintaining the flexibility of tendons and ligaments. It allows these tissues to stretch and recoil, ensuring our ability to perform a wide range of movements gracefully and comfortably.
Tendons and ligaments, supported by the remarkable ground substance, form an intricate system that allows us to move freely and effortlessly. These tissues work in harmony to provide strength, flexibility, and stability to our bodies. By understanding their importance and maintaining their health, we can ensure the longevity of our pain-free movements and continue to live an active and fulfilling life.
Collagen, the Strength Behind Tendons and Ligaments
Imagine yourself as a skilled builder, tasked with constructing a magnificent bridge that will connect a vibrant city to a serene countryside. This bridge, the tendons and ligaments of your body, has a vital role in facilitating movement and stability. Just as the sturdy pillars of a bridge require robust materials to withstand the weight of traffic, the tendons and ligaments rely on a crucial component: collagen.
Collagen, the primary building block of tendons and ligaments, is a remarkable protein that provides these tissues with exceptional strength and resistance. Picture it as tightly woven strands, resembling a dense fabric that can endure significant forces without snapping. This structural integrity is essential for tendons, which transmit the powerful forces generated by muscles to bones, allowing us to execute movements such as running, jumping, and lifting. Without collagen’s unwavering strength, these movements would be impossible.
Moreover, tendons and ligaments are constantly subjected to stretching and compression as we engage in various activities. Collagen’s resilient nature enables them to withstand these mechanical stresses without tearing or rupturing. This resilience is particularly crucial for athletes, who put immense strain on their tendons and ligaments during training and competition. Without collagen’s protective presence, injuries would be far more common, hindering performance and recovery.
The Function of Elastin for Elasticity and Flexibility in Tendons and Ligaments
In the intricate dance of body movement, tendons and ligaments play a crucial role, acting as the subtle yet strong connectors between muscles and bones. These specialized tissues share a common architectural tapestry, showcasing the remarkable interplay of collagen, elastin, and ground substance. Each component contributes its unique symphony to the overall harmony and health of our musculoskeletal system.
Among these components, elastin stands out as the maestro of elasticity and flexibility. This resilient protein weaves its golden thread throughout tendons and ligaments, bestowing upon them the ability to stretch, recoil, and rebound, much like a well-tuned rubber band.
Imagine a graceful ballerina executing a flawless pirouette. Elastin’s presence in her tendons allows her foot to elegantly point and her muscles to power each delicate turn. In every step we take, every jump we make, elastin is the silent choreographer, ensuring our movements flow with ease and grace.
Moreover, elastin’s remarkable properties protect tendons and ligaments from overexertion and strain. Picture a game of intense tennis: as the player lunges and swings, elastin provides the necessary give to prevent the connective tissues from snapping like taut strings. This cushioning effect safeguards against injury, allowing us to push the boundaries of our physical abilities with confidence.
The delicate balance between strength and flexibility is the cornerstone of healthy tendons and ligaments. Collagen provides the rock-solid anchor, while elastin adds the dynamic springiness. Together, they orchestrate the seamless interplay of muscle contractions and bone stability, empowering us to move, dance, and play with effortless grace.
The Vital Role of Ground Substance in Supporting Tendons and Ligaments
As we delve deeper into the intricate world of tendons and ligaments, we cannot overlook the crucial role played by ground substance, a fascinating and essential component that provides these tissues with their unique properties. Think of it as the lifeblood that nourishes and supports the very fabric of our connective tissues.
A Liquid Matrix of Support
Imagine a gelatinous cushion, a liquid matrix that envelops and surrounds the collagen and elastin fibers within tendons and ligaments. This matrix, known as ground substance, is composed primarily of hyaluronic acid, proteoglycans, and water. It acts as a shock absorber, protecting the fibers from excessive mechanical stress and facilitating their gliding movements.
Lubrication for Smooth Movement
The ground substance is not merely a passive cushion; it is an active participant in the intricate symphony of movement. Its lubricating properties ensure that tendons and ligaments slide smoothly over bones and other structures, enabling effortless joint mobility. Without this lubrication, movement would be jerky, painful, and ultimately debilitating.
A Reservoir of Nutrients
Furthermore, the ground substance serves as a nutrient reservoir, providing the essential building blocks for the maintenance and repair of tendons and ligaments. It facilitates the exchange of nutrients between blood vessels and the cells within these tissues, ensuring their optimal health and longevity.
In essence, the ground substance is the unsung hero of our connective tissues. Its cushioning, lubricating, and nutritive properties are indispensable for the seamless functioning of our bodies. It enables us to move with grace, agility, and ease, allowing us to navigate the world with confidence and vitality.
Tendons and Ligaments: The Vital Links in Movement
Tendons: The Essential Bridge Between Muscles and Bones
Imagine tendons as crucial bridges that allow muscles to exert their power on bones. These tough, fibrous cords connect muscles to bones, transmitting the forces generated by muscle contractions. Tendons are composed primarily of collagen, a protein known for its strength and resistance. They also contain elastin, which provides elasticity and flexibility, enabling tendons to withstand stretching and recoil after muscle contractions.
