Sodium: An Alkali Metal With 11 Protons And Distinct Isotopes
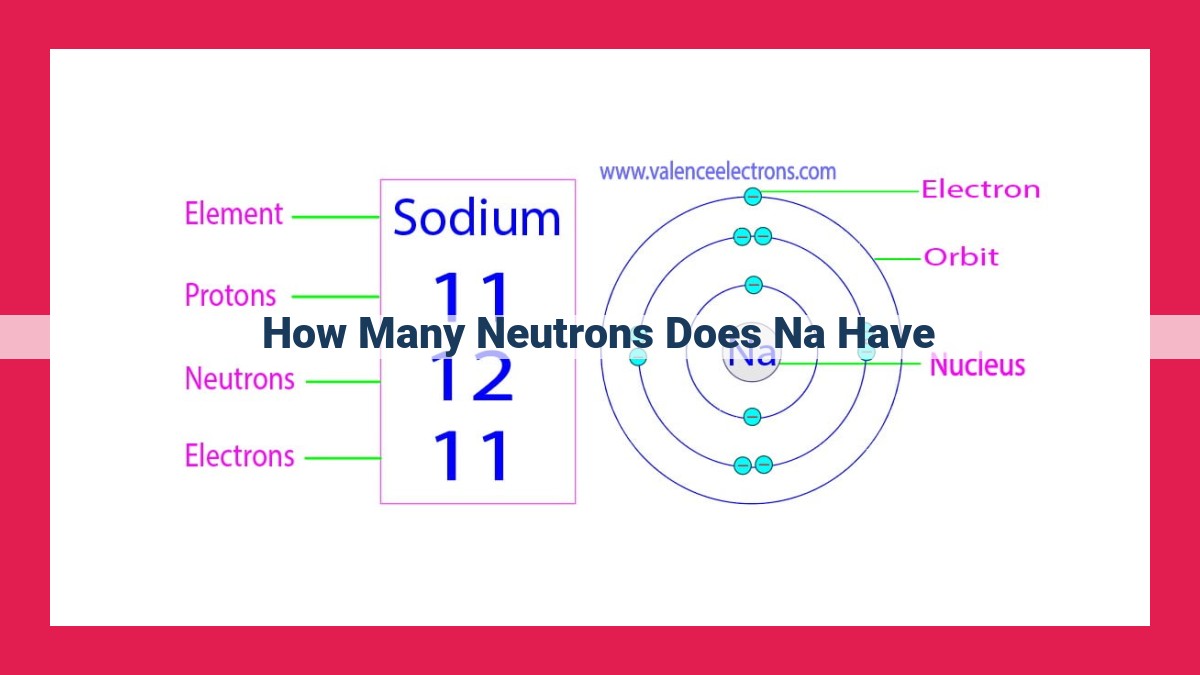
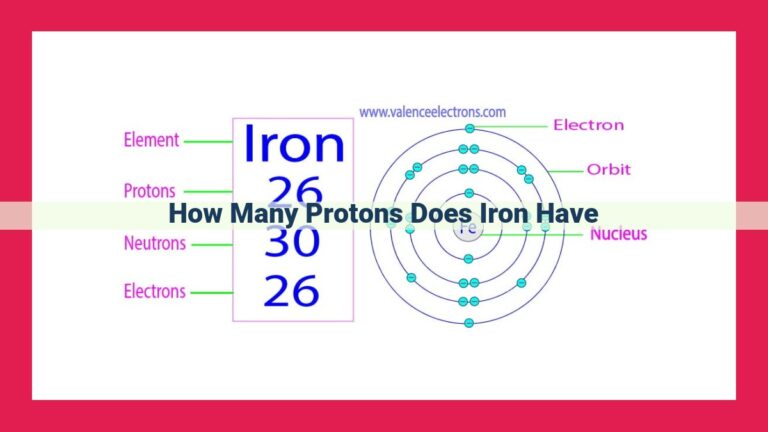
- Sodium (Na) is an alkali metal with an atomic number of 11, meaning it has 11 protons in its nucleus. 2. The most common isotope of sodium, denoted as Na-23, has 11 neutrons in its nucleus. 3. The neutron number contributes to the mass of the atom and helps distinguish between isotopes, which are atoms of the same element with different neutron numbers.
Atomic Structure:
- Explain the concept of atomic structure, focusing on the three fundamental concepts mentioned in the provided outline.
Atomic Structure: The Building Blocks of Matter
Picture this: the world around us is made up of tiny, indivisible units called atoms. These atoms, the fundamental building blocks of matter, are not just simple particles but intricate structures with a rich history.
