Stock Solutions: The Essential Guide For Accurate And Efficient Scientific Experiments
A stock solution is a highly concentrated solution prepared in advance and used to make other solutions of lower concentrations. It plays a crucial role in scientific applications by providing a convenient, accurate, and consistent source of reagents. Stock solutions are characterized by their concentration, typically expressed in molarity, and are prepared through precise weighing, dissolving, and diluting. Proper storage and handling are essential to maintain their stability and ensure reliable results. Stock solutions find wide applications in laboratory procedures like titration, spectrophotometry, and calibration, providing a valuable tool for researchers and analysts seeking accuracy and efficiency in their work.
Understanding Stock Solutions: The Foundation of Accurate Scientific Experiments
In the realm of scientific research, precision and consistency are paramount. Stock solutions play a crucial role in achieving these qualities, forming the backbone of innumerable experiments. Let us embark on a journey to unravel the intricacies of stock solutions, their immense importance, and the best practices surrounding their usage.
What are Stock Solutions?
A stock solution is a pre-prepared, concentrated solution of a substance used to create solutions of various concentrations. It serves as a starting point, providing a known concentration of the solute that can be diluted or further concentrated as needed. Scientists rely on stock solutions to ensure accuracy, consistency, and convenience in their experimental procedures.
Advantages of Stock Solutions
The benefits of using stock solutions are undeniable:
- Accuracy: Stock solutions eliminate the risk of measurement errors associated with weighing and dissolving solutes, ensuring precise and reliable results.
- Consistency: Multiple experiments can be performed using the same stock solution, guaranteeing consistency in the concentration of the solute across different batches.
- Convenience: Pre-made stock solutions save time and effort, allowing researchers to focus on their experiments rather than tedious solution preparation.
The Indispensable Role of Stock Solutions: Accuracy, Consistency, and Convenience
In the realm of scientific research, accuracy and consistency are paramount. For this reason, stock solutions have become invaluable tools, offering a myriad of advantages that enhance the precision and reliability of experimental procedures.
Accuracy and Precision
Stock solutions provide a precise and uniform source of reagents, minimizing the risk of errors due to variations in weighing and measuring. By preparing a large volume of a concentrated solution, researchers can ensure that all subsequent dilutions and experiments utilize the same exact concentration, eliminating potential discrepancies.
Convenience and Efficiency
Stock solutions offer immense convenience by simplifying the preparation of multiple solutions with different concentrations. Instead of painstakingly weighing and dissolving reagents for each experiment, researchers can simply dilute the stock solution to the desired concentration, saving time and effort.
Eliminating Variability
The use of stock solutions eliminates variability introduced by different batches of reagents or errors in measuring and handling. By preparing a large batch of the stock solution, researchers can ensure that all experiments are using the same source of reagents, thus minimizing the influence of batch-to-batch variations or human error.
Concentration and Dilution: The Art of Preparing Solutions with Precision
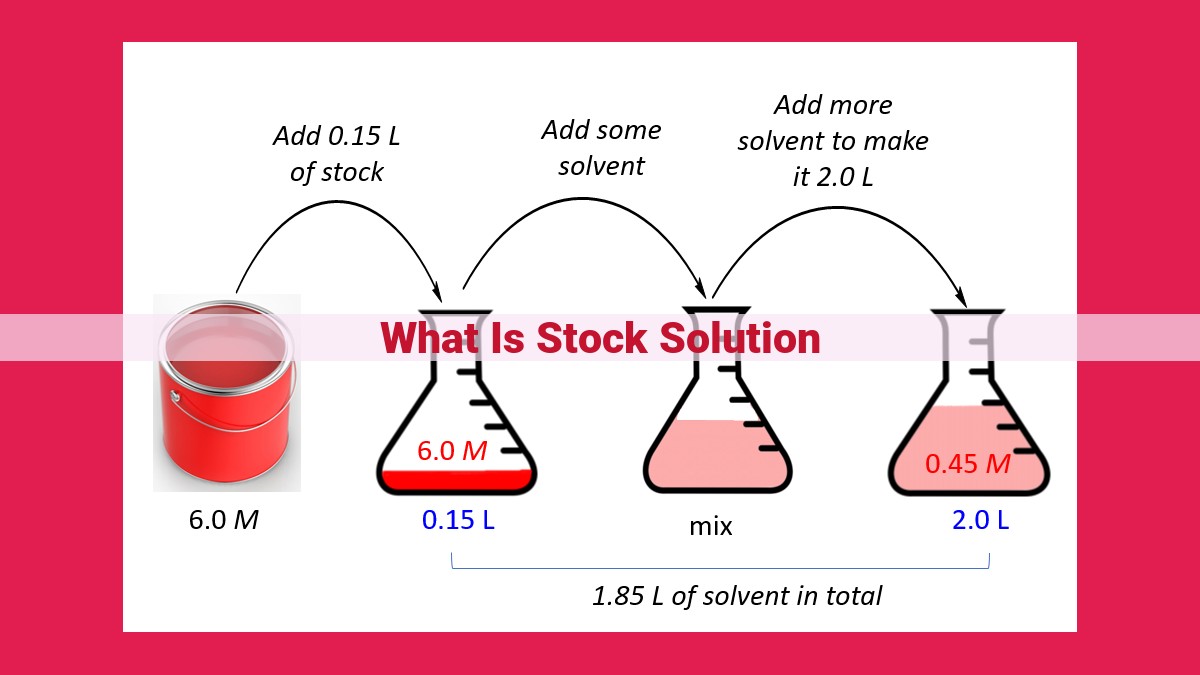
In the realm of scientific research, precision is paramount. When it comes to preparing solutions for experiments, stock solutions play a crucial role in ensuring accuracy and consistency. A stock solution is essentially a concentrated solution of a known substance, which is diluted to create solutions of different concentrations for various applications.
