Mastering Communication Competence: Essential Skills For Enhanced Interaction And Collaboration
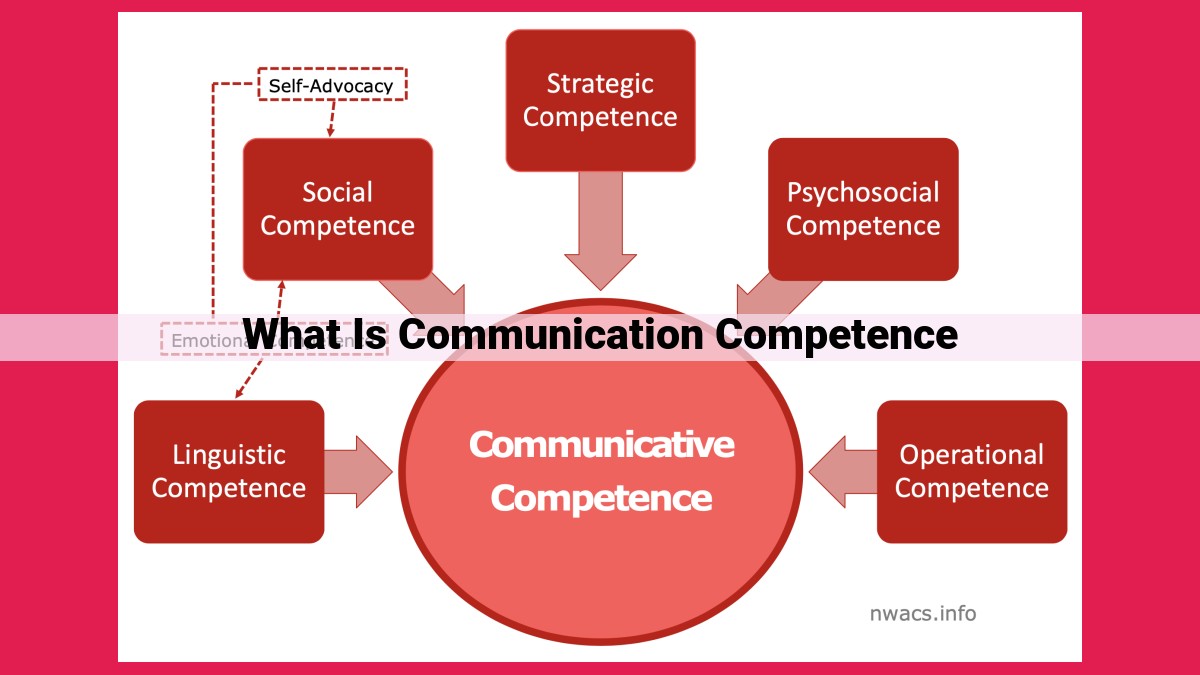
Communication competence encompasses the ability to effectively convey and interpret messages, adapting to diverse contexts. It incorporates verbal skills (language, speech, persuasion), nonverbal cues (body language, facial expressions), and active listening. Empathy fosters understanding and rapport, while cultural sensitivity and adaptability enhance communication across cultures. Effective message construction, questioning, feedback, and conflict management are key components of communication competence, facilitating growth, improvement, and harmonious interactions.
Defining Communication Competence: The Key to Effective Interactions
In the symphony of human interactions, communication stands as the conductor, guiding our messages and shaping our relationships. At its core lies communication competence, an indispensable skill that allows us to convey and interpret messages effectively.
Communication competence is the ability to transmit our thoughts, feelings, and intentions clearly and accurately while simultaneously understanding and responding appropriately to the messages of others. It’s a dynamic process that encompasses verbal and nonverbal communication, active listening, and a deep understanding of cultural nuances.
In the tapestry of life, communication competence plays a vital role. It enables us to build strong relationships, foster mutual understanding, and collaborate effectively in both personal and professional spheres. Its benefits are far-reaching, enhancing our ability to negotiate, resolve conflicts, and navigate the complexities of diverse cultural landscapes.
By honing our communication skills, we unlock the power to connect, influence, and inspire. We become more persuasive in our speech, more attentive in our listening, and more sensitive to the needs of those around us. Communication competence is not merely a skill; it’s a key to fulfilling relationships, successful careers, and a harmonious society.
Verbal Communication: The Bedrock of Language
Verbal communication forms the cornerstone of human interaction, allowing us to express thoughts, convey messages, and forge connections. It encompasses a diverse range of elements, including language, speech, listening, and persuasion, each playing a pivotal role in effective communication.
