Enhance Readability And Communication With Effective Paragraph Formatting Techniques
Paragraph formatting shapes the structure and appearance of written text, enhancing readability and organization. It encompasses alignment, indentation, line spacing, paragraph spacing, drop caps, tabs, and lists. These elements control the layout, density, and hierarchy of text, ensuring clarity, visual appeal, and effective communication. Best practices involve using appropriate alignment, indentation, and line spacing, incorporating drop caps and tabs for emphasis and structure, and selecting suitable font size, style, and color for readability and impact.
The Art of Paragraph Formatting: A Guide to Structuring Written Content
Picture yourself embarking on a literary journey. As you delve into the pages of a book or scroll through an article on your screen, you encounter a tapestry of words that weave stories, impart knowledge, and convey thoughts. But just as a painter relies on technique and composition to bring their canvas to life, so does the writer employ a subtle art to shape the structure and impact of their written work: paragraph formatting.
Defining Paragraph Formatting
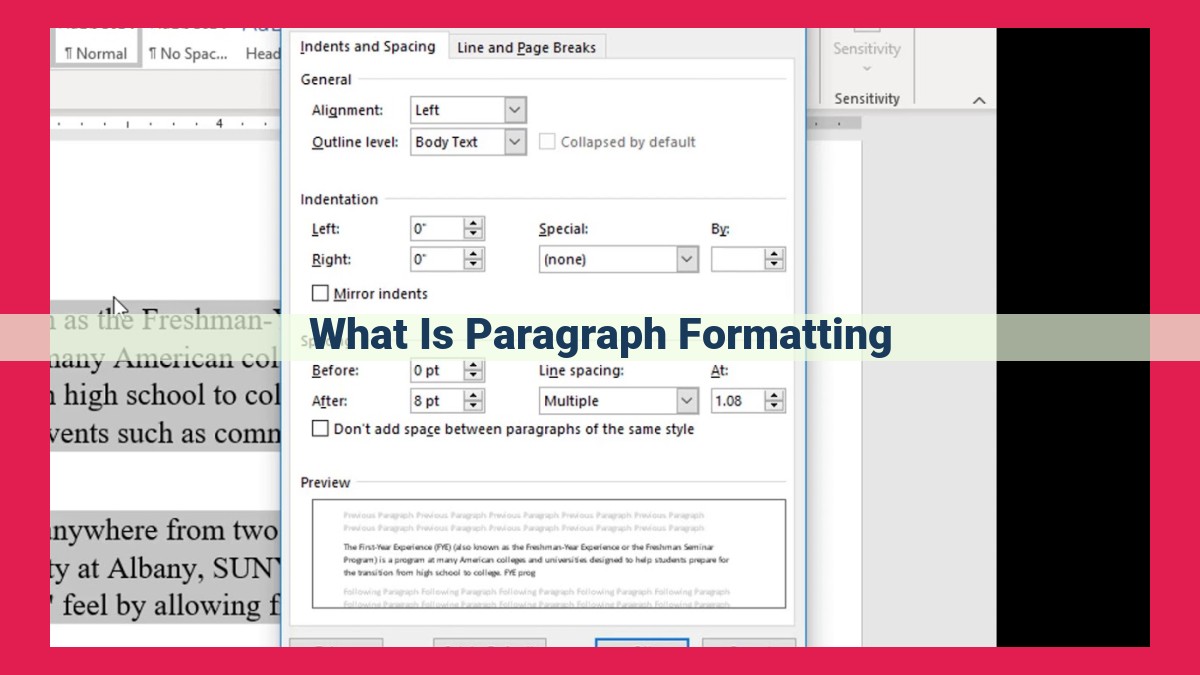
Paragraph formatting encompasses the techniques used to arrange and present text within paragraphs. It serves as the backbone of written content, offering a framework that guides the reader’s eye and enhances readability. From manipulating alignment to controlling spacing, each formatting element plays a vital role in creating a visually appealing and cohesive experience.
The Elements of Paragraph Formatting
-
Alignment: Just as a painting can be framed to highlight its subject, text alignment directs the reader’s gaze. Left alignment creates a familiar, conventional look, while right alignment adds a touch of elegance. Centering conveys formality, while justified alignment provides a polished, uniform appearance.
-
Indentation: Indentation serves as a visual cue, creating a “step” effect that separates paragraphs and emphasizes their beginnings. Hanging indents, an inverted form of indentation, further distinguish the first line of a paragraph.
-
Line Spacing: Also known as leading, line spacing controls the vertical distance between lines of text. Ample line spacing improves readability by reducing eye strain, while tighter spacing can create a more compact, formal look.
