Optimize Ph Title For Seo:ph Level: Understanding Acidity, Alkalinity, And Its Significance
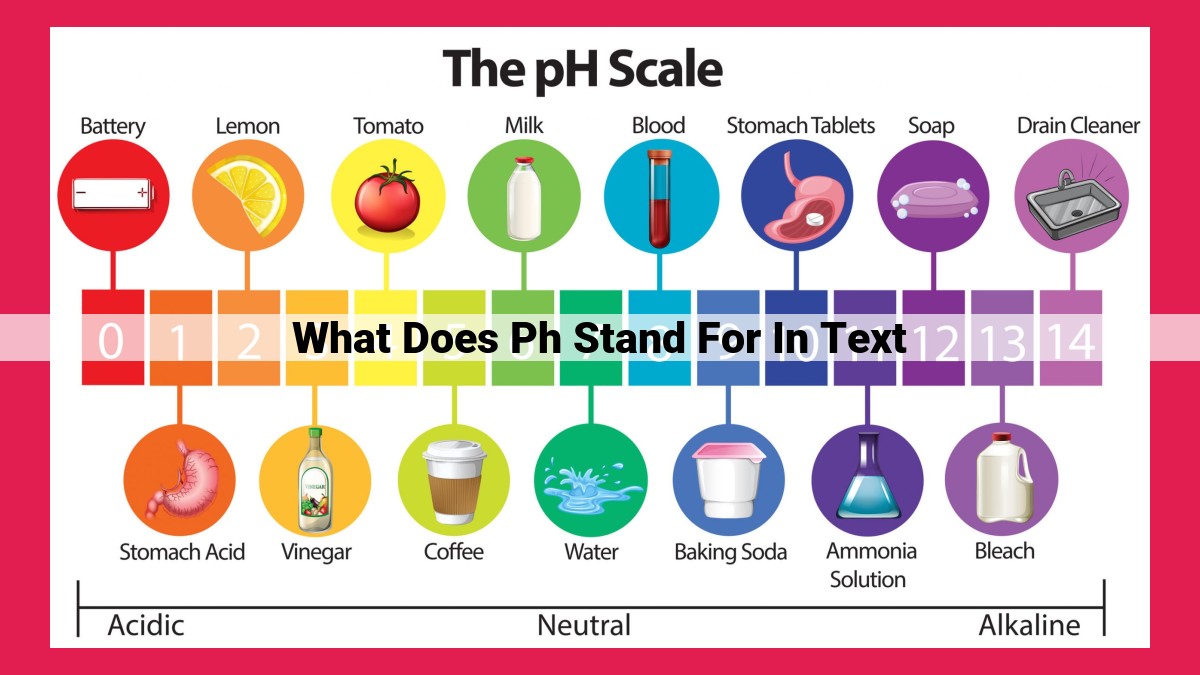
pH stands for “potential of hydrogen” and is a measure of the acidity or alkalinity of a solution. It ranges from 0 to 14, with 0 being the most acidic, 14 being the most alkaline, and 7 being neutral. pH is crucial in chemistry as it affects the behavior of molecules and reactions, and it plays a vital role in biological systems, such as regulating cellular processes.
Understanding pH: A Crucial Measure in Chemistry
In the vast tapestry of chemistry, pH stands as a beacon of understanding, illuminating the hidden realm of acidity and alkalinity, shedding light on the intricate dance of ions that shape our world.
Defining pH: The Key to Chemical Insight
pH, a diminutive acronym for “potential of hydrogen,” unveils the story of a solution’s acidity or alkalinity. It’s a numerical measure that quantifies the concentration of hydrogen ions (H+) in a liquid, offering a glimpse into the chemical landscape beneath the surface.
The pH Scale: A Spectrum of Acidity and Alkalinity
To grasp the significance of pH, we embark on a journey through its numerical range, spanning from 0 to 14. Each value represents a distinct level of acidity or alkalinity, with 0 being highly acidic, 14 extremely alkaline (basic), and 7 denoting a perfect balance: neutrality.
pH and Its Related Concepts
Acidity, Alkalinity, and Neutrality
The pH scale measures the acidity or alkalinity of a solution. A pH value of 7 indicates a neutral solution, while values below 7 are considered acidic and values above 7 are alkaline. The acidity or alkalinity of a solution is determined by the concentration of hydrogen ions (H+) and hydroxide ions (OH-) it contains.
pOH: A Complementary Measure
The pOH scale is a measure of the concentration of hydroxide ions in a solution. It is inversely related to the pH scale, meaning that as the pH increases, the pOH decreases. The pOH is calculated using the following formula:
pOH = -log[OH-]
Buffers: Maintaining pH Stability
Buffers are solutions that resist changes in pH when small amounts of acid or base are added. They contain a weak acid and its conjugate base, or a weak base and its conjugate acid. When acid is added to a buffered solution, the weak acid in the buffer reacts with the added acid to form more conjugate base, preventing a significant change in pH. Similarly, when base is added, the weak base in the buffer reacts with the added base to form more conjugate acid, again preventing a significant change in pH.
pH, acidity, alkalinity, pOH, and buffers are all interconnected concepts that play vital roles in understanding the chemical properties of solutions. pH is a crucial measure in chemistry, biology, and other scientific fields. By comprehending these concepts, we gain a deeper understanding of the behavior of solutions and the impact of pH on various chemical and biological processes.
The Concept of Text: A Medium of Communication
Text, an indispensable element of human civilization, encompasses both spoken and written language. It acts as a conduit of information and ideas, bridging the gap between individuals and enabling the sharing of knowledge, beliefs, and emotions.
The Essence of Text
Text is an intricate tapestry woven from language, the foundation of human communication. It consists of linguistics, the study of language, which provides the rules and principles that govern its structure and meaning. Through the act of writing, we encode our thoughts and ideas into symbols, creating tangible representations that can be shared and preserved for posterity.
The Art of Reading
Text comes to life through the interpretation of written symbols. This process, known as reading, involves decoding the symbols into words and sentences, and then comprehending their meaning. Through reading, we gain access to a wealth of knowledge, perspectives, and stories, expanding our horizons and enriching our lives.
pH and Text: A Tale of Interplay in Language and Communication
In the intricate world of chemistry, pH holds a pivotal role, determining the acidity or alkalinity of solutions and influencing biological processes. Its impact extends far beyond the realm of science, intertwining with the very fabric of language and communication.
pH in Biological Systems: A Delicate Balance
pH plays a crucial role in maintaining the delicate balance of biological systems. Within cells, its regulation ensures the proper functioning of enzymes, the building blocks of life. Alterations in pH can disrupt cellular processes, affecting everything from metabolism to DNA replication.
pH and Language: A Subtle Influence
Beyond the confines of the cell, pH exerts a subtle influence on language. The stability and meaning of words and phrases can be affected by their pH environment. For instance, in acidic conditions, certain words may become more stable or resistant to change. This phenomenon has implications for the preservation and interpretation of historical texts.
Additionally, pH can affect the reactivity of words to other words, influencing the formation of new compounds (phrases) and the interpretation of meaning. Like chemical reactions in a laboratory, the pH of a linguistic environment can create unique outcomes.
Interconnectedness: A Web of Influence
The interplay of pH and text is a testament to the interconnectedness of the world around us. pH, a fundamental measure in chemistry, extends its reach into the realm of communication, shaping the stability and meaning of language.
This interwoven relationship underscores the importance of understanding both pH and text, not only as separate entities but also as components of a larger system. By unraveling the threads that connect them, we deepen our appreciation for the intricate tapestry of our world and our ability to communicate within it.