Language: The foundation of verbal communication lies in language, a system of symbols and rules that enables us to encode and decode meanings. Our choice of words and grammatical structures conveys not only what we say but also our emotions, perspectives, and cultural backgrounds.
Speech: The act of speaking transforms words into sound, allowing us to convey messages orally. It involves elements such as volume, intonation, and pace, which can influence the impact of our words. Effective speech delivery enhances clarity, engages listeners, and builds credibility.
Listening: The art of listening is equally crucial to verbal communication. It involves not only hearing words but also paying attention, understanding, and interpreting their meaning. Active listening demonstrates respect, fosters empathy, and creates a foundation for productive dialogue.
Persuasion: Verbal communication also encompasses the ability to persuade. By crafting compelling arguments, addressing concerns, and appealing to emotions, we can influence others’ thoughts and actions. Persuasive communication is vital in various settings, including negotiations, sales presentations, and public speaking.
Impact of Language Choices and Speech Delivery:
The words we choose and the way we deliver them have a profound impact on communication effectiveness. Using clear and concise language ensures that messages are easily understood. Choosing appropriate words for the audience and context conveys respect and sensitivity. Speech delivery techniques such as maintaining eye contact, speaking at an optimal pace, and modulating intonation enhance engagement and credibility.
In conclusion, verbal communication is a complex and multifaceted skill that forms the foundation of our interactions with others. By honing our language skills, speech delivery, listening abilities, and persuasive techniques, we can communicate effectively, build meaningful connections, and navigate the challenges of verbal expression.
Nonverbal Communication: The Unspoken Language
Beyond the spoken word, there lies a realm of nonverbal communication that speaks volumes about our thoughts, feelings, and intentions. Body language, facial expressions, and vocal cues weave an intricate tapestry that conveys messages far more potent than mere words. Understanding these cues is crucial for effective communication and building strong relationships.
Body language encompasses a wide range of gestures, postures, and movements. The way we stand, sit, and walk can convey confidence, submission, or openness. Crossed arms may indicate defensiveness, while open arms suggest warmth and receptiveness. Observing someone’s body language can provide valuable insights into their emotional state and intentions.
Facial expressions are a powerful form of nonverbal communication. A simple smile can brighten a room and convey friendliness, while a frown can express disapproval or sadness. The eyes, in particular, play a significant role in conveying emotions. Direct eye contact often indicates sincerity and trust, while avoiding eye contact may suggest discomfort or deception.
Vocal cues, such as tone, pitch, and volume, can also convey subtle messages. A high-pitched voice may signal excitement or nervousness, while a low-pitched voice can suggest authority or confidence. Hesitations, pauses, and interruptions can also hint at underlying emotions or thoughts.
In addition to conveying messages, nonverbal cues play a crucial role in building rapport. Mirroring someone’s body language can foster a sense of connection and understanding. Maintaining eye contact and smiling during a conversation can create a warm and engaging atmosphere.
Understanding and utilizing nonverbal communication is an art that can enhance our communication skills and foster stronger connections. By paying attention to the unspoken language of body language, facial expressions, and vocal cues, we can communicate more effectively, build rapport, and create a more harmonious and fulfilling social environment.
The Art of Active Listening: Engaging the Whole Self
In the tapestry of human interactions, communication weaves its intricate threads, connecting souls and shaping destinies. However, to truly connect and understand, we must master the art of active listening. It’s not just about hearing words but about engaging our whole selves to grasp the depths of what’s being said and unsaid.
Principles of Active Listening
Active listening encompasses three fundamental principles: attentiveness, understanding, and empathy. When we are attentive, we give our undivided attention to the speaker, making eye contact, nodding, and maintaining an open and receptive body language. By doing so, we convey that we value their words and thoughts.
Understanding goes beyond simply decoding the spoken word. It requires us to interpret the speaker’s underlying message, their emotions, and their intentions. We must strive to understand not only what they say but why they say it. This requires us to ask clarifying questions, summarize key points, and paraphrase to ensure our understanding aligns with theirs.
Empathy: The Key to True Connection
Empathy, the ability to step into another’s shoes and see the world through their eyes, is the cornerstone of active listening. When we listen with empathy, we suspend our judgments and connect on a human level. We strive to understand their experiences, emotions, and perspectives, even if we don’t share them. By demonstrating empathy, we build bridges of trust and create a safe space for open and honest communication.
Listening Beyond the Words
Active listening encompasses not only verbal cues but also nonverbal cues, which often convey just as much, if not more, than words alone. Body language, facial expressions, and vocal tone can reveal hidden emotions, intentions, and cultural nuances. By observing these nonverbal cues, we gain a deeper understanding of the speaker’s message and build a more comprehensive connection with them.
