Plasma: The Dominant State Of Matter In The Universe
Plasma, a highly ionized gas, reigns supreme as the most prevalent state of matter in the universe, accounting for over 99% of its volume. This ionized state, characterized by free electrons and ions, dominates the interstellar medium, permeates the solar wind, and exists within celestial objects such as nebulae, supernova remnants, and active galactic nuclei.
Embarking on a Cosmic Odyssey: Exploring Plasma, the Dominant Force of the Universe
In the vast expanse of the cosmos, matter weaves itself into a symphony of states. From the solidity of Earth to the fluidity of water, from the ethereal expanse of gases to the enigmatic realm of plasmas, each form holds its own unique story. However, amidst this cosmic tapestry, one state stands out as the reigning sovereign – plasma.
Plasma, an ionized gas charged with free-ranging electrons, dominates the vast majority of the universe’s volume. It permeates the interstellar void, streams from the Sun, and ignites the splendor of celestial wonders like nebulae and supernova remnants. Plasma holds the key to unraveling the mysteries of astrophysics, guiding us towards a deeper understanding of the cosmos’s evolution and the birth, life, and death of stars.
As we delve into this cosmic realm, we shall explore the nature of plasma, its prevalence throughout the universe, and its profound implications for our comprehension of the cosmos. Along the way, we shall encounter the interconnectedness of celestial phenomena, where plasma plays a pivotal role in shaping the destiny of stars, galaxies, and the very fabric of our existence.
Plasma: The Dominant Force:
- Definition and characteristics of plasma.
- Importance and abundance in the universe.
Plasma: The Omnipresent Force Shaping the Cosmos
Plasma, the enigmatic fourth state of matter, reigns supreme in the vast expanse of our universe. Beyond the familiar realms of solid, liquid, and gas lies this extraordinary substance, characterized by its ethereal glow and unparalleled energy. Plasma is the dominant force in the cosmos, shaping the celestial tapestry with its ionized particles and electromagnetic fields.
Defining Plasma: A Universe of Charged Particles
Plasma, a superheated gas, is comprised of ionized atoms, their electrons stripped away from their nuclei, leaving behind a sea of free-floating charges. This unique composition grants plasma distinct properties that set it apart from other states of matter.
Abundance of Plasma: A Cosmic Majority
Plasma is omnipresent in the universe, accounting for a staggering 99% of its visible matter. It permeates interstellar space, engulfing stars, and fuels the enigmatic phenomena that captivate astronomers’ imaginations.
Significance of Plasma: Illuminating the Cosmos
Plasma’s importance extends far beyond its sheer abundance. It plays a pivotal role in astrophysics, influencing everything from the birth and death of stars to the enigmatic emissions of active galactic nuclei. Plasma’s ionized particles emit electromagnetic radiation, illuminating the cosmos with a myriad of colors and revealing the hidden wonders that lie beyond our immediate perception.
Plasma: The Omnipresent Force Shaping the Cosmos
In the vast expanse of the universe, where celestial wonders unfold, there exists a fundamental building block that pervades the cosmos – plasma. This extraordinary state of matter, omnipresent and dynamic, plays a pivotal role in shaping the celestial tapestry.
