Qin Dynasty’s Standardization And Efficiency In Transportation Infrastructure
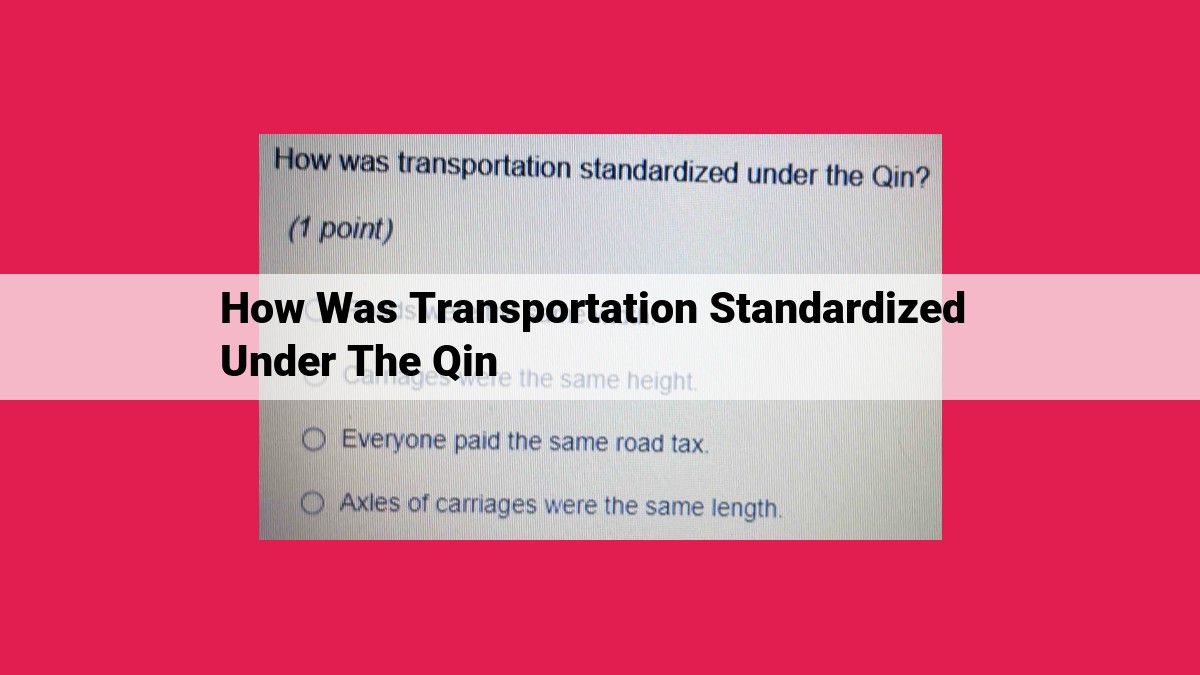
To standardize transportation, the Qin implemented a unified carriage system with consistent axle lengths, track widths, wheel sizes, and a fixed gauge, ensuring compatibility and efficiency. They also established a courier service network, setting up post stations along travel routes and utilizing a relay system to relay messages swiftly over vast distances.
A. Standard Axle Length: Describe the importance of establishing a consistent axle length for carriages, ensuring compatibility and efficient movement.
The Importance of a Standardized Axle Length: Ensuring Compatibility and Seamless Carriage Movement
In the world of transportation, standardization is key to ensuring compatibility, efficiency, and safety. When it comes to carriages, standardizing the axle length was a critical step in revolutionizing travel.
Imagine a vast network of carriage routes, but with each carriage sporting an arbitrary axle length. The chaos would be immense. Carriages would struggle to fit onto tracks designed for different axle lengths, leading to delays, disruptions, and even accidents.
By establishing a consistent axle length, however, this nightmare was averted. Carriages could now seamlessly connect to tracks and travel smoothly without fear of derailment. This standardization also made it possible to efficiently move carriages between different routes, reducing downtime and improving overall transportation logistics.
The benefits of a standardized axle length extended beyond compatibility. It also reduced maintenance costs by minimizing wear and tear on tracks. Carriages with appropriately sized axles evenly distributed their weight, preventing excessive damage to the tracks. This not only prolonged the lifespan of tracks but also improved safety, as well-maintained tracks are less prone to failure.
In short, the standardization of axle length for carriages was a game-changer in the development of a reliable and efficient transportation system. It paved the way for smoother, faster, and safer travel, revolutionizing the movement of people and goods across vast distances.
The Standardized Track Width: A Key to Smoother Travel and Carriage Exchange
In the annals of transportation history, the development of a standardized track width for carriages played a pivotal role in revolutionizing travel and trade. Before this standardization, carriages were built with varying track widths, making it cumbersome and inefficient to exchange them between different routes.
The benefits of a uniform track width were manifold. It ensured smoother travel by preventing carriages from derailing or becoming stuck due to misalignment with the tracks. This, in turn, reduced wear and tear on both carriages and tracks, extending their lifespan and minimizing maintenance costs.
Moreover, a standardized track width facilitated the exchange of carriages between different routes. This made it possible to transport goods and passengers across long distances without the need for costly and time-consuming transshipments. Carriages could be easily transferred from one track to another, allowing for seamless and uninterrupted journeys.
The establishment of a standardized track width also played a crucial role in the development of a nationwide courier service network. With carriages able to travel smoothly and efficiently over long distances, messages and goods could be transported with unprecedented speed and reliability. This facilitated commerce and communication, fostering economic growth and strengthening political cohesion.
In conclusion, the standardization of track width for carriages was a transformative innovation that revolutionized travel and trade. It enabled smoother travel, facilitated carriage exchange, and paved the way for the development of a courier service network that spanned vast distances. This standardization stands as a testament to the ingenuity and foresight of our ancestors, whose efforts continue to shape the way we move people and goods today.
