Unveiling The Interplay Of Nervous And Endocrine Systems: Coordinating Body’s Communication And Regulation
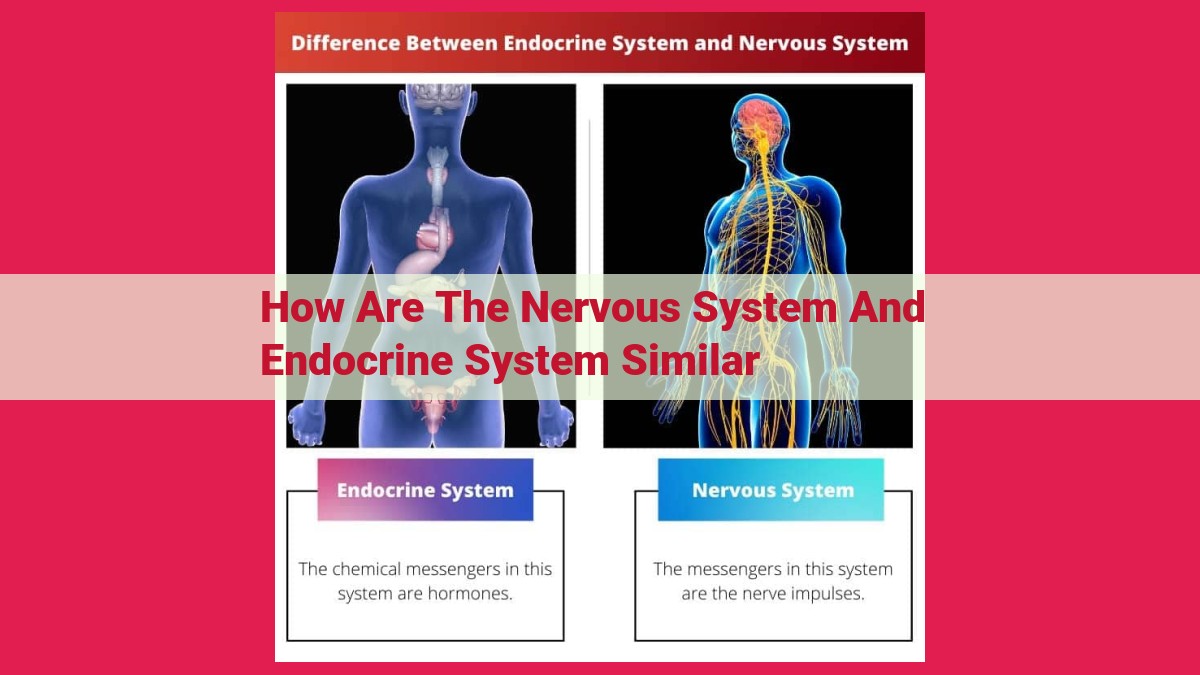
Both nervous and endocrine systems facilitate communication and information transmission throughout the body. They use chemical messengers (neurotransmitters and hormones) to transmit signals, ensuring targeted communication with specific cells and organs. This collaboration is crucial for maintaining homeostasis, regulating essential parameters like blood pressure and blood sugar levels. Their coordinated functioning is vital for survival, controlling movement, sensation, thought, metabolism, growth, and reproduction. Disruptions in these systems can lead to severe health implications.
Communication and Information Transmission
- Discuss the primary roles of the nervous system and endocrine system in transmitting information throughout the body.
- Explain how the nervous system relies on electrical signals and neurotransmitters while the endocrine system uses hormones.
Communication and Information Transmission in the Body: A Tale of Two Systems
Our bodies are intricate networks of systems that work in harmony to keep us alive and functioning optimally. Among these systems, the nervous system and endocrine system play a crucial role in carrying information throughout the body.
The nervous system, our body’s electrical wiring, is responsible for rapid communication. It operates through electrical signals that travel along neurons, carrying information from one part of the body to another with incredible speed. Specialized chemicals called neurotransmitters act as messengers, transmitting these electrical signals across synapses (the junctions between neurons). This allows for precise communication between neurons, enabling us to react quickly to stimuli, control movement, and process thoughts.
In contrast, the endocrine system relies on hormones as its chemical messengers. Hormones are secreted by glands and travel through the bloodstream, targeting specific cells or organs that have the appropriate receptors. This slower but more widespread communication allows the endocrine system to regulate long-term processes, such as growth, metabolism, and reproduction. By working in tandem, the nervous and endocrine systems ensure that information is transmitted throughout the body, coordinating our responses to stimuli and maintaining overall homeostasis.
Chemical Messengers
- Define hormones and neurotransmitters and explain their significance in the communication process.
- Describe how these chemical messengers enable targeted communication with specific cells and organs.
