Understanding Ordinary Annuities: A Comprehensive Guide To Regular Income Streams
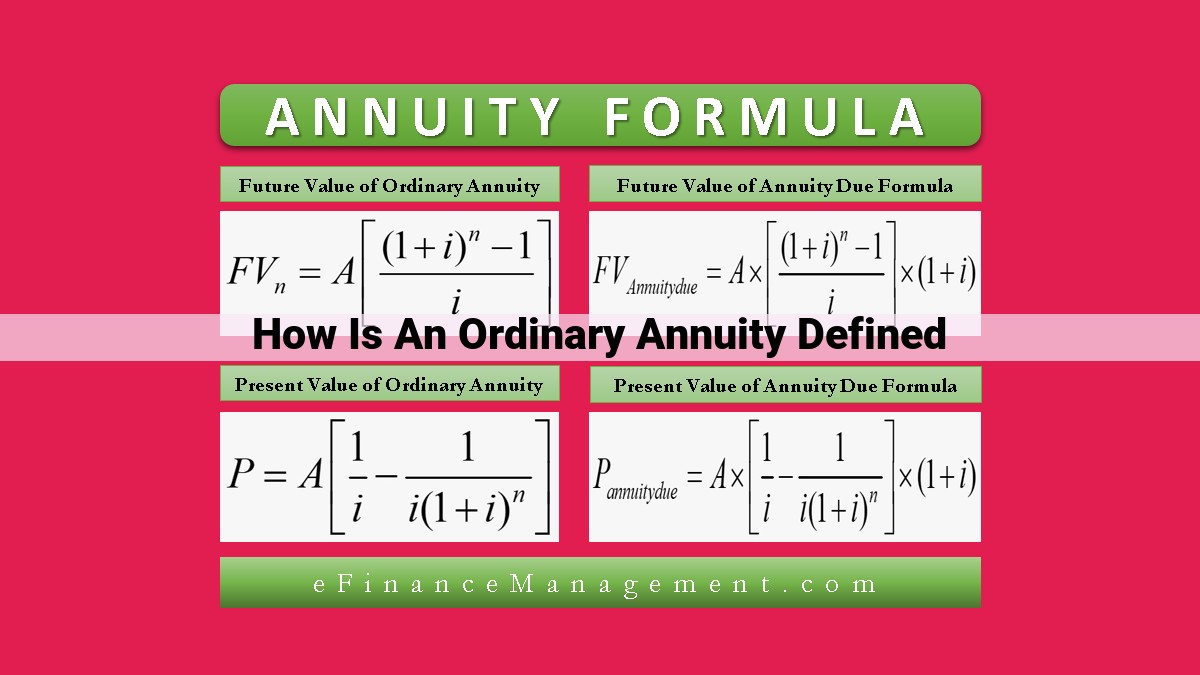
An ordinary annuity is a financial instrument that involves a series of regular and equal payments made at the end of specified intervals over a pre-determined period. It differs from other financial instruments as the payments are made at the end of each period, and it is a type of annuity where the payments are made at equal intervals, such as monthly or annually. Ordinary annuities are typically used for financial planning, such as retirement savings, where the payments can provide a steady stream of income over time.
Definition of an Ordinary Annuity
- Explain what an annuity is and how it differs from other financial instruments.
- Describe the characteristics of an ordinary annuity, including regular payments and specified intervals.
Understanding Ordinary Annuities: A Guide for Financial Stability
In the realm of financial planning, annuities play a pivotal role in ensuring a secure financial future. Among the different types of annuities, the ordinary annuity stands out as a fundamental tool for managing long-term financial goals.
What is an Ordinary Annuity?
An annuity is a contractual agreement between an individual and a financial institution where the institution promises to make a series of regular payments for a specified period. Unlike loans or bonds, which involve a fixed term and repayment schedule, annuities provide guaranteed income streams that can extend for years or even decades.
Characteristics of an Ordinary Annuity
An ordinary annuity is distinguished by its unique characteristics:
- Regular Payments: payments are made at equal intervals, typically monthly or annually.
- Specified Intervals: the payments continue for a predetermined duration, ensuring a steady flow of income.
- End-of-Period Payments: payments are made at the end of each period, meaning that the full amount is received at the end of the specified interval.
Ordinary Annuity vs. Other Types
Ordinary annuities differ from other annuity types, such as due annuities, in the timing of their payments. In a due annuity, payments are made at the beginning of each period, while in an ordinary annuity, payments are made at the end. This distinction has implications for the time value of money, as the present value of an ordinary annuity is lower than that of a due annuity.
Applications of Ordinary Annuities
Ordinary annuities offer numerous practical applications in financial planning:
- Retirement Planning: Annuities provide a guaranteed income stream in retirement, ensuring financial security during a time when earning potential may be diminished.
- Investment Planning: Annuities can be used to generate a consistent return on investments while managing risk.
- Estate Planning: Annuities can be set up to provide income for heirs or beneficiaries after the annuitant’s death.
Understanding the concept of an ordinary annuity is crucial for anyone seeking financial stability and long-term income security. By providing regular payments at specified intervals, ordinary annuities offer a valuable tool for managing retirement planning, investment goals, and securing a comfortable future.
