Safeguarding The Airway: The Role Of Aryepiglottic Folds In Swallowing
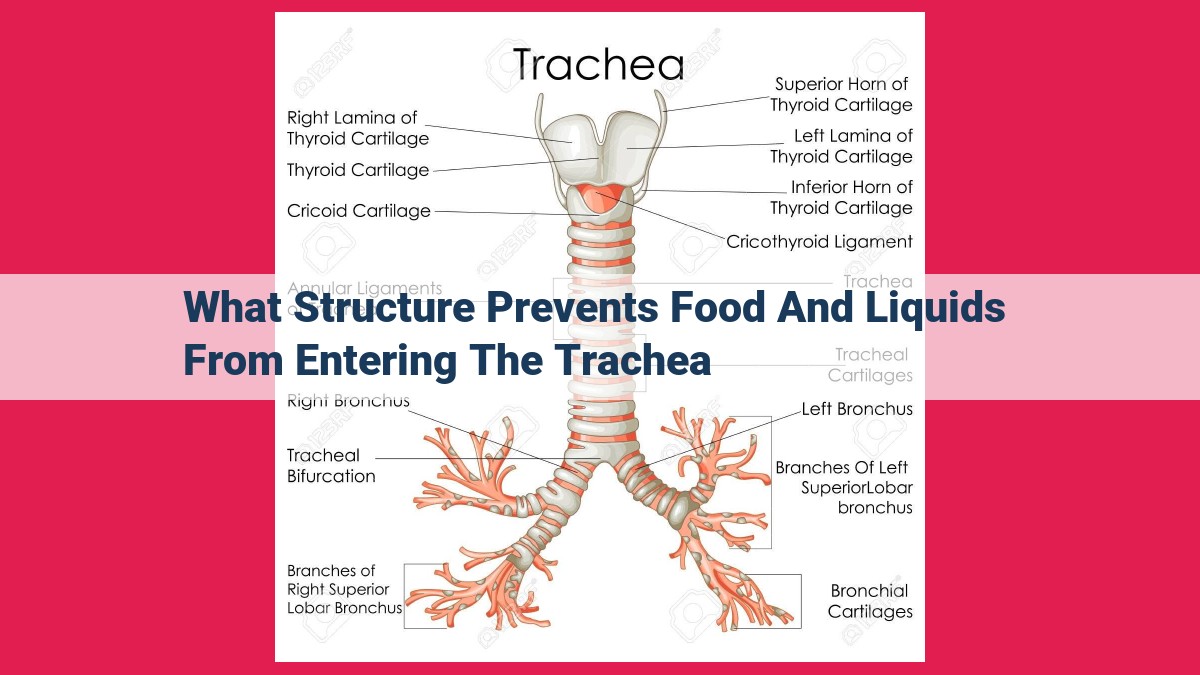
The aryepiglottic folds, two leaf-shaped structures, play a vital role in safeguarding the airway during swallowing. Located at the base of the epiglottis, these folds seal the entrance to the larynx, acting as a barrier that prevents food and liquids from accidentally entering the trachea and causing potential harm to the respiratory system.
- Overview of the importance of the epiglottis, larynx, and other structures in protecting the airway.
The Guardians of the Airway: A Story of Protection and Harmony
Every breath we take is a testament to the remarkable teamwork of our respiratory system. Within this intricate symphony of organs, a select group of structures stands out as the guardians of our airway, safeguarding us from potential harm while facilitating the effortless passage of air to and from our lungs. Let’s embark on a journey to meet these unsung heroes and uncover their vital roles in keeping us breathing safely.
The Epiglottis: The Leaf-Shaped Sentinel
The epiglottis, a leaf-shaped cartilage, is a crucial player in protecting the airway during swallowing. Situated at the top of the larynx, or voice box, it acts as a flip-down lid that closes over the opening of the larynx when we swallow. This swift action ensures that food and liquid are directed into the esophagus and away from the delicate airways.
