Mnemonic For Memorizing Carpal Bones: Enhanced For Seo
To recall the carpal bones, use the mnemonic “Anatomical Snuffbox (Scaphoid, Trapezium, Trapezoid), Boxer’s Fracture (Metacarpal), Carpal Boat (Lunate, Triquetrum, Hamate), Hamate Hook (Pisiform), Pisiform Pea (Hook of the Hamate), Scaphoid Scapha (Trapezium, Trapezoid, Capitate), Trapezium Trap (Scaphoid, Trapezoid, Thumb), Capitate Capital (Lunate, Hamate, Triquetrum), Lunate Luna (Scaphoid, Capitate, Triquetrum), Triquetrum Triangle (Lunate, Capitate, Hamate).”
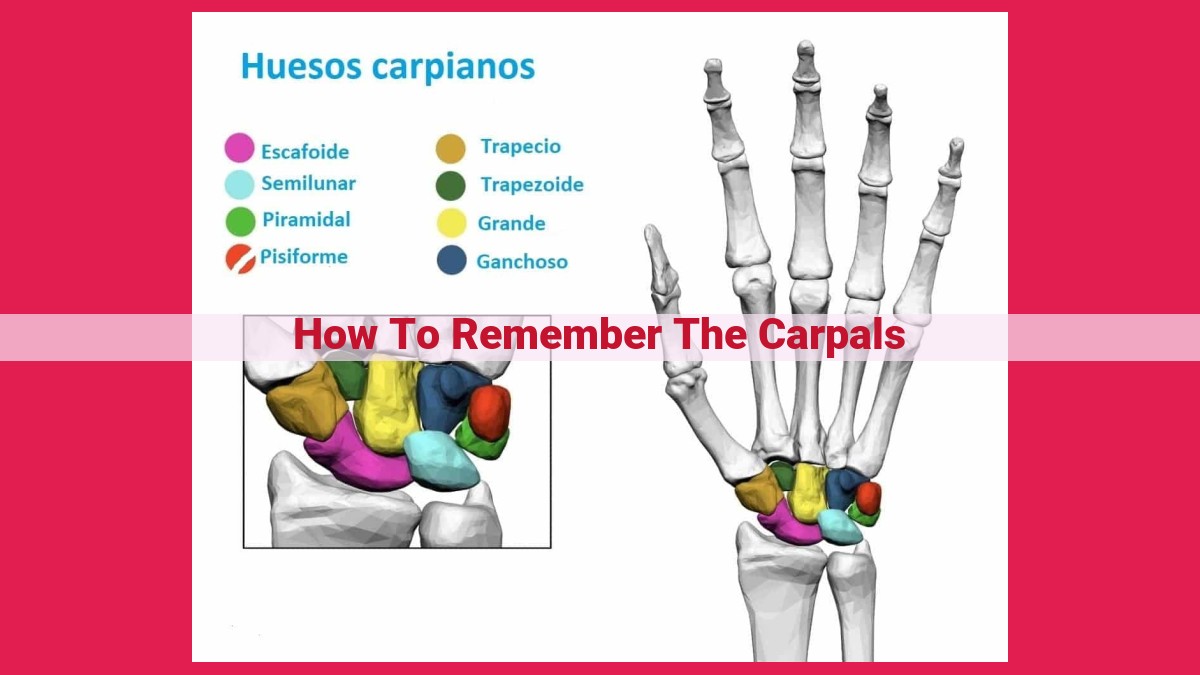
Understanding the Carpal Bones: A Comprehensive Guide
The human wrist is a complex and intricate joint that plays a pivotal role in our everyday activities. At its core lies a series of eight small bones known as the carpal bones. Understanding the arrangement of these bones is essential for comprehending the intricacies of wrist anatomy and ensuring its optimal function.
The carpal bones are located between the forearm and the hand, forming a bridge that connects the two. They are arranged in two rows: a proximal row closest to the forearm and a distal row closest to the hand. The proximal row consists of the scaphoid, lunate, triquetrum, and pisiform bones, while the distal row comprises the trapezium, trapezoid, capitate, and hamate bones.
Each carpal bone has a specific shape and function, contributing to the overall stability and flexibility of the wrist. By gaining a thorough understanding of these bones, we can better appreciate the remarkable complexity of the human body and the importance of maintaining wrist health.
A Mnemonic Device for Unlocking the Secrets of Your Carpal Bones
Memorizing the intricacies of the human body can be a daunting task, but when it comes to the eight tiny bones that make up your wrist, a clever mnemonic device can turn this challenge into a playful adventure.
Enter the mnemonic device: a tool that helps you remember information by associating it with something more memorable. For the carpal bones, we’ll embark on a magical journey, trekking through a landscape of landmarks and characters.
