Master Syllable Division: Advanced Techniques For Open, Closed, And Complex Syllables
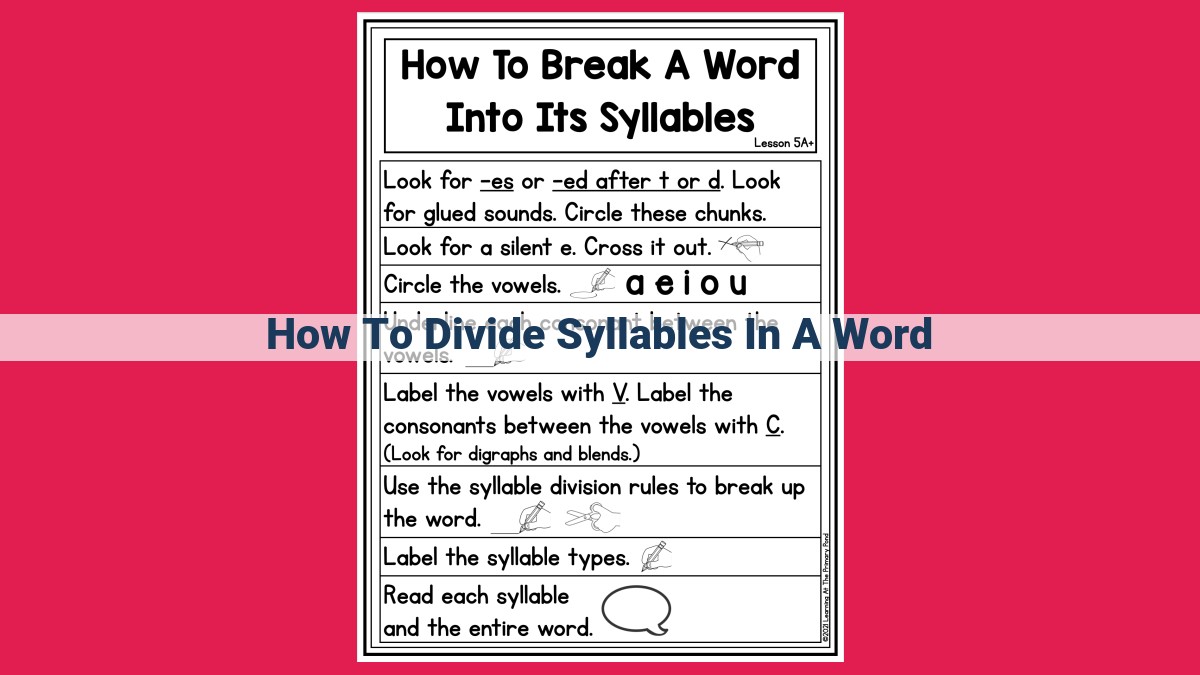
To divide syllables, consider the syllable types (open/closed), vowel teams, consonant blends, diphthongs, and silent letters. Apply the rules by separating open syllables before closed syllables, dividing vowel teams but keeping consonant blends together. Diphthongs remain intact, while silent letters are usually ignored. In advanced techniques, prefixes are divided before the root word, and suffixes are separated. For instance, “example” divides into “ex-am-ple” and “undecided” becomes “un-de-ci-ded.”
Delving into the World of Syllables: Open and Closed
In the intricate symphony of language, syllables are the fundamental building blocks. Understanding their types is akin to deciphering the secret code of words. Let’s embark on a journey to explore open and closed syllables.
Open Syllables: A Vocal Finale
An open syllable, like a door ajar, ends with a melodious vowel. It’s a gateway to a world of pure vocal delight. Words like “fate,” “bee,” and “bone” showcase this openness, their final notes lingering in the air.
Closed Syllables: A Consonant Coda
In contrast, closed syllables stand tall like sentinels, concluding with a consonant. They bring a sense of closure, a rhythmic punctuation mark at the end of each sound. Words like “cat,” “stop,” and “dog exemplify this type of syllable, their final consonants providing a satisfying conclusion.
The Dance of Open and Closed: Shaping the Rhythm
By understanding the differences between open and closed syllables, we unlock the secrets of rhythm and flow in language. Open syllables create an airy, expansive feeling, while closed syllables provide a sense of stability and grounding. This interplay creates a harmonious tapestry of sounds that captivates the ear.
Vowel Combinations: The Bonds That Form Unique Sounds
In the realm of language, where words dance across our lips and pages, vowel combinations stand as versatile architects of sound and meaning. These are duos or trios of vowels that unite to craft unique pronunciations, adding depth and nuance to our spoken words.