The Larynx: Voicebox and Airway Protector
The larynx, commonly known as the voicebox, not only generates our voice but also plays a vital role in protecting the airway. Its intricate arrangement of cartilages and muscles allows for the production of sound while simultaneously preventing food or liquid from entering the lungs. This dual function makes the larynx an essential organ for both communication and airway safety.
The Epiglottis: The Leaf-Shaped Sentinel
- Description of the epiglottis’s structure, location, and function during swallowing.
The Epiglottis: The Sentinels of the Airway
Nestled at the base of the tongue’s root, shielded beneath the soft palate’s gentle embrace, lies a guardian of the airway, the epiglottis. The leaf-shaped sentinel stands ready to protect the delicate mechanisms of the respiratory system from the chaos of swallowing.
Imagine a flexible gate, its smooth contours mirroring a verdant leaf. This is the epiglottis, a muscular flap of cartilage that rests in a relaxed position, allowing air to pass freely into the larynx. When the swallowing reflex is triggered, the epiglottis swiftly swings into action, flipping down like a drawbridge. This downward motion effectively seals the opening to the larynx, blocking the entry of food and liquids.
As the morsels of sustenance journey through the pharynx, the epiglottis remains steadfast, its presence ensuring that every bite and sip finds its destined path towards the esophagus and not the treacherous depths of the lungs. With its leafy shield in place, the airway remains safe, allowing the lungs to continue their vital exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide.
Once the swallowing process concludes, the epiglottis retreats, gracefully returning to its upright position. The airway is reopened, and the harmonious rhythm of breathing resumes. This intricate interplay between the epiglottis and the act of swallowing epitomizes the elegant symphony of the human body, where every component plays a vital role in maintaining our well-being and sustaining life.
**The Larynx: Voicebox and Airway Protector**
Nestled within our necks, the larynx, commonly known as the voicebox, plays a crucial dual role in our daily lives: producing sound and safeguarding our airway. This fascinating organ is an intricate symphony of cartilage, muscles, and ligaments.
As the gateway to our lungs, the larynx stands guard, ensuring that every breath we take reaches its intended destination. When we swallow, its protective mechanism kicks into gear, preventing food and liquids from veering off course and entering our windpipe.
But the larynx’s talents extend far beyond breathing and swallowing. It is the maestro of our vocal cords, the tiny folds of tissue that vibrate to create sound. When air passes through these cords, they oscillate, producing a wide range of frequencies that we perceive as speech, laughter, and song.
The versatility of the larynx is truly remarkable. It allows us to communicate, express emotions, and connect with others through the power of voice. At the same time, it tirelessly protects our airway, ensuring that we can breathe freely and nourish our bodies without hindrance.
So, let us marvel at the wonders of the larynx, the voicebox and airway protector. Its intricate design and unwavering functionality are a testament to the brilliance of our bodies.
The Pharynx: The Throat, a Muscular Conduit
The pharynx, commonly known as the throat, is a muscular tube that plays a crucial role in connecting the nose and mouth to the larynx (voice box) and esophagus (food pipe). Its primary function is to facilitate the passage of air, food, and liquids into their respective destinations.
As part of the digestive system, the pharynx acts as a muscular conduit, propelling food and liquids down the esophagus through a series of peristaltic contractions. These coordinated muscle movements help guide the bolus (mass of chewed food) smoothly towards the stomach.
Furthermore, the pharynx also contributes to the process of swallowing. When food enters the mouth, the tongue pushes it backward against the palate, triggering a complex series of reflexes that involve the pharynx. The muscles of the pharynx then contract, raising the larynx and epiglottis to prevent food from entering the airway. Simultaneously, the opening to the esophagus widens, allowing the bolus to pass into the digestive tract.
In summary, the pharynx is a vital component of both the respiratory and digestive systems, providing a seamless passageway for air, food, and liquids. Its intricate muscular structure enables the coordinated movements necessary for swallowing and protects the delicate airway from foreign objects during this process. As a true master of multi-tasking, the pharynx stands as a testament to the remarkable complexity of the human anatomy.
