Unleash The Power Of Random Number Tables: A Comprehensive Guide To Generating Unbiased Numbers
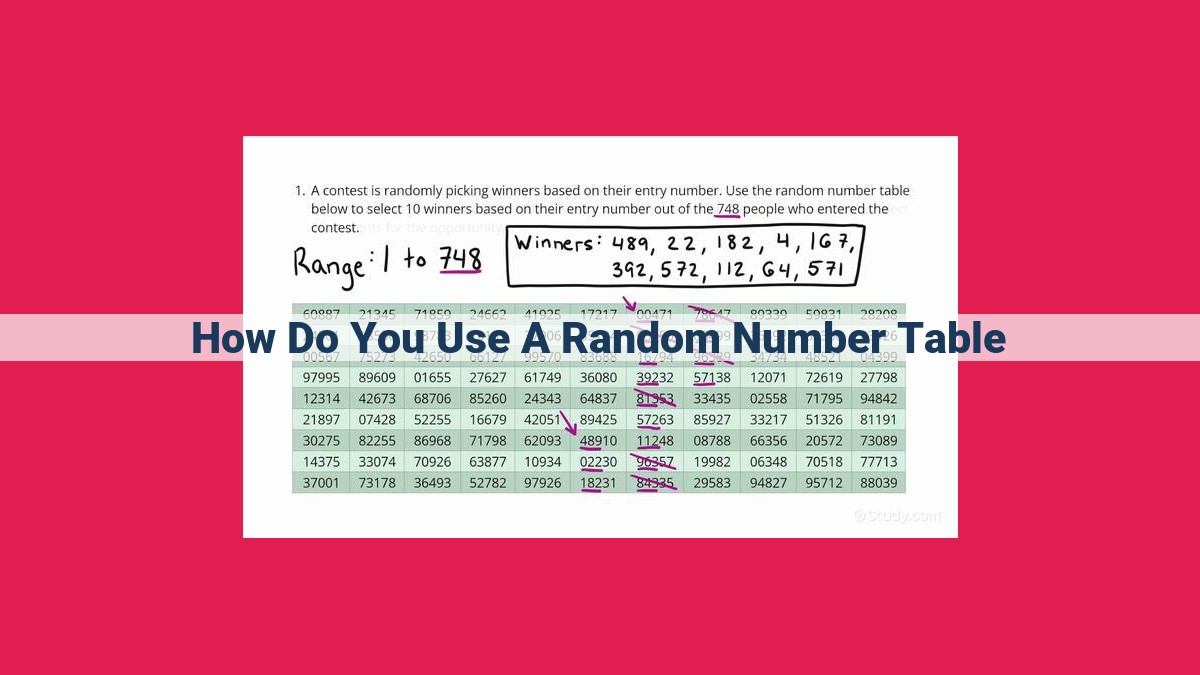
To use a random number table, locate a starting point by randomly selecting a row and column. Read the numbers sequentially, treating each digit as a separate random number. Convert decimal numbers to integers if necessary. Repeat the process as needed, ensuring a consistent direction and skipping patterns to maintain randomness. Random number tables provide an unbiased and objective way to generate random numbers for applications in statistics, research, and decision-making.
Unveiling the Power of Random Numbers
In the realm of data and decision-making, random numbers reign supreme. These enigmatic digits play a pivotal role in various fields, from research and statistics to sampling and probability theory. Their significance stems from their ability to eliminate bias and introduce an element of objectivity into our methods.
By using random numbers, we can ensure that our results are not influenced by preconceived notions or personal preferences. They create a level playing field where every outcome has an equal chance of being selected. In this era of information overload, random numbers provide us with a way to cut through the noise and derive insights based on true randomness.
For instance, in scientific research, random numbers are used to select participants for studies. This ensures that the sample is representative of the population, eliminating any bias that could arise from non-random selection. Similarly, in quality control, random samples are selected to ensure that products meet the required standards. By incorporating randomness, we increase the accuracy and reliability of our findings.
Concept 1: Understanding Randomization
- Explain the concept of randomization and its role in probability theory.
- Discuss the different methods of generating random numbers, including physical and computational techniques.
- Emphasize the need for statistical principles to ensure true randomness.
Understanding Randomization: The Foundation of Unbiased Data
In the realm of research, data collection, and decision-making, randomization plays a pivotal role in ensuring objectivity and unbiased results. Randomization, simply put, is the process of selecting elements from a set in an unpredictable manner.
This concept is deeply ingrained in probability theory, providing a mathematical framework for analyzing and predicting the likelihood of events. Randomization serves as the cornerstone of statistical inference, allowing researchers to draw meaningful conclusions from samples and generalize them to populations.
There are numerous methods for generating random numbers, ranging from physical techniques like dice rolling to computer algorithms. Physical methods, while straightforward, can be time-consuming and impractical for large datasets.
On the other hand, computational techniques leverage pseudo-random number generators (PRNGs) to produce seemingly random sequences of numbers. These algorithms are designed to mimic randomness but are ultimately deterministic, relying on seeds or initial values.