Picture this: you’re standing at the Anatomical Snuffbox, a mysterious depression on the back of your wrist. As you peer inside, you notice the Scaphoid, a large boat-shaped bone resembling a scapha (Greek for “boat”). Next, you encounter the Trapezium, a triangular trap guarding the thumb, and the Trapezoid, a smaller trap tucked beside it.
Continuing your journey, you come across a Boxer’s Fracture, a break in the metacarpal bone caused by a forceful blow. Just beyond, you stumble upon the Carpal Boat, a concave arch formed by the lunate, triquetrum, and hamate bones.
As you approach the peak of your expedition, you encounter the Hamate Hook, a projection on the hamate bone that resembles a fishing hook. Nearby, you spot the Pisiform Pea, a tiny, bean-shaped bone often mistaken for a pea.
Descend from your adventure, and you’re greeted by the Scaphoid Scapha, the large boat-shaped bone you encountered earlier. It snuggles up to the Trapezium Trap, Trapezoid, and Capitate Capital, the bone that sits atop the Lunate Luna.
Finally, as you reach the base of your journey, you encounter the Triquetrum Triangle, a bone shaped like a triangle, and the Lunate Luna, a bone resembling the moon.
So, there you have it, the magical world of carpal bones, navigated through the lens of a memorable mnemonic device. Remember, understanding the anatomy of your wrist is not just about memorizing names; it’s about unlocking the secrets to movement, dexterity, and the fascinating symphony of your body.
Concept 1: Anatomical Snuffbox
- Explanation of the anatomical snuffbox as a triangular depression on the back of the wrist
- Related concepts: Radius, Ulna, Scaphoid, Trapezium, Trapezoid
Discover the Anatomical Snuffbox: A Deeper Dive into Wrist Anatomy
Introduction
Embark on a journey to unravel the secrets of the wrist, a complex and intricate part of our musculoskeletal system. Today, we delve into the world of carpal bones, focusing specifically on the enigmatic Anatomical Snuffbox.
Understanding the Anatomical Snuffbox
Nestled on the posterior aspect of the wrist, the Anatomical Snuffbox is a triangular depression that holds historical significance. In the days of old, gentlemen would store their snuff tobacco in this very location.
Anatomical Landmarks
Bordering the Anatomical Snuffbox are several key anatomical landmarks:
- Ulnar styloid process: A projection of the ulna bone that forms the medial boundary.
- Radial styloid process: A projection of the radius bone that constitutes the lateral boundary.
- Scaphoid tubercle: A bony prominence on the scaphoid bone that forms the proximal apex of the triangle.
- Trapezium bone: A small trapezoidal bone that lies laterally to the scaphoid tubercle.
- Trapezoid bone: Another trapezoidal bone located distal to the trapezium bone.
Underlying Structures
Beneath the Anatomical Snuffbox lies the scaphoid bone, a boat-shaped bone that plays a crucial role in wrist motion. It articulates with both the radius and the lunate bone.
Clinical Significance
The Anatomical Snuffbox is not merely an anatomical curiosity but has important clinical implications:
- Scaphoid fractures: Fractures of the scaphoid bone, often caused by falling on an outstretched hand, can be difficult to diagnose due to their subtle nature. Examining the Anatomical Snuffbox can aid in identifying these fractures.
- Carpal tunnel syndrome: This condition, characterized by compression of the median nerve, can lead to pain, numbness, and tingling in the hand. The Anatomical Snuffbox helps locate the median nerve and facilitates diagnosis.
Conclusion
The Anatomical Snuffbox, though a small and seemingly innocuous depression, is a fascinating anatomical feature that reveals the intricacies of wrist anatomy. Its historical significance and clinical utility make it a valuable landmark for medical professionals and enthusiasts alike.
Understanding Boxer’s Fracture: An Injury to Remember
What is a Boxer’s Fracture?
Imagine a fierce boxing match where a fighter’s fist collides with an opponent’s face. The impact can cause a break in the bone located at the base of the little finger. This injury is known as a boxer’s fracture, so named because it’s commonly seen in boxers and other athletes who engage in contact sports.
The Role of the Metacarpal Bone
The metacarpal bones are the long bones that form the back of the hand. They connect the wrist bones to the finger bones. The fifth metacarpal, which supports the little finger, is the one most susceptible to boxer’s fracture.
Causes and Symptoms
A boxer’s fracture occurs when excessive force is applied to the neck of the fifth metacarpal. This can happen during a direct blow, such as the impact of a punch. Symptoms may include pain, swelling, bruising, and difficulty moving the little finger.
Treatment and Recovery
Treatment typically involves immobilizing the injured hand in a cast or splint. This allows the bone to heal properly. In severe cases, surgery may be necessary to stabilize the fracture. Recovery time varies, but it usually takes several weeks to regain full function of the hand.