Aryepiglottic Folds: Unsung Heroes of Swallowing and Breathing
Nestled within the depths of our throat, like sentinels guarding against intruders, lie the aryepiglottic folds. These delicate yet crucial structures play an indispensable role in ensuring the safe passage of food and liquids into the esophagus while preventing their entry into the larynx (voice box).
The aryepiglottic folds are thin and pliable, extending from the upper rim of the epiglottis to the sides of the larynx. As we swallow, these folds form a protective barrier that directs food and liquids away from the larynx, preventing them from entering the airway.
This intricate mechanism is achieved through the coordinated movement of the aryepiglottic folds. As the epiglottis flips down to cover the larynx during swallowing, the aryepiglottic folds simultaneously close together, creating a watertight seal that effectively blocks the entry of foreign bodies into the airway. This seamless interplay ensures that we can breathe and swallow simultaneously without the risk of aspiration.
The aryepiglottic folds are not only essential for protecting the airway but also play a crucial role in voice production. They help to amplify sound waves by vibrating against the vocal cords, creating the resonance that gives our voices their unique quality.
In conclusion, the aryepiglottic folds may be unassuming structures, but their significance cannot be overstated. They are the guardians of our airway, ensuring that we can breathe and swallow effortlessly, and they contribute to the melodious symphony that is our voice.
Vallecula: The Epiglottis’s Neighbor
Nestled amidst the laryngeal anatomy, there is a hidden nook – the vallecula. Situated just beneath the epiglottis, this unsung hero plays a crucial role in guiding nourishment safely on its journey to the esophagus.
Imagine a tiny valley, cradled between the epiglottis and the base of the tongue. That’s where you’ll find the vallecula. Like a skilled traffic controller, it directs food and liquids away from the larynx, the gateway to the airway.
As you swallow, the epiglottis flips down, sealing off the larynx to prevent food from going astray. But what prevents food from slipping into that narrow gap beneath the epiglottis? Enter the vallecula, like a vigilant sentry guarding the passageway.
The vallecula’s structure amplifies its protective prowess. Its sloped walls gently guide food and liquids away from the larynx and towards the esophagus. It’s akin to a funnel, ensuring a smooth transition without any unwanted detours.
Without the vallecula, swallowing would be a perilous endeavor, potentially leading to aspiration, where food or liquids enter the airway. But this unsung hero, working in harmony with its anatomical neighbors, silently safeguards our respiratory system.
So, next time you swallow, spare a thought for the vallecula, the humble yet indispensable guardian of your airway. It’s a testament to the intricate symphony of the human body, where even the smallest of structures play vital roles in our well-being.
The Cuneiform Cartilage: A Silent Supporter in the Larynx’s Symphony
Tucked away within the depths of the larynx, the cuneiform cartilage quietly plays an indispensable role in the graceful symphony of breathing and swallowing. This small, triangular-shaped cartilage serves as a silent guardian, supporting the epiglottis and aryepiglottic folds, ensuring the airway remains clear while food and liquids travel safely down the esophagus.
Like a hidden gem, the cuneiform cartilage resides in the posterior wall of the larynx, wedged between the epiglottis and the arytenoid cartilages. Its unassuming size belies its crucial function. As the epiglottis descends to seal off the larynx during swallowing, the cuneiform cartilage lends its support, stabilizing the epiglottis and preventing it from slipping into the airway.
Furthermore, the cuneiform cartilage collaborates with the aryepiglottic folds, two muscular walls that line the sides of the larynx. Together, they form a protective barrier, preventing food and liquids from straying into the larynx and potentially causing aspiration. The cuneiform cartilage, acting like a reliable anchor, secures these protective folds, ensuring their effectiveness.
Without the cuneiform cartilage’s unwavering support, the epiglottis and aryepiglottic folds would falter in their vital roles. Breathing and swallowing would become compromised, potentially leading to serious health issues. Yet, this diminutive but mighty cartilage works diligently behind the scenes, safeguarding the airway and enabling seamless swallowing.
In the grand orchestra of the larynx, the cuneiform cartilage may not be the star performer, but its supportive role is essential for the symphony’s success. It stands as a testament to the intricate interconnectedness of the human body, where even the smallest components play a profound part in our well-being.