The concentration of a solution is typically expressed in terms of molarity, which represents the number of moles of solute dissolved per liter of solution. Molarity is a critical parameter for many chemical reactions and analytical techniques. Using a stock solution allows researchers to easily create solutions of known concentrations by simply diluting it with a specific volume of solvent.
For instance, let’s say you have a stock solution of 1 M sodium chloride (NaCl). If you need a solution with a concentration of 0.1 M NaCl, you would dilute 100 mL of the stock solution with 900 mL of solvent. This would result in a solution with a concentration of 0.1 M, as the amount of solute remains unchanged while the total volume increases.
The process of dilution requires careful calculations to ensure the desired concentration. The formula for dilution is:
C1 * V1 = C2 * V2
where:
- C1 is the concentration of the stock solution
- V1 is the volume of the stock solution used
- C2 is the desired concentration of the diluted solution
- V2 is the total volume of the diluted solution
By precisely diluting stock solutions, researchers can create solutions with the exact concentrations required for their experiments, ensuring reliable and reproducible results. This process is essential for maintaining accuracy, consistency, and efficiency in scientific research, particularly in applications such as titration, spectrophotometry, and calibration.
Preparing Stock Solutions: A Step-by-Step Guide
In the bustling laboratory, where precision and accuracy reign supreme, stock solutions serve as the cornerstone of countless experiments. To unlock the full potential of these valuable reagents, it’s essential to master the art of their preparation. Let’s delve into the intricate steps involved in creating these indispensable laboratory building blocks.
1. Weighing the Solutes
First and foremost, you’ll need to accurately weigh the required mass of your chosen solute. This step sets the foundation for the subsequent steps and ensures the desired concentration of your stock solution. Precision scales are your trusted allies in this crucial task, helping you achieve the utmost accuracy.
2. Dissolving the Solutes
Once the solutes are precisely weighed, it’s time to dissolve them in a suitable solvent. This step transforms the solid solutes into a homogenous solution. Gradually add the solvent while stirring or vortexing to facilitate complete dissolution. Patience is key here, as some solutes require gentle coaxing to fully dissolve.
3. Diluting to the Desired Volume
With the solutes dissolved, the next step involves diluting the solution to the desired volume. This crucial step ensures the precise concentration of your stock solution. Calculate the required volume of solvent and carefully add it to the solution, ensuring thorough mixing to achieve a uniform concentration throughout.
4. Storing Your Stock Solution
Once your stock solution is prepared, proper storage is paramount to maintain its integrity. Choose the appropriate storage conditions, such as refrigeration or freezing, based on the stability of your solutes. Labeling your stock solutions clearly with the date of preparation, concentration, and any other pertinent information is also essential for future reference.
Understanding these precise steps empowers you to prepare stock solutions with confidence, laying the foundation for accurate and reliable experiments. By mastering the art of stock solution preparation, you unlock the potential for groundbreaking discoveries and contribute to the advancement of scientific frontiers.
Storage and Stability: Preserving the Integrity of Stock Solutions
Appropriate storage conditions are crucial to maintaining the integrity and stability of stock solutions over time. These solutions serve as the foundation for numerous laboratory experiments, hence ensuring their accuracy and reliability is paramount.
Carefully storing stock solutions away from direct sunlight minimizes potential photodegradation, especially for light-sensitive compounds. Exposure to intense UV rays can break down chemicals and alter their concentrations.
Temperature control plays a critical role in stock solution stability. Some compounds are temperature sensitive, and storage at optimum temperatures preserves their stability and prevents degradation. Ideal storage temperatures are typically between 2-8°C for refrigerated solutions and below -20°C for frozen ones.
Air exposure poses another threat to stock solutions. Oxygen can lead to oxidation reactions, which alter the compound’s structure and concentration. To prevent this, store stock solutions in airtight containers or under an inert gas atmosphere.