To ensure true randomness, it is crucial to adhere to statistical principles and employ rigorously tested PRNGs. These principles include independence, where each number is generated without influence from previous or subsequent numbers, and uniform distribution, where all possible numbers have an equal probability_ of being selected.
Navigating Random Number Tables: Unlocking the Secrets of Chance
In the realm of probability and statistics, random numbers hold immense power. From generating unbiased samples to powering simulations, they play a pivotal role in ensuring the integrity and objectivity of data and results. Among the various methods of obtaining random numbers, random number tables stand out as a foundational tool that has been used for decades.
Structure and Organization of Random Number Tables
Random number tables are structured in a grid format, consisting of columns and rows, each containing a sequence of digits. The digits are generated using statistical principles to ensure their randomness and unpredictability. By carefully arranging these digits, tables create a vast collection of random numbers that can be accessed and used for various applications.
Locating Specific Numbers
Navigating random number tables is relatively straightforward. To locate a specific number, simply identify the column and row that correspond to the desired digit. For instance, if you need the third digit, move to the third column. Similarly, to find the fifth digit in the second row, go to the intersection of column 5 and row 2.
Applications in Data Retrieval and Manipulation
Random number tables serve as valuable resources for data retrieval and manipulation in numerous fields. In research, they assist in selecting unbiased samples and assigning randomized treatments to subjects. In engineering, random numbers are used to simulate complex systems and generate test cases. Additionally, tables facilitate the creation of pseudorandom sequences and permutation patterns for various applications.
By understanding the structure and organization of random number tables, you can unlock the power of randomness in your own projects. Whether you’re conducting research, simulating scenarios, or simply need to generate unbiased values, random number tables remain an indispensable tool in the world of probability and statistics.
Concept 3: Demystifying the Numbers in Random Number Tables
Imagine yourself on an adventure, embarking on a quest to decipher the secrets of random numbers. Like ancient runes hidden in a forgotten scroll, random numbers hold the power to unravel the enigmas of uncertainty.
In this realm of randomness, we encounter tables brimming with enigmatic digits, seemingly unrelated and chaotic. But don’t despair, for within these tables lies a treasure trove of insights, waiting to be discovered.
Let us begin our exploration by unraveling the various formats in which these numbers present themselves. They may appear as decimal fractions, ranging from 0 to less than 1, or as whole integers, each carrying a unique tale.
The art of interpreting these numbers is akin to a delicate dance, where intuition and precision intertwine. Decimals, like graceful ballerinas, float effortlessly between numbers. Integers, on the other hand, are like stoic knights, standing firm and whole.
To draw meaningful insights from these numbers, we must awaken our inner detectives. Each digit hints at a hidden pattern, a clue to unraveling the puzzle. By scrutinizing the sequence and distribution of numbers, we can uncover trends and make informed predictions.
Visualizing random numbers can be a transformative experience, akin to peering into a kaleidoscope of possibilities. Through graphs and charts, we can paint a vivid picture of the data, revealing patterns that might otherwise remain elusive.
Numbers, once mysterious and aloof, now become our trusted companions on this extraordinary journey. They guide us towards a deeper understanding of randomness and its immeasurable power to shape our world.
Concept 4: Navigating the Practical Applications of Random Numbers
Beyond theoretical concepts, random numbers find widespread applications that impact our daily lives. Let’s explore some fascinating use cases:
Research and Sampling
Random numbers play a pivotal role in scientific research. Researchers use them to:
- Select unbiased samples: By randomly selecting participants or data points, researchers can ensure that their results are not influenced by bias.
- Conduct experiments: Randomization in experiments controls for variables that might skew the results, enhancing the reliability of conclusions.
Statistical Validation
Statistical methods, such as hypothesis testing, leverage random numbers to determine the significance of findings. By comparing the results obtained from random sampling to those expected by chance, researchers can:
- Validate hypotheses: They can accept or reject hypotheses based on the probability of obtaining the observed results by chance.
- Quantify the strength of evidence: Random numbers help determine the likelihood of an event occurring due to factors other than chance.
Decision-Making
Random numbers can aid in making fair and impartial decisions:
- Lotteries and drawings: Random selection guarantees equal opportunities for participants and eliminates bias.
- Resource allocation: Random numbers can objectively allocate scarce resources, such as research funds or medical treatments.
Ethical Considerations and Potential Biases
While random numbers aim to eliminate bias, certain considerations must be noted:
- Ethical implications: The use of random numbers should not violate ethical guidelines or harm participants.
- Potential biases: Sampling techniques and data collection methods can introduce biases that may affect the randomness of the results. Researchers must carefully design their studies to minimize these biases.
Embracing Randomness for Informed Decisions
Random numbers are a powerful tool that helps us navigate the world with objectivity and impartiality. Their applications extend beyond theoretical concepts into research, sampling, statistical validation, and decision-making. By understanding the principles behind random numbers, we can harness their power to make informed choices and advance our knowledge.