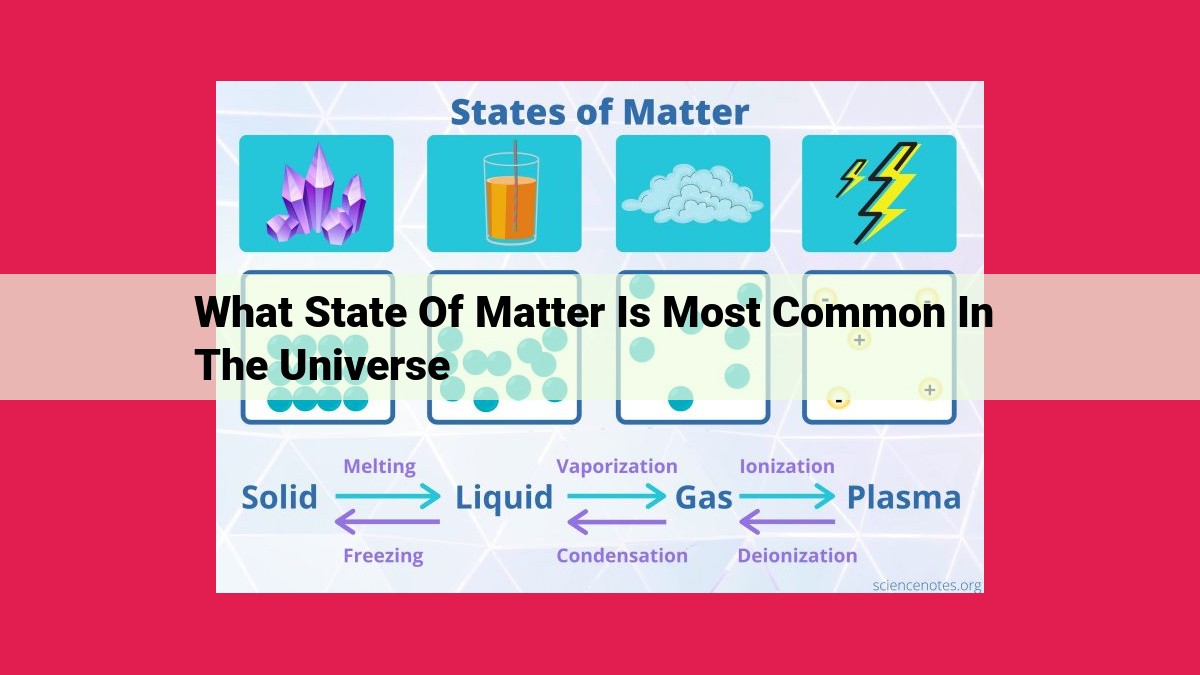
Plasma, the fourth state of matter after solids, liquids, and gases, is ionized gas. When atoms lose their electrons, they become ions, and the sea of free electrons and ions creates a conductive medium. This unique property makes plasma highly responsive to electromagnetic fields, enabling it to transmit and manipulate energy across vast distances.
In the vastness of space, plasma reigns supreme. It comprises over 99% of the observable universe, from the solar wind that envelops our planet to the distant reaches of active galactic nuclei. This ethereal substance holds the key to understanding the formation, evolution, and interaction of celestial bodies.
Interstellar Medium: A Plasma Playground
Nestled between the stars lies the interstellar medium (ISM), a vast reservoir of gas, dust, and plasma. Here, plasma plays a dominant role in shaping the behavior of the ISM. The ethereal glow of radio waves emitted by plasma in the ISM provides a window into the mysterious depths of space.
Solar Wind: A Plasma Symphony
Emanating from the Sun’s corona, the solar wind is a continuous stream of charged particles, primarily plasma. This energetic outflow of plasma travels through the solar system, interacting with the magnetic fields of planets and shaping their atmospheres. The spectacular aurora borealis and aurora australis are vivid reminders of the solar wind’s impact on Earth.
As we delve deeper into the cosmos, we encounter a myriad of celestial phenomena where plasma takes center stage, from the ethereal glow of nebulae to the explosive energy of supernova remnants. Each of these celestial wonders bears witness to the profound influence of plasma on the evolution and spectacle of the universe.
Occurrences of Plasma in the Universe:
- Interstellar Medium:
- Role of plasma in the diffuse nature of the ISM.
- Radio wave emissions from plasma in the ISM.
- Role of plasma in the diffuse nature of the ISM.
- Radio wave emissions from plasma in the ISM.