Annuities: A Series of Payments Over Time
Annuities are a type of financial instrument that provides a series of regular payments over a specified period of time. They’re distinct from other instruments as they guarantee a predictable income stream for the recipient, making them a popular option for retirement planning and other long-term financial goals.
Unlike a bond, which typically provides a single payment at maturity, an annuity offers a stream of periodic payments. Imagine it as a series of individual payments, made like clockwork, ensuring a consistent flow of income that can be used to cover expenses or supplement other sources of income.
It’s crucial to remember the time value of money when evaluating annuities. The payments you receive today are worth more than those you’ll receive in the future. This is because the value of money decreases over time due to inflation and other factors. Therefore, it’s essential to consider the present value of the future payments when making annuity decisions.
Ordinary Annuity vs. Other Annuity Types
- Differentiate ordinary annuities from other types of annuities, such as due annuities.
- Explain when it is appropriate to use an ordinary annuity versus other options.
Ordinary Annuity vs. Other Annuity Types
In the financial realm, annuities play a crucial role in securing future financial well-being. Among the various types of annuities, ordinary annuities stand out with their distinct characteristics.
Ordinary Annuity: A Path to Financial Security
An ordinary annuity, also known as an annuity-in-arrear, is a series of payments made at regular intervals over a specified period. Unlike other annuity types, these payments occur at the end of each period, rendering them unique in their temporal aspect.
Due Annuities: Payments Upfront
In contrast to ordinary annuities, due annuities feature payments made at the beginning of each period. This upfront payment schedule sets them apart from their ordinary counterparts.
Choosing the Right Annuity Type
When selecting an annuity type, it’s essential to consider your financial goals and circumstances. Ordinary annuities are ideal for individuals seeking a steady stream of income over an extended period. Their end-of-period payments align with common expense schedules, making them a suitable option for retirement planning and other long-term financial objectives.
Other Annuity Options
In addition to ordinary and due annuities, other types include:
- Deferred Annuities: Payments commence at a later date after an initial accumulation period.
- Variable Annuities: Payments vary based on the performance of underlying investments.
- Lifetime Annuities: Payments continue throughout the individual’s lifetime, providing a guaranteed income stream.
The choice of annuity type depends on your specific financial needs, risk tolerance, and investment preferences. Consult with a financial professional to determine the most appropriate option for your circumstances.
Payments at the End of Each Period: The Impact on Time Value of Money
In an ordinary annuity, payments are made at the end of each period, as opposed to the beginning. This seemingly subtle distinction has significant implications for the time value of money.
Time Value of Money
The time value of money recognizes that money today is worth more than the same amount in the future due to its earning potential. The longer money is held, the more interest it can accumulate, increasing its value.
Implications for Ordinary Annuities
Since payments in an ordinary annuity are made at the end of periods, the full amount is not available at the beginning to earn interest. As a result, the time value of money is reduced compared to an annuity with payments at the beginning of periods (known as a due annuity).
For example, consider an ordinary annuity with a $1,000 payment at the end of each year for three years. The time value of money over three years at 5% interest is $284.36. This means that the payment received at the end of the third year is worth $1,000 * (1 + 0.05)^3 = $1,284.36 today.
However, in a due annuity, the same $1,000 payment is made at the beginning of each year. The time value of money over three years at 5% interest is $310.58. This means that the payment received at the beginning of the third year is worth $1,000 * (1 + 0.05)^3 = $1,310.58 today.
The difference in time value of money between ordinary and due annuities highlights the importance of considering payment timing when evaluating financial investments.
Practical Applications of Ordinary Annuities
Understanding the practical applications of ordinary annuities is crucial for your financial planning journey. An ordinary annuity, a series of consistent payments made at the end of each period over a predefined duration, offers numerous advantages for achieving long-term financial goals.
Retirement Planning:
Ordinary annuities are a popular choice for retirement planning as they provide guaranteed income streams. This feature ensures a constant cash flow during your retirement years, mitigating the risk of outliving your savings. By investing in an ordinary annuity, you can set up a steady income source that supplements your Social Security or pension benefits.
Investment Vehicle:
Annuities can also serve as conservative investment vehicles. They offer a low-risk way to grow your wealth over time while minimizing market volatility. Ordinary annuities typically have fixed interest rates, providing a stable return regardless of economic conditions.
Estate Planning:
Ordinary annuities can be incorporated into your estate plan to provide income for your beneficiaries. By establishing an annuity trust, you can ensure that your loved ones receive regular payments upon your passing, supporting their financial well-being.
Long-Term Savings:
For those with long-term savings goals, ordinary annuities provide a disciplined approach. With regular contributions and a fixed payment schedule, you can accumulate wealth gradually and reach your financial objectives. Annuities offer a sense of financial security by guaranteeing a future income stream.
Considerations:
When considering ordinary annuities, it’s essential to weigh the benefits against the potential drawbacks. Annuity contracts are legally binding, so it’s crucial to thoroughly understand the terms and conditions before signing up. Additionally, annuities may have tax implications and surrender charges, which can impact your overall return.