Chemical Messengers: The Unsung Heroes of Communication
In the captivating symphony of life, the nervous system and endocrine system play a harmonious duet, sending vital messages to every corner of our bodies. Among their most essential tools are chemical messengers, molecules that orchestrate communication with unparalleled precision.
Defining Hormones and Neurotransmitters
Hormones, secreted by glands, are long-distance travelers, carried by the bloodstream to target cells far and wide. Neurotransmitters, on the other hand, are the messengers of the nervous system, bridging the gap between neurons to transmit electrical impulses.
Targeted Communication: A Masterful Precision
Both hormones and neurotransmitters carry information within their molecular structure, coded in specific receptors found on target cells. When a chemical messenger docks with a receptor, it triggers a cascade of events, enabling targeted communication with remarkable accuracy.
Hormones, with their ability to reach distant cells, regulate long-term physiological processes. For instance, insulin, secreted by the pancreas, directs cells to absorb glucose from the bloodstream. In contrast, neurotransmitters facilitate rapid communication within the nervous system, mediating everything from muscle contractions to the perception of thoughts and emotions.
Homeostasis: Maintaining Balance in the Body’s Ecosystem
Our bodies are intricate systems, constantly working to maintain equilibrium amidst a changing environment. The concept of homeostasis plays a central role in this dynamic balance, ensuring the proper functioning of our cells, tissues, and organs.
Maintaining Homeostasis: A Balancing Act
Homeostasis involves regulating essential parameters within narrow ranges to support optimal cellular processes. Key parameters include blood pressure, body temperature, and blood sugar levels. Just like a thermostat regulates the temperature of a room, the nervous and endocrine systems work together to ensure these parameters remain within acceptable limits.
The Nervous System’s Electrical Signals
The nervous system acts as the body’s quick-response communication network, transmitting electrical signals along nerve fibers. When sensors detect changes in the internal or external environment, they send signals to the brain or spinal cord. From there, the brain coordinates appropriate responses to maintain homeostasis.
The Endocrine System’s Chemical Messengers
The endocrine system, on the other hand, uses hormones as its chemical messengers. Hormones are released by glands directly into the bloodstream, where they travel to target cells in various parts of the body. These target cells possess receptors that bind to specific hormones, triggering specific responses.
Collaboration for Homeostasis
For example, when blood pressure drops, the nervous system triggers the release of hormones like adrenaline, which increases heart rate and blood vessel constriction. This response restores blood pressure to normal levels. Conversely, if blood pressure rises, the endocrine system releases hormones like insulin, which helps to lower blood sugar levels and promote blood vessel relaxation.
Maintaining Body Temperature
Body temperature is another critical parameter regulated by the nervous and endocrine systems. When the body becomes too cold, the nervous system initiates shivering to generate heat. In contrast, when the body becomes too warm, the endocrine system releases hormones that promote sweating, cooling the body down.
The nervous and endocrine systems form a vital communication network, working tirelessly behind the scenes to ensure the delicate balance of homeostasis. Their coordinated actions allow our bodies to adapt to changing conditions and maintain optimal health. Without these systems, the body would struggle to survive, highlighting their indispensable role in our overall well-being.
The Essential Role of Communication and Coordination in Our Survival
The human body is an intricate masterpiece, a symphony of systems working in harmonious unity. Among the most vital are the nervous and endocrine systems, the orchestrators of communication and coordination that ensure our survival.
These systems work tirelessly together to maintain homeostasis, the delicate balance essential for our well-being. They coordinate complex functions such as regulating blood pressure, body temperature, and blood sugar levels. Imagine a thermostat controlling the temperature in your home, constantly adjusting to keep it comfortable. The nervous and endocrine systems do the same for our bodies, ensuring our optimal functioning.
But their importance extends far beyond homeostasis. The nervous system governs our movement, sensation, and thought, while the endocrine system controls our metabolism, growth, and reproduction. Together, they paint the canvas of our existence, shaping our physical and cognitive abilities, our instincts and desires.
Disruptions to these systems can have severe consequences. Neurological disorders, for example, can impair our ability to move, speak, or remember. Endocrine imbalances can lead to hormonal disorders, affecting our growth, development, and fertility. Without the seamless communication and coordination of these essential systems, our survival would be imperiled.
The nervous and endocrine systems are the cornerstones of our survival, the invisible conductors orchestrating the symphony of life within us. They work in concert, ensuring our bodies function optimally, from maintaining homeostasis to controlling our thoughts and actions, from enabling growth to perpetuating our species. Understanding their critical role is not just an academic exercise but a profound appreciation of the remarkable machinery that allows us to thrive in the face of adversity and embrace the fullness of human existence.