The Power of Active Listening
The benefits of active listening extend far beyond enhanced communication. It fosters mutual respect, builds trust, and creates an environment where people feel heard and valued. In personal relationships, active listening strengthens bonds and deepens intimacy. In the workplace, it improves collaboration, minimizes misunderstandings, and boosts productivity.
Becoming an Active Listener
Becoming an active listener is a skill that can be honed with practice. Start by paying attention to your own listening habits. Are you truly present when someone is speaking? Do you understand their perspective? Practice asking clarifying questions, summarizing what you’ve heard, and using nonverbal cues to show that you’re engaged.
Seek out opportunities to listen attentively to others, both in personal and professional settings. Remember, active listening is not about dominating the conversation but about creating a space for meaningful exchange. By engaging our whole selves in the listening process, we unlock the true power of communication and build stronger, more fulfilling relationships.
Empathy: The Key to Effective Communication
Empathy, the ability to step into another’s shoes and understand their thoughts, feelings, and motivations, is an integral component of effective communication. It allows us to transcend our own perspectives and connect with others on a deeper level.
Imagine yourself in a conversation with a close friend who has just shared some upsetting news. As they pour their heart out, you don’t simply listen with your ears but with your entire being. You tune into their voice, their body language, and their unspoken emotions. This ability to empathize enables you to truly understand their pain and offer comforting words.
Empathy is not just about feeling for others but about actively seeking to understand their experiences, without judgment. It allows us to build stronger relationships, resolve conflicts peacefully, and foster a supportive and compassionate environment. By cultivating empathy, we unlock the power to connect with others on a meaningful level, leaving a lasting impact on their lives and our own.
Cultural Sensitivity: Navigating the Cultural Landscape
In an increasingly interconnected world, effective communication transcends linguistic boundaries. It encompasses appreciating and understanding the rich tapestry of cultural differences that shape our interactions. Cultural sensitivity lies at the heart of this endeavor, fostering harmonious communication and building bridges across diverse backgrounds.
Comprehending cultural nuances is paramount to preventing misunderstandings and fostering genuine connections. Beliefs, values, and social norms vary significantly across cultures, influencing everything from communication styles to nonverbal cues. For instance, in some cultures, direct eye contact is considered a sign of respect, while in others, it may be seen as confrontational. By being mindful of these cultural variations, we can avoid misinterpretations and create a welcoming and inclusive communication environment.
Cross-cultural communication presents both challenges and opportunities. One challenge is the potential for cultural misunderstandings, which can arise from differences in language, gestures, and social conventions. To overcome this hurdle, active listening and empathy are crucial. By listening attentively and seeking to understand the perspectives of others, we can bridge cultural gaps and build rapport.
Another challenge lies in the unconscious biases we may hold. These biases can influence our perceptions and communication patterns, leading to unintentional offenses. By actively examining our own cultural assumptions and being open to learning from others, we can mitigate these biases and communicate with greater sensitivity.
Effective cross-cultural communication requires embracing adaptability and flexibility. Different cultures have distinct communication norms, and it’s essential to be adaptable in our approach. This may involve adjusting our communication style, using appropriate gestures, or seeking guidance from cultural experts. By being flexible, we can create communication strategies that are both respectful and effective.
Navigating the cultural landscape requires a conscious effort to understand, appreciate, and adapt to different cultural contexts. By embracing cultural sensitivity, we break down communication barriers, foster meaningful connections, and create a truly inclusive and harmonious communication environment.
Adaptability: Embracing Change and Diversity in Communication
In the ever-evolving tapestry of human interaction, adaptability reigns supreme as a cornerstone of effective communication. It’s the dynamic ability to navigate the shifting sands of diverse perspectives, cultural nuances, and communication styles with grace and finesse.
Flexibility is the key that unlocks the door to adaptable communication. It empowers us to bend and mold our approach to suit the unique needs of each situation, bridging the gaps between individuals and fostering meaningful connections.
Cultural sensitivity plays an equally vital role. By attuning ourselves to the cultural beliefs, values, and communication norms of others, we can overcome barriers and build bridges of understanding. It’s not about adopting every custom but rather respecting and honoring the differences that make us unique.
Imagine encountering a colleague from a culture where direct confrontation is common. Adapting your communication style to embrace their forthrightness ensures a productive exchange of ideas. Conversely, communicating in a more reserved manner with someone from a culture that values indirect communication shows respect for their sensibilities.
Adaptability knows no boundaries. It extends to nonverbal communication, empowering us to interpret body language, facial expressions, and vocal cues within different cultural contexts. By embracing adaptability, we maximize our ability to convey and receive messages effectively, fostering harmony and understanding in our diverse world.
