The Periodic Table: Understanding Periods, Epochs, Eras, And Ages
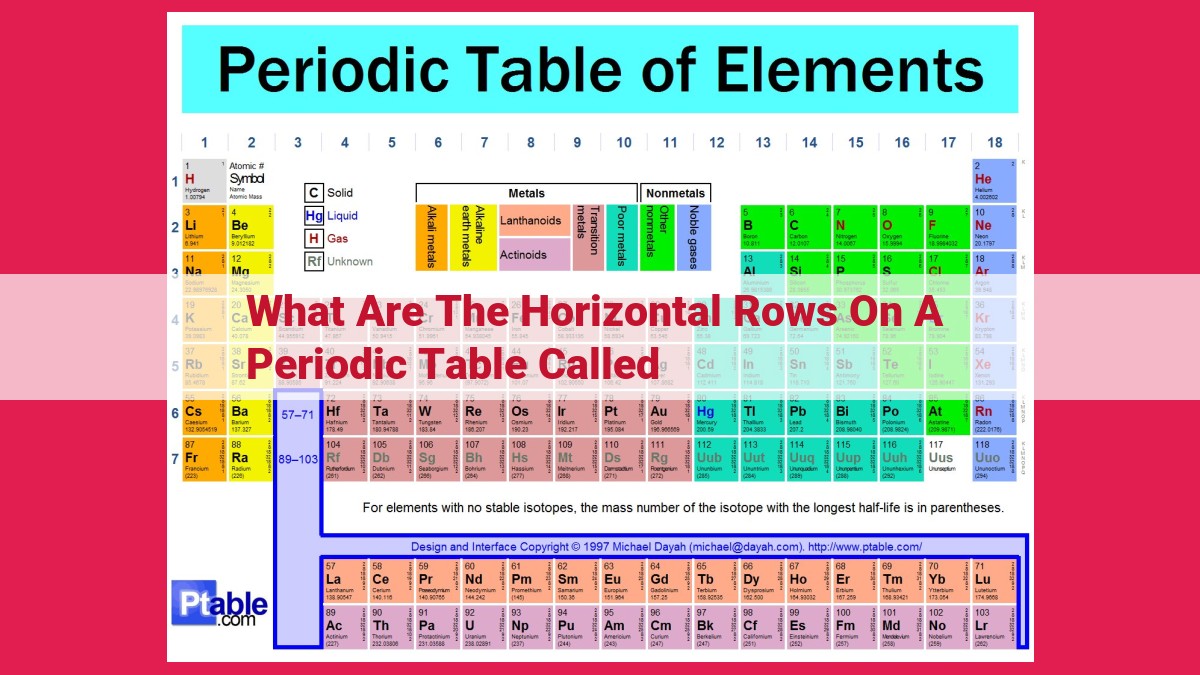
The horizontal rows on a periodic table are called periods. They represent the order in which the elements fill their electron orbitals and correspond to a specific energy level. Each period is subdivided into epochs, eras, and ages based on specific electron configurations and geological time intervals. The elements in a period share similar chemical properties because they have the same number of electron shells and similar electron configurations.
What Are Periods?
- Explain that the horizontal rows on a periodic table are called periods.
- Discuss that periods represent the order in which the elements fill their electron orbitals.
- State that each period corresponds to a specific energy level of the electron orbitals.
Understanding Periods: The Horizontal Rows of the Periodic Table
In the enigmatic tapestry of the periodic table, the horizontal rows that grace its landscape are known as periods. They offer a profound insight into the intricate dance of electrons, unraveling the mysteries of how elements fill their ethereal shells.
Each period corresponds to a specific energy level of the electron orbitals. As you progress from one period to the next, the energy level increases, and electrons venture into progressively higher levels. This orderly progression dictates the placement of elements within the periodic table.
Within each period, elements share a remarkable kinship. Their outermost electron shells are occupied by the same number of electrons, bestowing upon them similar chemical properties. This shared characteristic makes it possible to predict the reactivity and behavior of an element based solely on its position within a period.
Understanding the Layers of Time: Periods and Their Chronological Story
In the tapestry of time, the periodic table weaves a fascinating tale of the universe’s evolution. Its horizontal rows, known as periods, are not mere lines but chronicles of how the elements emerged through the ages. Each period represents an enchanting chapter in this cosmic narrative, painting a vivid picture of the dance between energy and matter.
Time’s Symphony: Epochs, Eras, Ages, and Eons
Like subplots within a grand symphony, the periods are further subdivided into epochs, eras, and ages. These intricate divisions stem from the unique electron configurations and geological events that characterized specific eras in Earth’s history. Epochs mark shorter intervals within periods, while eras represent broader sweeps of time, encompassing multiple epochs. Ages encompass even more extensive time scales, offering glimpses into the gradual transformation of Earth’s landscapes and life forms.
The grandest of these time scales are the eons, vast and almost unfathomable stretches of time that span billions of years. Each eon witnesses the rise and fall of continents, the diversification of species, and the ebb and flow of epochs, eras, and ages.
Periods: A Chronological Guide
The periods of the periodic table, from 1 to 7, serve as markers in this vast expanse of time. Each period corresponds to a specific energy level for electrons within an atom. As elements fill their electron orbitals with increasing energy, they are placed in subsequent periods.
This ordering provides a historical account of element formation. Elements within a given period were born during the same time interval, sharing similar electronic structures and forming the building blocks of the universe as we know it.
The Timeline of the Universe: Unraveling the Relationship Between Periods and Time
The periodic table, a masterpiece of scientific organization, not only arranges elements based on their chemical properties but also holds a hidden timeline within its structure. The horizontal rows of the table, known as periods, represent the sequential order in which elements fill their electron orbitals – the building blocks of all matter. Each period corresponds to a specific energy level of these orbitals.
As we journey from the first to the seventh period, we traverse an astonishing eons-long history of the universe. Each period encapsulates a distinct time interval during which the elements within it emerged. The elements in a particular period share a common ancestry, boasting identical numbers of electron shells and similar electron configurations. This shared heritage bestows upon them remarkable similarities in chemical properties, making them close cousins in the periodic family.
The relationship between periods and time doesn’t end there. Periods intertwine with other temporal units such as epochs, eras, ages, and time intervals, forming a comprehensive tapestry of geological time. The elements within each period formed during specificepochs, eras, and ages, reflecting the distinct conditions prevailing at those times.
By studying the periodicity of the elements, scientists can trace the chronological unfolding of the universe, unlocking the secrets of its evolution and the origins of the matter that surrounds us. Periods serve as guideposts in this grand narrative, providing invaluable insights into the cosmic timeline and the intricate interplay between the elements and time.