-
Paragraph Spacing: The vertical space between paragraphs denotes their separation. Generous spacing enhances clarity, while minimal spacing creates a sense of continuity.
-
Drop Caps: These enlarged, ornamental letters at the start of paragraphs draw attention to important words or concepts, adding a touch of visual interest and hierarchy.
-
Tabs: Tabs act as invisible markers, aligning text horizontally and creating structured layouts. They can be used for table-like content, aligning dates, or indenting quotations.
-
Bulleted or Numbered Lists: Lists transform dense text into easy-to-digest segments, improving readability, organization, and clarity. They can be used to present steps, details, or alternative perspectives.
Paragraph formatting is an essential aspect of effective writing. By mastering the art of alignment, spacing, and other elements, writers can create visually appealing, readable, and well-organized content. Whether crafting a novel, writing an academic paper, or composing a compelling article, understanding paragraph formatting empowers writers to shape their words with precision and convey their message with impact.
Concepts of Paragraph Formatting: Enhancing Readability and Visual Appeal
Alignment: Visual Impact and Readability
- Left alignment: The preferred choice for readability, as it aligns text consistently, making it easier for readers to follow along.
- Right alignment: Creates a formal look and is suitable for headings, captions, and short lines.
- Center alignment: Draws attention to specific text sections but can be harder to read in long passages.
- Justified alignment: Aligns text evenly on both sides, resulting in a professional appearance. However, it may create uneven spacing and reduce readability.
Indentation: Organization and Emphasis
- Indentation is the space added to the beginning of a paragraph, enhancing organization and visual hierarchy.
- Hanging indents: Indents subsequent lines of a paragraph while leaving the first line flush left, used for highlighting headings, quotes, or lists.
- First line indents: Indents only the first line of a paragraph, providing a subtle separation between paragraphs.
Line Spacing: Readability and Text Density
- Line spacing (leading): The vertical space between lines of text, affecting readability.
- Optimal line spacing improves readability by providing space for the eyes to move easily from one line to the next.
- Tight line spacing can strain eyes and make reading challenging, while excessive spacing can reduce text density.
Paragraph Spacing: Enhancing Clarity
- Vertical spacing between paragraphs creates visual breaks, making written content easier to digest and comprehend.
- Adequate paragraph spacing improves readability and allows readers to transition smoothly between thoughts and ideas.
Drop Caps: Visual Interest and Hierarchy
- Drop caps: Enlarged initial letters at the beginning of paragraphs or sections, attracting attention and improving hierarchy.
- Drop caps add a touch of elegance and can be used to emphasize important words or concepts.
Tabs: Organization and Alignment
- Tabs create horizontal spaces within paragraphs, aligning specific sections and creating structured layouts.
- Tabs help organize tabular data, align headings, and format text in columns, enhancing readability and clarity.
Bulleted or Numbered Lists: Enhanced Readability and Clarity
- Lists use bullet points or numbers to present information in a structured and easy-to-scan format.
- Bulleted lists: Great for itemizing, highlighting points, or presenting related ideas.
- Numbered lists: Ideal for outlining steps in a process, ranking items, or presenting sequential information.
Advanced Concepts in Paragraph Formatting
As we delve deeper into the intricacies of paragraph formatting, let’s explore some advanced concepts that can elevate the readability and visual appeal of your written content.
Font Size: The Power of Scale
Font size plays a crucial role in readability. Larger fonts improve accessibility, making your text more effortless to read. Conversely, smaller fonts lend a sense of formality and condense information into tighter spaces. Choose your font size wisely based on the context and desired impact.
Font Style: Emphasis and Hierarchy
Font styles such as bold, italic, and underline are powerful tools for emphasis. Bold text instantly draws attention, highlighting key points and creating a visual hierarchy. Italic text adds a touch of subtlety, while underline serves as an unmistakable indicator of importance. Use these styles judiciously to guide your readers’ eyes through your content.
Text Color: The Language of Contrast
Color plays a significant role in text formatting, influencing readability and visual impact. Choose colors that contrast well with your background to ensure optimal legibility. Consider the color scheme of your document and brand guidelines when making color selections. Remember, a splash of color can invigorate your text, but avoid overpowering your readers with excessive use.
By mastering these advanced paragraph formatting techniques, you can transform your written content into a visually appealing and highly readable experience. Employ these concepts strategically, keeping in mind the overall readability, organization, and desired impact of your writing. Remember, effective paragraph formatting is an art form that enhances the clarity, engagement, and impact of your written words.