Plasma’s Omnipresence in the Interstellar Medium
In the vast cosmic tapestry, plasma, the fourth state of matter, reigns supreme. It permeates the interstellar medium (ISM), the rarefied material that fills the spaces between stars. Plasma’s properties shape the ISM’s enigmatic nature.
The ISM’s diffuse character is largely attributable to plasma’s charged particles. These particles collide with neutral atoms and molecules, scattering them and preventing them from clumping together to form stars. Plasma also plays a pivotal role in the ISM’s radio wave emissions. When plasma interacts with magnetic fields, it can generate electromagnetic waves that astronomers can detect with radio telescopes. These emissions provide valuable insights into the structure and dynamics of the ISM.
Solar Wind: The Plasma Messenger from the Sun
In the vast cosmic playground, the Sun, our celestial beacon, not only illuminates our world but also sends out a constant stream of charged particles known as the solar wind. This plasma, made up of ionized gases, travels through space, carrying the Sun’s presence far beyond our planet.
Origin and Composition
The solar wind originates in the corona, the Sun’s outer atmosphere. As the corona reaches incredibly high temperatures, it heats the gases within it, stripping them of electrons and creating a sea of plasma. The solar wind then escapes through holes in the corona called coronal holes.
Effects on Earth
The solar wind’s journey doesn’t end at the edge of the solar system. It reaches Earth and interacts with our planet’s magnetic field, creating a protective magnetosphere. This shield deflects most of the solar wind, but charged particles can still penetrate and interact with our atmosphere.
Earth’s Magnetic Field and Auroras
When solar wind particles enter Earth’s atmosphere, they collide with atoms and molecules, exciting them and releasing their energy in the form of light. This phenomenon gives rise to the mesmerizing auroras, also known as the Northern and Southern Lights. The interplay between the solar wind and Earth’s magnetic field transforms the skies into a vibrant canvas, painting the nights with ethereal colors.
Plasma in Nebulae: Where Cosmic Beauty Lies
Beyond the realm of our terrestrial existence, the universe holds a captivating canvas adorned with celestial wonders. Among these cosmic gems, nebulae stand out as ethereal clouds of gas and dust, offering a mesmerizing glimpse into the enigmatic tapestry of space. And at the heart of these celestial masterpieces lies an omnipresent force: plasma.
Plasma, the ionized state of matter, permeates the universe, carrying a potent charge that illuminates and shapes the cosmos. In nebulae, plasma plays a pivotal role in orchestrating their radiant beauty and unveiling the secrets of their formation.
As stellar winds from aging stars spew forth into the interstellar medium, they collide with surrounding gas and dust, triggering an intricate ballet of interactions. The intense energy released by these cosmic collisions ionizes the gas particles, transforming them into a plasma state. This plasma, with its high energy and charged particles, becomes the engine that powers the nebula’s ethereal glow.
Within the nebula, the plasma’s charged particles emit a symphony of radiation across the electromagnetic spectrum. These emissions manifest in the vibrant hues that paint the nebulae, from the ethereal reds and oranges of ionized hydrogen to the haunting blue-green glow of doubly ionized oxygen. The interplay of plasma with different elements within the nebula creates a breathtaking kaleidoscope of colors and patterns, mirroring the celestial dance of matter and energy.
Moreover, plasma in nebulae serves as a celestial sculptor, shaping their diverse and awe-inspiring forms. As the ionized gas interacts with magnetic fields, it contorts into intricate filaments, bubbling clouds, and towering pillars that dance across the cosmic canvas. These dynamic structures bear witness to the formative power of plasma, guiding the evolution and sculpting the ethereal beauty of nebulae.
The study of plasma in nebulae offers invaluable insights into the intricacies of stellar evolution and the birth of stars. The plasma’s composition unveils the chemical history of the nebula, providing clues to the origins of its constituent elements. By unraveling the secrets held within these cosmic laboratories, scientists gain a deeper understanding of the fundamental processes shaping our universe.
