Negative Charged Water: Benefits, Properties, And Impact On Health
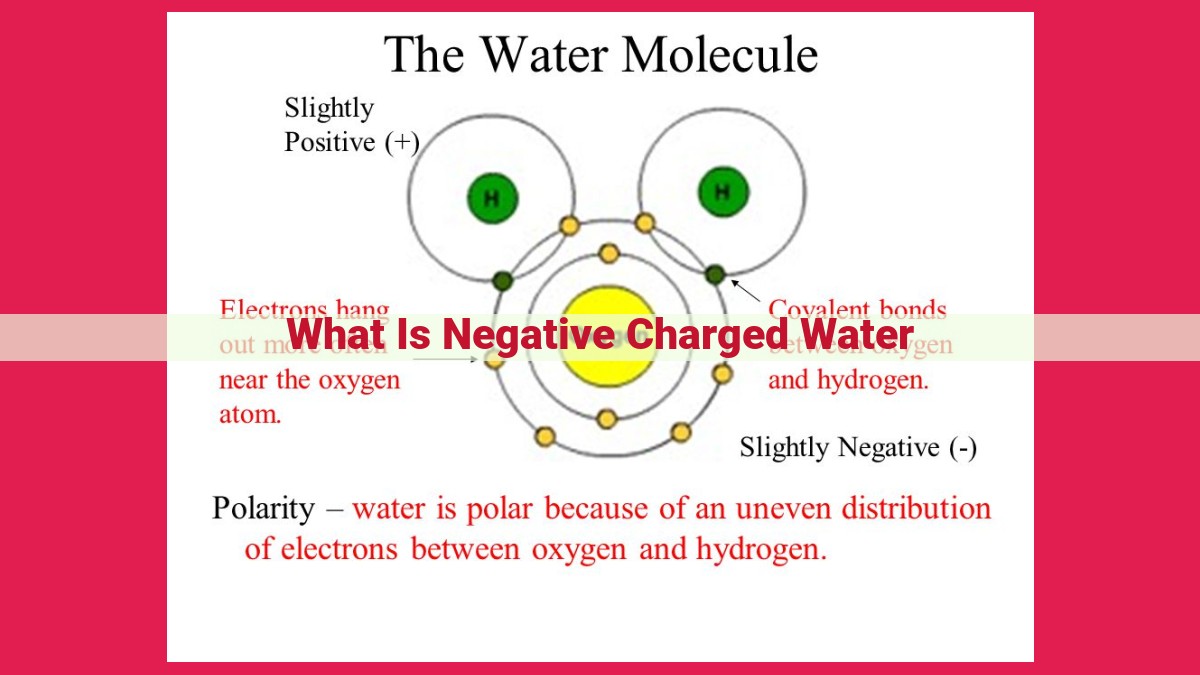
Negative charged water is characterized by its high pH (indicating alkalinity) and negative ORP (indicating antioxidant properties). Electrolysis separates hydrogen and oxygen ions, leading to an accumulation of OH- ions in water. This alkaline nature neutralizes free radicals, which are unstable molecules that can damage cells. Hydrated electrons, present in negative charged water, further enhance its antioxidant capabilities, potentially benefiting health and wellness.
Delving into the Wonders of Negative Charged Water: Exploring its Properties and Creation
As we embark on a journey to unravel the mysteries of negative charged water, let us first establish an understanding of its essence. Negative charged water, also known as alkaline water or ionized water, possesses unique characteristics that set it apart from ordinary water. It’s time to dive deep into its properties, unraveling the secrets that make it a subject of intrigue for health enthusiasts.
Unveiling the Secrets of Negative Charged Water: High pH and Negative ORP
Negative charged water distinguishes itself with its high pH level, which indicates its alkaline nature. This alkalinity results from the presence of an abundance of hydroxyl ions (OH-) in the water, which neutralize acids and create an environment that is less conducive to the survival of disease-causing microorganisms.
Another defining characteristic of negative charged water is its negative Oxidation-Reduction Potential (ORP). ORP is a measure of the tendency of a substance to oxidize or reduce other substances. A negative ORP indicates that the water has strong antioxidant properties, meaning it can neutralize free radicals, which are unstable molecules that can damage cells and contribute to aging.
Electrolysis: The Catalyst for Negative Charge Transformation
Electrolysis, a process that splits water molecules into hydrogen and oxygen ions, plays a crucial role in the creation of negative charged water. During electrolysis, a direct electric current passes through water, causing the positively charged hydrogen ions (H+) to migrate towards the negative electrode (cathode), while the negatively charged hydroxyl ions (OH-) are drawn to the positive electrode (anode). As a result, a higher concentration of hydroxyl ions accumulates in the water, elevating its pH level and bestowing upon it a negative ORP.
Navigating the pH Spectrum: A Measure of Acidity or Alkalinity
The pH scale, ranging from 0 to 14, serves as a universal yardstick for measuring the acidity or alkalinity of a solution. Substances with a pH below 7 are considered acidic, while those with a pH above 7 are deemed alkaline. Negative charged water typically boasts a pH greater than 7, firmly placing it in the alkaline realm.
Unveiling the Secrets of Negative Charged Water: A Comprehensive Overview
Negative charged water possesses properties that set it apart from ordinary water, including high pH and negative ORP. Electrolysis, a process that utilizes electricity to split water molecules, plays a fundamental role in producing negative charged water. Understanding the properties and creation of negative charged water opens up avenues for exploring its potential benefits and applications.