Ligaments: The Bonds that Unite Bones
Ligaments, on the other hand, are sturdy bands of tissue that connect bones to each other, providing stability and support to joints. Similar to tendons, ligaments contain collagen and elastin, but their primary function is to prevent excessive joint movement. Ligaments restrict the range of motion at joints, ensuring that bones remain aligned and stable.
The Interdependence of Tendons and Ligaments
Tendons and ligaments work in harmony to facilitate movement. Tendons transmit the force from muscles, enabling bones to move, while ligaments maintain joint integrity by limiting the extent of that movement. Together, they form an intricate network that provides both flexibility and stability to the musculoskeletal system.
Collagen, Elastin, and Ground Substance: The Building Blocks
- Collagen: The primary structural protein of tendons and ligaments, providing strength and resistance to stretching.
- Elastin: A flexible protein that allows tendons and ligaments to recoil after stretching, ensuring elasticity and adaptability.
- Ground Substance: The lubricating and cushioning matrix that surrounds collagen and elastin fibers, providing support and reducing friction.
Tendons and ligaments are indispensable to mobility and stability. They enable us to move freely, execute complex movements, and maintain the structural integrity of our skeletal system. Understanding their functions and components is crucial for appreciating the intricate mechanics of human movement and the importance of maintaining healthy tendons and ligaments for optimal physical function.
Tendons and Ligaments: The Invisible Symphony Driving Your Every Move
In the intricate tapestry of the human body, tendons and ligaments play an unsung role, yet their contribution to our graceful movements and unwavering stability is simply astonishing. These connective tissues, though often overshadowed by their more glamorous counterparts like muscles and bones, are the silent maestros that orchestrate the harmonious symphony of body movement.
Tendons: The Mighty Bridges
Tendons, the unyielding messengers of our will, connect muscles to bones, allowing us to control every twitch and flex. Their sturdy structure, composed of tightly woven collagen fibers, ensures the seamless transmission of force between these disparate components. Without tendons, our muscles would be mere prisoners, unable to execute the intricate dance of movement.
Ligaments: The Unbreakable Bonds
Ligaments, the silent guardians of our joints, link bones together, providing unwavering stability and preventing our bodies from disintegrating into a haphazard mess of disconnected parts. Their tenacious grip, also made of collagen fibers, keeps our joints in place, allowing us to twist, bend, and pivot with ease.
The Interdependent Unity
Tendons and ligaments, though distinct in their roles, share a deep interdependence, like two sides of the same coin. Both rely on the supportive cushioning of ground substance, a gel-like matrix that lubricates and nourishes these tissues. Their shared collagenous architecture provides the strength and flexibility necessary for the fluid movements that define our physical existence.
The Role of Collagen, Elastin, and Ground Substance
Collagen, the backbone of these connective tissues, grants them their unyielding strength, while elastin, its more pliable counterpart, lends elasticity and flexibility. Ground substance, like a benevolent guardian angel, bathes these fibers in a nurturing embrace, providing lubrication and shock absorption. Together, this trio forms the bedrock upon which our mobility and stability rests.
The Vital Importance of Healthy Tendons and Ligaments
The health of our tendons and ligaments is paramount for optimal movement. When these tissues are compromised, either through injury or age-related degeneration, our ability to move freely and painlessly can be severely hampered. Therefore, nurturing these silent heroes through proper exercise, nutrition, and a healthy lifestyle is essential for maintaining the vibrant symphony of body movement.
Tendons and Ligaments: The Hidden Heroes of Movement
In the intricate tapestry of our bodies, tendons and ligaments play a pivotal role, connecting muscles to bones and bones to bones, respectively. These resilient connective tissues are our silent heroes, enabling us to move with grace and agility.
Tendons: The Muscular Messengers
Imagine tendons as sturdy bridges that connect muscles to bones. They’re composed of collagen, a protein that provides strength and resistance. Each time we flex our muscles, tendons transmit the force, allowing us to move freely.
Ligaments: The Bone Connectors
Ligaments, on the other hand, are like flexible ropes that bind bones together, forming stable joints. They’re also rich in collagen, but with added elastin, a protein that gives them elasticity and flexibility. This unique blend of strength and flexibility ensures the stability of our joints.
The Dynamic Duo: Interdependence and Support
Tendons and ligaments work in harmony, sharing structural components and supporting each other. The ground substance, a fluid-filled matrix surrounding the cells, provides both cushioning and nourishment, ensuring the smooth functioning of these tissues.
The Building Blocks of Strength and Mobility
Collagen, the primary protein in tendons and ligaments, provides unmatched strength. Elastin lends elasticity, allowing for flexibility and resilience. Ground substance cushions and lubricates, protecting against wear and tear.
Maintaining Healthy Tendons and Ligaments: A Vital Investment
For optimal movement, it’s crucial to nurture the health of our tendons and ligaments. A balanced diet, rich in protein and vitamin C, supports collagen production. Regular exercise strengthens these tissues, while stretching improves flexibility. Maintaining a healthy weight reduces stress on joints and connective tissues.
In conclusion, tendons and ligaments are the unsung heroes of movement, enabling us to glide, stride, and soar through life. By understanding their vital roles and investing in their health, we can maintain optimal mobility and stability for years to come.