The Importance of Uniform Wheel Sizes in the Standardized Unified Carriage System
In the intricate network of the Standardized Unified Carriage System, uniform wheel sizes emerged as a critical factor in ensuring the smooth and efficient movement of carriages. Beyond their obvious role in supporting the carriage, these standardized wheels played a vital role in reducing wear and tear on the tracks and enhancing overall safety.
Reduced Wear and Tear
The use of uniform wheel sizes ensured that the weight of the carriage was distributed evenly across the track. This uniform distribution prevented excessive stress on any particular part of the track, thereby reducing the likelihood of premature wear and damage. By minimizing wear and tear, the lifespan of the tracks was extended, reducing maintenance costs and disruptions to carriage traffic.
Improved Safety
Uniform wheel sizes also contributed significantly to the safety of the carriage system. When wheels of different sizes were used, there was a greater chance of derailment as the carriage encountered uneven sections of track. By standardizing wheel sizes, this risk was significantly reduced, ensuring that carriages could navigate the tracks safely and preventing derailments that could lead to injuries or damage.
Moreover, uniform wheel sizes allowed for the implementation of standard safety measures. For example, track gauges could be designed to fit perfectly with the standardized wheels, ensuring that carriages remained securely on the rails even during sharp turns or high speeds. This enhanced safety measures helped protect not only the passengers and cargo but also the track infrastructure itself.
In conclusion, the standardization of wheel sizes in the Standardized Unified Carriage System was a critical step in ensuring the smooth, efficient, and safe movement of carriages. By reducing wear and tear on tracks and enhancing safety, uniform wheel sizes played a pivotal role in the development of a reliable and interconnected transportation network.
D. Fixed Gauge: Elaborate on the role of a fixed gauge in maintaining consistent track spacing and enabling seamless carriage movement.
D. Fixed Gauge: The Anchor of Seamless Carriage Movement
In the pioneering era of rail transportation, establishing a fixed gauge played a pivotal role in ensuring consistent track spacing and enabling effortless carriage movement. This fundamental principle became the cornerstone of a reliable and efficient transportation system that would revolutionize travel and trade.
A fixed gauge refers to the precise distance between the inner edges of the parallel rails. By standardizing this distance, carriages could roll smoothly along the tracks without the risk of derailment or excessive wear and tear. It ensured that carriages from different manufacturers could seamlessly traverse the same tracks, creating a network of interconnected routes.
Imagine the chaos that would ensue if each carriage had a unique wheelbase or axle length. Travel would be fraught with delays and accidents, and the efficient exchange of goods and messages would be a distant dream. The fixed gauge acted as an invisible guide, keeping carriages firmly on track and ensuring a uniform and reliable journey.
The implementation of a fixed gauge also facilitated the development of more sophisticated rail infrastructure. With the assurance of consistent track spacing, engineers could design bridges, tunnels, and junctions with precision, knowing that carriages would navigate these structures without hindrance. This standardization laid the foundation for the sprawling rail networks that would crisscross continents and transform the global landscape.
In short, the fixed gauge played an indispensable role in the development of the standardized unified carriage system. It provided a stable and predictable framework within which carriages could move seamlessly, fostering trade, communication, and the advancement of civilization.
The Establishment of Post Stations: A Vital Link in the Relay System
In the days before modern communication, the exchange of messages and goods relied heavily on the swift and efficient movement of couriers. To facilitate this, a network of post stations was established along travel routes, serving as resting places and providing essential facilities for couriers and their horses.
These post stations were strategically positioned at regular intervals, ensuring that couriers could travel long distances without becoming exhausted. At each station, they could find shelter from the elements, fresh horses, and provisions. This allowed them to maintain a consistent pace and deliver messages with utmost urgency.
The post stations also played a crucial role in the relay system that was used to transport messages swiftly over vast distances. Upon arriving at a post station, a courier would hand off the message to a fresh courier, who would then continue the journey on a new horse. This process was repeated at each subsequent post station, allowing messages to reach their destination with remarkable speed and reliability.
Optimized for SEO on page
- Keywords: post stations, travel routes, couriers, horses, relay system
- Heading tags:
<
h2> and
<
h3>
* Bold and italic formatting for emphasis
* Descriptive and informative content
Relay System for Dispatching Messages: A Swift and Efficient Communication Chain
In the era before modern communication technologies, a relay system served as the vital backbone for transporting messages across vast distances. This intricate network played a pivotal role in the development of efficient courier services, enabling the swift and reliable exchange of information.
The Postal Nexus
At the heart of the relay system lay a strategic network of post stations established at regular intervals along major travel routes. These stations functioned as hubs of activity, providing resting and refreshment stops for couriers and their trusty horses.
The Courier’s Role
Couriers were the tireless messengers who carried the messages, traveling tirelessly from station to station. The relay system utilized multiple couriers and horses, with each segment of the journey being assigned to a different team. This division of labor ensured that messages could travel at a breakneck pace, with riders exchanging their exhausted horses for fresh mounts at each post station.
Swift and Secure Transit
The relay system enabled messages to traverse long distances with remarkable speed and efficiency. The use of multiple couriers and horses eliminated the need for a single messenger to undertake the entire journey, reducing fatigue and the risk of delays. Moreover, the ability to change horses at post stations guaranteed that the couriers could maintain a consistent pace, ensuring the timely delivery of messages.
In addition to its speed, the relay system also provided a high level of security. By utilizing multiple couriers, the risk of any single courier being intercepted or waylaid was minimized. The secure transit of messages was paramount, as they often contained sensitive information that could impact political, military, or commercial affairs.