Maintaining appropriate pH levels is essential for certain stock solutions. Changes in pH can affect the chemical equilibrium and stability of the solution. Therefore, store solutions at their optimal pH ranges to minimize degradation.
Regularly monitoring stock solution stability is advisable. Simple tests, such as measuring absorbance or pH, can provide an indication of potential changes over time. Discarding degraded stock solutions and preparing fresh ones ensures accurate and reliable results in laboratory experiments.
Factors Affecting the Stability of Stock Solutions: Ensuring Reliable Results
Stock solutions form the backbone of many laboratory procedures, providing a precise and consistent source of reagents. However, maintaining their stability over time is crucial to ensure accurate and reliable results. Several factors can influence the stability of stock solutions, impacting their efficacy and longevity.
1. Degradation:
Over time, stock solutions may undergo chemical degradation, resulting in a loss of concentration or formation of unwanted byproducts. Factors such as temperature, light exposure, and presence of contaminants can accelerate degradation processes.
2. Half-Life:
Every stock solution has a characteristic half-life, which represents the time it takes for its concentration to decrease by half. The half-life depends on the chemical stability of the solute, storage conditions, and presence of catalysts. By understanding the half-life, researchers can estimate the expected shelf life of their stock solutions.
3. Shelf Life:
The shelf life of a stock solution refers to the period during which it remains stable and usable. It is influenced by factors such as storage temperature, exposure to air or moisture, and the chemical nature of the solute. Proper storage practices and regular monitoring of stock solutions can extend their shelf life and ensure their continued reliability.
Recognizing and mitigating these factors is essential for preserving the integrity of stock solutions. By adhering to proper storage and handling protocols, researchers can ensure the accuracy and reproducibility of their experimental results.
Applications of Stock Solutions: Essential Tools in Laboratory Procedures
Stock solutions are indispensable components in a myriad of laboratory procedures, streamlining and enhancing the accuracy and consistency of experiments. They serve as the foundation for preparing solutions of precise concentrations, ensuring reliable results and minimizing errors.
Titration
In titration, stock solutions are employed as known concentrations against which unknown solutions are titrated. By carefully adding the stock solution to the unknown, the exact volume required to reach the endpoint can be determined. This information enables the calculation of the unknown solution’s concentration with high accuracy.
Spectrophotometry
Spectrophotometry relies on the absorption of light by solutions to measure concentration. Stock solutions provide a standardized reference with known absorbance values. By comparing the absorbance of an unknown solution to that of the stock solution, the unknown’s concentration can be quantified.
Calibration
Calibration is crucial for ensuring that laboratory instruments are accurate and reliable. Stock solutions with known concentrations are used to calibrate these instruments, allowing them to precisely measure concentrations in unknown samples. This process ensures that consistent and trustworthy measurements are obtained.
Additional Applications
Beyond these fundamental applications, stock solutions find widespread use in various laboratory procedures:
- Sample Preparation: Preparing accurate and repeatable samples for analysis
- Buffer Solutions: Maintaining a constant pH for enzymatic reactions
- Mobile Phases: In chromatography, stock solutions serve as mobile phases to separate and analyze components in a mixture
Best Practices for Using Stock Solutions: Ensuring Reliable and Accurate Results
Stock solutions are an invaluable tool in scientific laboratories, offering precision, consistency, and convenience. However, to maximize their effectiveness, it’s crucial to follow meticulous practices for handling, dilution, and storage.
Proper Handling:
- Minimize exposure to air: Oxygen can degrade some stock solutions. Dispense only the required amount, using pipettes or dispensers, and immediately reclose the container.
- Handle carefully: Avoid spills or contamination by ensuring steady movements and using clean equipment.
Accurate Dilution:
- Use calibrated glassware: Volumetric flasks, pipettes, and graduated cylinders must be meticulously calibrated to ensure precise dilutions.
- Dilute sequentially: For accurate dilutions, perform multiple dilutions in steps, starting with a concentrated stock solution.
- Mix thoroughly: Gently swirl or mix diluted solutions to ensure homogeneous distribution of components.
Optimal Storage:
- Suitable containers: Store stock solutions in appropriate containers, such as glass bottles or amber vials, to prevent degradation or contamination.
- Proper temperature: Keep stock solutions at recommended temperatures, typically 2-8°C for refrigerated storage or room temperature for ambient storage.
- Protect from light: Exposure to light can accelerate degradation. Store stock solutions in opaque containers or protected from direct sunlight.
Additional Considerations:
- Label clearly: Label stock solutions with the compound name, concentration, date of preparation, and expiration date.
- Check expiration dates: Monitor the expiration dates and discard expired solutions to avoid unreliable results.
- Monitor stability: Observe stock solutions regularly for any signs of degradation, such as precipitation or discoloration.
By adhering to these best practices, you can ensure the integrity and accuracy of your stock solutions, leading to reliable and reproducible results in your scientific experiments.