In the cosmic tapestry, nebulae serve as cosmic canvases where plasma dances and weaves its magic, illuminating the universe with breathtaking beauty and unraveling the mysteries of stellar evolution. As we gaze upon these celestial masterpieces, we marvel at the transformative power of plasma, a force that shapes, colors, and illuminates the cosmos, leaving an enduring legacy in the vast expanse of space.
Occurrences of Plasma in the Universe (cont.):
- Supernova Remnants:
- Plasma release and expansion in supernova remnants.
- Importance for understanding the death of massive stars.
- Plasma release and expansion in supernova remnants.
- Importance for understanding the death of massive stars.
Supernova Remnants: The Echoes of Cosmic Destruction
In the vast expanse of the cosmos, where stars ignite and perish, supernova remnants stand as ethereal remnants of celestial explosions. These remnants are not mere leftovers but vibrant, plasma-infused cauldrons that unveil the cataclysmic end of massive stars.
Plasma, the dominant state of matter in the universe, plays a pivotal role in the formation and evolution of supernova remnants. As a massive star collapses at the end of its life, a powerful explosion releases an enormous amount of energy that ionizes the surrounding gas, creating a superheated plasma. This plasma expands rapidly, forming a shell that glows with a multitude of colors.
The expansion of the supernova remnant is driven by the outward pressure of the plasma. As the plasma collides with the surrounding interstellar medium, it generates shock waves that heat and compress the gas, further fueling the expansion. The intensity and duration of the plasma emissions depend on the energy of the explosion and the composition of the surrounding environment.
Supernova remnants are crucial for understanding the life cycle of stars. They provide insights into the death of massive stars and the enrichment of the interstellar medium with heavy elements. By studying the plasma in these remnants, astronomers can unravel the mysteries of stellar evolution and the formation of new stars and galaxies.
Plasma’s Contribution to Our Cosmic Understanding
Plasma not only dominates the vastness of the universe but also plays a fundamental role in shaping our understanding of astrophysics. By studying plasma in supernova remnants, astronomers have gained valuable insights into:
- The properties of exploding stars and the mechanisms responsible for their deaths.
- The distribution and abundance of heavy elements in the interstellar medium.
- The formation and evolution of cosmic structures, such as galaxies and clusters.
Plasma is the key that unlocks the secrets of the cosmos, guiding our exploration into the mysteries of the universe and deepening our appreciation for the interconnectedness of all things.
Plasma in Active Galactic Nuclei (AGN): A Cosmic Maelstrom
The universe is a vast and enigmatic tapestry, woven with myriad celestial wonders. Among these cosmic marvels, there lies an extraordinary phenomenon called plasma, the enigmatic fourth state of matter. Its dominance in the universe is undeniable, shaping the very fabric of our cosmos.
In the heart of active galactic nuclei (AGN), the powerhouses of galaxies, plasma reigns supreme. These maelstroms of energy are fueled by the relentless consumption of matter by supermassive black holes. Within their fiery vortexes, plasma is ignited, releasing tremendous amounts of electromagnetic radiation.
The tumultuous plasma in AGN drives a multitude of astounding phenomena. It emits powerful jets of particles, which traverse vast cosmic distances, shaping the intergalactic medium. These jets illuminate their surroundings, casting an ethereal glow upon the celestial stage.
The magnetic fields within AGN plasma are unfathomably strong, guiding the flow of charged particles and amplifying the brightness of the nuclear regions. These fields create a cosmic laboratory, where the fundamental laws of physics are put to the test.
The study of plasma in AGN provides unprecedented insights into some of the most energetic processes in the universe. It illuminates the evolution of galaxies, the formation of stars, and the fabric of the cosmic web.
In conclusion, plasma in AGN is a testament to the power and beauty that exists within the universe. Its ubiquity and influence underscore its crucial role in shaping the cosmos. By unveiling the secrets of plasma in AGN, we unlock profound knowledge about the fundamental forces that govern our cosmic tapestry.