At the heart of every atom lies a nucleus, the control center where protons and neutrons reside. Protons, carrying a positive charge, balance the equally charged electrons that orbit the nucleus. Neutrons, on the other hand, remain neutral and contribute to the atom’s stability.
Electrons, the third key component of an atom, dance around the nucleus in specific energy levels. These levels dictate the atom’s chemical properties and reactivity. The number of electrons in an atom must always equal the number of protons, maintaining its electrical neutrality.
With this understanding of atomic structure, we can now paint a clear picture of the world around us and appreciate the complexity hidden within the smallest of particles.
Neutron Number: A Keystone in Understanding Atomic Structure
In the vast and intricate realm of atomic structure, the neutron number stands out as a fundamental concept with profound implications. Neutrons, along with protons and electrons, form the building blocks of atoms. As we delve deeper into this intriguing realm, let’s explore the significance of neutron number, its connection to other atomic properties, and its role in nuclear physics.
The neutron number, often denoted by the symbol n, represents the number of neutrons residing within an atom’s nucleus. These enigmatic particles lack electrical charge, distinguishing them from protons, which carry a positive charge. The balance between protons and neutrons determines the stability of an atom.
Neutron number plays a pivotal role in shaping the identity and properties of isotopes. Isotopes are variations of the same element that share the same number of protons but differ in neutron number. This subtle distinction results in different mass numbers for isotopes, as neutrons contribute to an atom’s mass but not its charge.
understanding neutron numbers is essential in the realm of nuclear physics. The manipulation of neutron numbers, through processes like nuclear reactions, underlies various applications, including nuclear power generation and medical imaging. By harnessing the properties of neutrons, scientists can unravel the secrets of atomic nuclei and probe the fundamental nature of matter.
Sodium (Na): The Element of Abundance and Reactivity
Sodium, an alkali metal, is as common as it is essential. Found in the Earth’s crust and seawater, this silvery-white element plays a crucial role in various chemical and biological processes.
Sodium’s Unique Characteristics
Sodium possesses distinctive qualities that set it apart from other elements. As an alkali metal, it exhibits:
- High chemical reactivity: Sodium easily loses its valence electron, forming positive ions (Na+).
- Ionic bonding: Sodium forms ionic bonds with non-metals, readily transferring electrons to achieve a stable electron configuration.
Sodium’s Importance in Everyday Life
Sodium is indispensable in various applications, including:
- Table salt: Sodium chloride (NaCl) is an essential component of our diet.
- Industrial processes: Sodium compounds are crucial in the production of glass, soap, paper, and textiles.
- Biological functions: Sodium ions play a vital role in maintaining fluid balance, nerve transmission, and muscle contraction.
The Importance of Understanding Sodium’s Neutron Number
Every atom of an element has a specific number of neutrons in its nucleus. This number, known as the neutron number, is crucial in identifying different isotopes of the element.
- Atomic number: The number of protons in an atom’s nucleus is known as its atomic number. For sodium, the atomic number is 11.
- Neutron number: Sodium has 12 neutrons in its most common isotope, denoted as Na-23. This means that the nucleus of a Na-23 atom contains 11 protons and 12 neutrons.
- Isotopes: Isotopes are atoms of the same element with different neutron numbers. Sodium, for example, has several isotopes, including Na-22 and Na-24.
Understanding the neutron number is essential for identifying the specific isotope of an element. It provides valuable information about the atom’s nuclear stability and its behavior in various chemical reactions.
Neutron Number of Sodium (Na):
- State the atomic number of sodium and explain its significance.
- Mention the most common isotope of sodium and its neutron number.
- Emphasize the importance of understanding the neutron number in determining the specific isotope of an element.
Neutron Number of Sodium (Na)
In the realm of atomic structure, understanding the neutron number is crucial for comprehending the specific isotopic nature of elements. Let’s delve into the fascinating world of sodium (Na) to illustrate this concept.
Sodium, an alkali metal, holds a unique position in the periodic table. With an atomic number of 11, it boasts 11 protons in its nucleus. This atomic number plays a pivotal role in determining the element’s chemical properties.
Among the isotopes of sodium, the most common form is sodium-23 (²³Na). This isotope possesses 11 protons, as dictated by the atomic number, and an additional 12 neutrons in its nucleus. It is the neutron number that distinguishes ²³Na from other sodium isotopes.
Understanding the neutron number is essential in isotope identification. Isotopes of an element share the same atomic number (number of protons), but differ in their neutron number. The varying neutron numbers result in different atomic masses and physical properties.
In summary, the neutron number of sodium-23 is 12. This number, coupled with the atomic number of 11, allows us to distinguish this isotope from other forms of sodium. Understanding neutron numbers is fundamental in nuclear physics and isotope analysis, providing valuable insights into the composition and behavior of elements.