Prevention
Preventing boxer’s fractures is crucial, especially for athletes. Proper training techniques, protective gear, and avoiding excessive force on the hands can help minimize the risk.
Concept 3: Carpal Boat
- Description of the lunate, triquetrum, and hamate bones forming a concave arch resembling a boat
- Related concepts: Lunate, Triquetrum, Hamate
Concept 3: The Carpal Boat
Picture this: the lunate, triquetrum, and hamate bones, nestled together, form an arch that resembles a boat. This concave arch is called the carpal boat.
Imagine the lunate as the bow of the boat, curving gently like the hull. The triquetrum acts as the stern, providing stability at the back. And the hamate forms the deck, sloping slightly towards the palm.
This arrangement is not just for aesthetics. The carpal boat serves as a protective barrier for the median nerve and tendons that pass through the wrist. It also plays a crucial role in wrist mobility, allowing for a wide range of movements, from delicate finger gestures to powerful grasping.
So, next time you’re gazing at the back of your wrist, envision the hidden masterpiece within – the carpal boat, a symphony of bones working together to keep your wrist moving with grace and ease.
Concept 4: Hamate Hook
- Explanation of the hamate hook as a projection on the hamate bone
- Related concept: Pisiform
Concept 4: The Intriguing Hamate Hook and Its Guardian, the Pisiform
Unveil the secrets of the wrist’s fascinating anatomy with the Hamate Hook, a bony projection that extends from the Hamate bone like an eagle’s talon. Strategically located on the ulnar side of the wrist, this hook-like structure plays a pivotal role in maintaining wrist stability.
Intriguingly, nestled beneath the Hamate Hook lies the Pisiform bone, a small yet significant guardian of the wrist joint. Resembling a pea in shape, this bone serves as a crucial attachment point for ligaments and tendons that stabilize the wrist during everyday movements.
In concert, the Hamate Hook and Pisiform form an intricate alliance, working together to safeguard the wrist joint from excessive force and potential injury. The hook-like projection of the Hamate bone provides a secure anchorage for ligaments, while the Pisiform acts as a buffer zone, absorbing and distributing forces across the wrist joint.
Moreover, the Hamate Hook has clinical significance. Its proximity to the ulnar nerve makes it vulnerable to compression, which can lead to a condition known as ulnar nerve entrapment. This condition can cause numbness, tingling, and pain in the hand and fingers.
Understanding the anatomy of the Hamate Hook and Pisiform is essential for healthcare professionals, particularly orthopedists and physiotherapists, to effectively diagnose and treat wrist injuries. By comprehending the intricate interplay between these two structures, medical practitioners can provide optimal care and enhance the overall health of their patients’ wrists.
The Tiny Pisiform Pea, a Hidden Gem in Your Wrist
Nestled amidst the intricate network of carpal bones within your wrist, there lies a small, unassuming bone affectionately known as the pisiform. Its diminutive size belies its remarkable role in the complex symphony of hand movements.
The pisiform, aptly named for its resemblance to a pea, is the smallest of the eight carpal bones. It sits quietly on the ulnar (little finger) side of the wrist, nestled snugly against the hamate bone. Despite its humble stature, the pisiform plays a vital role in stabilizing the wrist during powerful grasping and gripping motions.
An intriguing characteristic of the pisiform is its intimate relationship with the hook of the hamate, a hook-shaped projection on the nearby hamate bone. The pisiform snugly fits into this hook, forming a stable articulation that further enhances wrist stability.
A Bridge Between Bones
The pisiform acts as a bridge between the bones of the forearm and the hand. It articulates with both the radius and the ulna, the two forearm bones, providing a secure connection to the wrist joint. Additionally, it articulates with several adjacent carpal bones, including the triquetrum, hamate, and capitate, forming a complex network of interlocking joints.
A Beacon for Wrist Health
The pisiform bone is more than just a structural component; it is also a potential indicator of health issues. Inflammation of the pisiform, known as pisiformitis, can cause pain, swelling, and tenderness in the wrist. This condition typically arises from repetitive hand movements or trauma to the wrist.
Though small in size, the pisiform pea is an indispensable component of the wrist. Its intricate connections with neighboring bones, its role in stabilizing the wrist, and its potential as an indicator of wrist health make it a fascinating and essential part of our musculoskeletal system.
Concept 6: Scaphoid Scapha
- Description of the scaphoid as a large, boat-shaped bone known as the “scapha”
- Related concepts: Trapezium, Trapezoid, Capitate
Concept 6: Scaphoid Scapha
The scaphoid bone holds a prominent position within the wrist, standing out as the largest among the carpal bones. Its distinctive shape, akin to a small boat, has earned it the nickname “scapha“.