Imagine the letter “e” and the letter “a” joining forces to create the vibrant “ea” sound in the word “meat.” It’s a blend that dances playfully on our tongues, a harmonious union that gives the word its distinctive flavor. Similarly, the “ee” in “feet” and the “ie” in “lie” represent vowel combinations that transform everyday words into vibrant sound tapestries.
These vowel alliances are not mere linguistic curiosities; they serve as vital cogs in the machinery of language. They help us differentiate between words like “pair” and “pear,” “fine” and “fun,” giving each word its own sonic identity and meaning.
Understanding vowel combinations is crucial for mastering the intricacies of pronunciation and spelling. When we recognize these vocal partnerships, we gain the tools to tackle challenging words with precision and confidence. By unraveling the secrets of vowel combinations, we unlock a deeper appreciation for the beauty and complexity of language.
Consonant Combinations: Blends – The Dynamic Duo of Speech
In the enchanting tapestry of language, words are woven together by individual units known as syllables. Each syllable dances with a unique rhythm, influenced by the harmonious interplay of vowels and consonants. Among these consonants, we encounter blends – spirited combinations that effortlessly glide off our tongues.
Blends are pairs or groups of consonants that merge to create a singular sound. They’re like a secret handshake between letters, working together to produce a vibrant and expressive melody. Take the “bl” blend in “blue” – its rounded shape and gentle flow conjure the image of the boundless sky.
Blends come in a kaleidoscope of forms, adding character and vitality to our speech. From the playful “tr” in “tree” to the sophisticated “thr” in “throne,” they inject a richness that transforms ordinary words into extraordinary. They’re the architects of our language’s rhythm, giving it a vibrant beat and an unforgettable symphony.
The world of blends is vast, spanning from the iconic “sp” in “splash” to the enigmatic “tch” in “watch.” Each blend carries its own unique character, contributing to the rich vocabulary of our language. So embrace these dynamic duos of speech – they’re the secret ingredient that empowers us to communicate with clarity and charm.
Unveiling the Secrets of Diphthongs: A Smooth Vocal Transition
In the tapestry of language, diphthongs emerge as vibrant threads that add a touch of melody to our speech. They are enchanting blends of two distinct vowel sounds that intertwine seamlessly, creating a harmonious transition.
A diphthong is not merely a mere combination of vowels; it’s a symphony of sounds that evoke a gentle glide from one vowel to another. Imagine the graceful merging of “ah” and “ee” in the word “out” or the fluid movement from “oh” to “oo” in “boat.” These are the quintessential examples of diphthongs, where the first vowel smoothly ushers us into the embrace of the second.
How Diphthongs Enchant Our Language
Diphthongs possess a captivating ability to infuse language with a sense of rhythm and lyrical beauty. They lend a melodious charm to our words, transforming everyday speech into a delightful symphony. Consider the harmonious blend of “eye” in “eyelid” or the captivating dance of “air” in “airplane.” Diphthongs are the secret behind the magic of our spoken language, weaving together sounds that resonate with our emotions and connect with our listeners on a deeper level.
Harnessing the Power of Diphthongs
Embracing the power of diphthongs in your writing or speech can elevate your communication to new heights. By incorporating these mellifluous vowel combinations, you can add depth, richness, and emotional resonance to your words. Poetry, prose, and even casual conversation become vibrant and captivating when infused with the enchanting melody of diphthongs.
Mastering the Art of Diphthongs
Like any skill, mastering the art of diphthongs requires practice and dedication. Listen attentively to native speakers and immerse yourself in their natural use of vowel transitions. Experiment with different diphthong combinations and play with their pronunciations until you find your own harmonious balance. Remember, the key is to create a seamless glide from one vowel to another, allowing the sounds to flow effortlessly off your tongue.
Diphthongs are the unsung heroes of our language, adding a touch of musicality and lyrical charm to our words. By understanding their nature and embracing their power, you can unlock a new level of expressiveness in your communication. Let the melody of diphthongs guide your speech and writing, painting vivid soundscapes that captivate your audience and leave a lasting impression.
Silent Letters: Unveiling Words’ Hidden Secrets
In the realm of language, words often conceal letters that don’t make a sound. These silent letters play a subtle role in shaping pronunciation and adding depth to our written vocabulary.