Electrolysis: The Key to Producing Negative Charged Water
A Tale of Splitting Water into Its Constituent Ions
In the realm of water purification, electrolysis emerges as a transformative technique, harnessing the power of electricity to unlock the secrets within ordinary water. This remarkable process holds the key to unlocking the mysteries of negative charged water, a liquid imbued with exceptional properties that have garnered widespread attention in the health and wellness community.
Imagine water as a tranquil sea, its molecules intertwined in a harmonious dance. Electrolysis, like a mischievous sorcerer, disrupts this serene equilibrium, introducing two electrodes into the watery depths. As electricity courses through these electrodes, a magical transformation unfolds.
Negatively charged electrons, like eager dancers seeking freedom, detach themselves from hydrogen ions (H+), setting them adrift. Simultaneously, positively charged oxygen ions (O-2) shyly gather around the opposite electrode, forming the foundation of a new compound.
But the story doesn’t end there. As the hydrogen ions embark on their journey, they encounter hydroxyl ions (OH-), who had previously been hiding in the watery shadows. Like moths drawn to a flame, the hydroxyl ions flock to the hydrogen ions, forming water molecules (H2O) once more.
However, the story takes an unexpected turn. Within this newly formed water, the hydroxyl ions linger, their newfound independence granting the water a unique characteristic: alkalinity. This surge in alkalinity bestows upon the water a high pH, tipping the balance towards a more benevolent environment.
And so, through the transformative power of electrolysis, ordinary water is reborn as negative charged water, a liquid brimming with potential benefits and ready to embark on its mission of enhancing health and wellness.
The pH of Negative Charged Water: Unveiling its Alkaline Nature
Delving into the realm of negative charged water, we encounter a unique characteristic that sets it apart from ordinary water: its alkaline nature. This inherent alkalinity stems from its elevated pH levels, a measure of a solution’s acidity or alkalinity.
The pH scale, ranging from 0 to 14, gauges a solution’s acidity or alkalinity. Substances with a pH below 7 are considered acidic, while those above 7 are alkaline. Negative charged water boasts a pH greater than 7, indicating its alkaline nature.
This alkalinity of negative charged water stems from the electrolysis process that creates it. Electrolysis separates hydrogen and oxygen ions, leaving an abundance of OH- ions in the water. These OH- ions contribute to the elevated pH, giving negative charged water its characteristic alkalinity.
ORP: Oxidation-Reduction Potential and the Antioxidant Power of Negative Charged Water
- ORP: A Crucial Indicator of Antioxidant Capacity
Oxidation-reduction potential (ORP), is a measure of the tendency of a substance to gain or lose electrons. When ORP is negative, it indicates the presence of reducing agents, which are substances that can donate electrons. Negative charged water, with its negative ORP, has the remarkable ability to neutralize free radicals.
- Free Radicals: The Damaging Culprits
Free radicals are unstable molecules that can cause oxidative stress in our bodies by stealing electrons from cells. This can damage DNA and lead to inflammation and chronic diseases. Antioxidants, on the other hand, are compounds that can donate electrons to free radicals, neutralizing their harmful effects.
- Negative Charged Water: A Scavenger of Free Radicals
Negative charged water excels as an antioxidant due to its high concentration of hydrated electrons. These electrons are loosely bound to water molecules, making them readily available to neutralize free radicals. When negative charged water encounters free radicals, these electrons are transferred, effectively rendering the free radicals harmless.
- The Power of Electrons
Studies have shown that drinking negative charged water can increase the body’s antioxidant capacity, reducing oxidative stress and protecting against cellular damage. This is especially significant for individuals exposed to environmental pollutants, smoke, or other sources of free radicals.
- Supporting Health and Wellness
The antioxidant properties of negative charged water have potential benefits for various aspects of health and wellness. It may aid in:
- Reducing inflammation
- Improving immune function
- Enhancing recovery from exercise
- Slowing down the aging process
ORP is a crucial indicator of the antioxidant potential of negative charged water. Its negative ORP and high concentration of hydrated electrons make it an effective scavenger of free radicals, protecting against cellular damage and supporting overall health and wellness.
Hydrated Electrons: The Foundation of Negative Charged Water’s Remarkable Properties
In the realm of water, negative charged water stands apart, imbued with unique characteristics that have sparked intrigue among researchers and health enthusiasts alike. Understanding the role of hydrated electrons is crucial to unraveling the secrets behind this extraordinary liquid.
Hydrated electrons, as their name suggests, are electrons surrounded by a protective shield of water molecules. This unique arrangement grants them exceptional stability, allowing them to exist in water for extended periods. Their presence in negative charged water is pivotal to its remarkable properties, including its high pH and potent antioxidant abilities.
Negative charged water’s alkaline nature stems from an abundance of hydroxyl ions (OH-). Electrolysis, a process that separates water into hydrogen and oxygen ions, plays a key role in generating these ions. As hydrogen ions are removed, OH- ions accumulate, increasing the solution’s pH. This alkalinity neutralizes free radicals, potentially reducing their harmful effects on cells.
Moreover, negative charged water possesses a negative Oxidation-Reduction Potential (ORP). ORP measures a substance’s ability to gain or lose electrons, and a negative ORP indicates strong antioxidant properties. Hydrated electrons within negative charged water act as potent scavengers, neutralizing free radicals and shielding cells from oxidative damage.
The benefits of negative charged water, thanks to its hydrated electrons, extend to various aspects of health and wellness. Studies suggest it may enhance hydration, reduce fatigue, strengthen the immune system, and promote overall well-being. While further research is needed to fully elucidate its potential, the intriguing properties of hydrated electrons hold promise for a healthier future.