This boat-shaped bone plays a crucial role in the wrist’s anatomy, forming a part of the proximal row of carpal bones. It establishes secure connections with its neighboring bones, including the trapezium, trapezoid, and capitate.
Understanding the scaphoid’s relationship with these neighboring bones is essential. It articulates with the trapezium and trapezoid laterally, creating a stable foundation for the thumb. By interlocking with the capitate medially, it forms a solid base for the movement of the hand and wrist.
In addition to its functional significance, the scaphoid’s distinct shape makes it easily recognizable on wrist X-rays. Its boat-like contour provides radiologists with a clear landmark, aiding in the accurate diagnosis of wrist injuries.
Understanding the Trapezium: The Triangular Trap in Your Wrist
In the intricate anatomy of your wrist, a series of eight small bones known as the carpal bones play a crucial role in your ability to move and grasp effortlessly. Of these carpal bones, one particular bone has a distinctive shape and a name that befits its function: the trapezium, also known as the “trap” bone.
The trapezium, aptly named for its triangular shape, resides in the proximal row of carpal bones, closest to the forearm. Like a wedge, its triangular form complements the scaphoid (or scapha) bone, which is shaped like a boat. Together, the trapezium and scaphoid form a stable connection that helps distribute forces across the wrist.
The trapezium’s “trap” feature also plays a significant role in thumb movement. It articulates with the base of the first metacarpal, which connects to the thumb. The triangular shape of the trapezium provides stability and support for this vital joint, allowing us to perform intricate movements like grasping and pinching with ease.
Whether you’re a musician performing a complex chord or a carpenter wielding a hammer, the trapezium bone quietly serves as an anchor, ensuring smooth and precise movements. By understanding its role, we can appreciate the intricate harmony of our bodies and the remarkable function of each bone in our complex musculoskeletal system.
Concept 8: Capitate Capital
The capitate bone, located in the center of the wrist, stands tall as the “capital” bone, the leader of the carpal bone family. Its central position and prominent size make it a key player in the intricate symphony of wrist movements.
Like a regal king, the capitate presides over its fellow carpal bones, the lunate, hamate, and triquetrum. These bones form a tightly knit group, with the capitate acting as the bridge, connecting them to the radius and ulna bones of the forearm.
The capitate’s unique shape, resembling an inverted pyramid, provides stability and strength to the wrist joint. Its prominent ridge, known as the styloid process, serves as an anchor for the ligaments that bind the wrist bones together, preventing excessive movement and ensuring the wrist’s integrity.
Lunate Luna: The Moon-Shaped Carpal Bone
As we unravel the intricacies of the wrist’s anatomy, we encounter the lunate, a captivating bone that has earned its poetic name, “luna,” for its uncanny resemblance to the celestial body. Nestled amidst the wrist’s carpal bones, the lunate is a vital component of the wrist’s intricate mechanics.
The lunate’s distinctive crescent-like shape, reminiscent of the moon’s phases, sets it apart from its fellow carpal bones. This moon-shaped bone forms a crucial connection with its neighboring bones, the scaphoid, capitate, and triquetrum, creating a harmonious arch that supports the wrist’s range of motion.
The lunate’s role extends beyond its structural significance. It plays a pivotal part in transmitting force from the forearm to the hand. Its smooth, rounded surface facilitates effortless wrist movements, allowing us to perform everything from delicate writing to powerful gripping.
Unveiling the lunate luna is not merely an anatomical exercise but a journey into the wonders of the human body. Its poetic name and unique shape captivate our imagination, inviting us to appreciate the intricate symphony of bones that make up our physical form.
Concept 10: Triquetrum Triangle
Nestled amidst the intricate network of carpal bones that orchestrate the symphony of wrist movements, there lies a triangular gem known as the triquetrum. True to its name, this little bone boasts a three-sided configuration that sets it apart from its carpal brethren.
Like a tiny pyramid nestled within the wrist’s anatomy, the triquetrum plays a pivotal role in stabilizing and guiding every flick of the hand, every graceful twist of the wrist. Its triangular shape interlocks seamlessly with neighboring bones, forming a secure framework for the wrist joint.
Imagine a master architect designing a perfectly balanced structure. The triquetrum’s triangular shape is not mere coincidence but a calculated masterpiece. Its angles and vertices align precisely to distribute forces evenly across the wrist, ensuring stability and freedom of movement.
Furthermore, the triquetrum’s triangularity lends itself to a harmonious relationship with its companions, the lunate, capitate, and hamate. These bones, like pieces of a intricate puzzle, fit snugly around the triquetrum, forming a stable foundation for the delicate carpal tunnel and its vital nerve and tendon pathways.