One of the most common silent letters is the “e” at the end of words. Take the word knife. Though the “e” is present in writing, it remains silent, leaving only the “kn” sound. This silent “e” serves a sneaky purpose—it alters the pronunciation of the “i” before it, giving it a long, “eye” sound instead of a short, “ih” sound.
Silent letters can also appear in the middle of words. In the word debt, the “b” is silent, leaving only the “det” sound. This hidden “b” creates a subtle pause in the pronunciation, emphasizing the word’s weight and significance.
Another example of a silent letter is the “h” in the word hour. While it appears clear and present in writing, it’s ultimately a silent guardian, influencing the pronunciation of the following vowel.
These silent players may seem like minor characters in the language’s symphony, but they wield a surprising influence. They guide us in pronouncing words correctly, shape their meaning, and add a touch of elegance to our written communication. So, as we navigate the complexities of language, let’s give these unsung heroes their due recognition.
Syllable Division: A Step-by-Step Guide to Breaking Words Down
In the realm of language, syllables serve as the building blocks of spoken words. Understanding how to divide words into syllables is crucial for both reading and pronunciation. Let’s embark on a journey to unravel the guidelines for applying syllable division rules.
General Guidelines:
-
Keep Diphthongs and Vowel Combinations Intact: Vowel sounds that flow together smoothly (diphthongs) and combined vowel sounds that represent a single syllable (vowel combinations) should not be separated. For instance, “out” has one syllable, with the diphthong “ou,” while “heat” has one syllable, with the vowel combination “ea.”
-
Divide on Consonant Boundaries: When a word contains multiple consonants together, divide the syllables after the first consonant, unless the consonants form a blend that makes a single sound. For example, “clam” has two syllables: “cla-m.”
Advanced Techniques:
-
Prefixes and Suffixes: Prefixes and suffixes are added to words to change their meaning. When dividing syllables, keep prefixes and suffixes separate from the root word. For instance, “un-dec-i-ded” has three syllables.
-
Consonant Digraphs and Blends: Consonant digraphs (two consonants making one sound) and blends (multiple consonants making one sound) can complicate syllable division. Generally, divide the syllables after the digraph or blend if it occurs at the end of the root word, like “black” or “blue.” However, if it occurs within the root word, divide after the first consonant of the digraph or blend, like “ro-bot” or “a-gree.”
Example:
Let’s apply these rules to the word “example“:
- Divide after the consonant “m”: ex-am-
- Keep the vowel combination “a” intact: ex-am-
- Divide after the consonant “p”: ex-a-m–
- Divide after the consonant “l”: ex-a-m-ple
Therefore, the word “example” has three syllables.
By following these guidelines, you can transform yourself from a syllable novice to a proficient divider. Remember, practice makes perfect, so don’t hesitate to experiment with different words. With a little bit of effort, you’ll soon be navigating the intricacies of syllable division with ease.
Advanced Syllable Division Techniques: Unraveling the Complexities
Syllabification: The art of dividing words into their component syllables can become more challenging when faced with prefixes, suffixes, or other complexities. But fear not, for these advanced techniques will guide you through the linguistic labyrinth.
Prefixes and Suffixes
Prefixes and suffixes are word parts that are added to the beginning or end of a word to change its meaning. When dividing words with prefixes or suffixes, remember the following rules:
-
If the prefix ends with a consonant and the root word begins with a vowel, the prefix remains with the first syllable.
- Example: un-happy
-
If the prefix ends with a vowel and the root word begins with a consonant, the prefix is usually separated from the root word by a syllable break.
- Example: trans-form
-
Suffixes are generally separated from the root word by a syllable break.
- Example: re-ject-ed
Other Complexities
Beyond prefixes and suffixes, other complexities can arise when dividing syllables. These include:
-
Double consonants: When two identical consonants appear together, they are usually divided between syllables.
- Example: kit-ten
-
Consonant clusters: When three or more consonants appear together, they are often divided into smaller groups.
- Example: struc-ture
-
Vowel teams: When two or more vowels appear together and form a single sound, they are usually treated as a single syllable.
- Example: ea in great
Putting It All Together: An Example
Let’s take the word “undecided” as an example. Using the rules above, we can divide it into syllables as follows:
- The prefix “un” ends with a consonant and the root word “decide” begins with a vowel, so the prefix remains with the first syllable: un-
- The root word “decide” has three syllables: de-ci-de
- Therefore, the complete syllable division is: un-de-ci-ded
Mastering these advanced syllable division techniques will empower you to conquer any word, no matter how complex its structure. Remember, practice makes perfect, so don’t hesitate to experiment and consult resources when needed.