Message Construction: Crafting Meaningful Content
In the realm of communication, crafting meaningful messages is an art that transcends mere words. It’s a skill that empowers us to convey our thoughts, ideas, and emotions effectively, fostering understanding and connection.
To construct messages that resonate, we must adhere to the principles of effective message construction:
-
Organization: Well-structured messages have a logical flow, guiding the reader through your ideas smoothly. Use headings, subheadings, and paragraphs to organize your content and make it easy to follow.
-
Clarity: Use precise language and avoid jargon. Aim for clarity in every sentence, ensuring your message is easily understood. Eliminate unnecessary words and phrases that cloud your message.
-
Conciseness: Brevity is key. Trim unnecessary details and focus on the essential points. Say what you need to say in the fewest possible words, without sacrificing clarity.
-
Coherence: Ensure your message flows seamlessly, with each idea building upon the previous one. Use transitions and connecting words to guide the reader’s understanding and create a coherent narrative.
Structuring Messages Effectively
The structure of your message plays a crucial role in its impact. Use the following tips to enhance the effectiveness of your messages:
-
Attention-grabbing opening: Start with a strong hook or an intriguing question to capture the reader’s attention.
-
Body paragraphs: Develop each main idea in separate paragraphs, providing evidence, examples, or stories to support your points.
-
Conclusion: Summarize the key points of your message, restate your thesis statement, and end with a strong closing statement.
Using Language Effectively
The choice of words can make or break your message. Consider the following principles to use language effectively:
-
Appropriate vocabulary: Use words that are relevant to your audience and purpose. Technical terms may be appropriate in some contexts, while simpler language is more effective for general audiences.
-
Figurative language: Use metaphors, similes, and analogies to make your message more vivid and engaging. These literary devices can help you create a lasting impression.
-
Voice and tone: Your message should reflect your voice and tone. Be genuine and authentic, and tailor your language to match the context and audience.
By adhering to these principles, you can craft messages that are clear, concise, organized, and coherent. These well-constructed messages will empower you to convey your ideas effectively, fostering understanding and connection with your audience.
Effective Questioning: Unlocking Knowledge and Understanding
In the realm of communication, a well-crafted question can be a key that unlocks hidden knowledge, clarifies murky ideas, and sparks profound engagement. The art of effective questioning goes beyond simply asking for information; it involves understanding the different types of questions and their unique roles in facilitating meaningful dialogue.
The Importance of Asking Thoughtful Questions
Questions are the fuel that drives conversations and ignites discussions. They allow us to elicit information, express curiosity, challenge assumptions, and probe deeper into the complexities of a topic. By posing thoughtful questions, we demonstrate our active engagement, encourage others to share their perspectives, and create a space where knowledge can be shared and expanded.
Types of Questions and Their Roles
There are various types of questions, each serving a distinct purpose in communication:
- Closed-Ended Questions: Questions that require a specific answer, often a “yes” or “no.” They are useful for gathering factual information or confirming details.
- Open-Ended Questions: Questions that invite a more elaborate response, allowing individuals to express their thoughts and opinions. They encourage exploration, critical thinking, and the sharing of personal experiences.
- Leading Questions: Questions that subtly suggest a desired answer or opinion. While they can be used to elicit specific information, they should be used with caution to avoid bias.
- Probing Questions: Questions that delve deeper into a topic, asking for clarification, additional details, or the rationale behind a statement. They help uncover hidden assumptions and provide a more thorough understanding.
- Reflective Questions: Questions that paraphrase or summarize what has been said, demonstrating active listening and fostering a sense of understanding and connection.
Fostering Engagement and Understanding
Effective questioning not only elicits information but also promotes engagement and understanding. By asking thought-provoking questions, we challenge our listeners to think critically, consider different perspectives, and articulate their ideas with clarity. When questions are used to clarify misunderstandings, resolve conflicts, or facilitate problem-solving, they become powerful tools for fostering constructive dialogue and achieving shared goals.
In conclusion, effective questioning is a skill that empowers us to unlock knowledge, clarify ideas, and foster engagement. By understanding the different types of questions and their purposes, we can ask thoughtful questions that ignite discussions, stimulate critical thinking, and create a space where knowledge and understanding can flourish.
Feedback: Fueling Growth and Improvement
In the realm of communication, feedback acts as an indispensable tool, propelling us towards personal and professional growth. As we navigate the social landscape, feedback provides invaluable insights, helping us refine our communication skills and fostering a culture of continuous learning.
The Purpose of Constructive Feedback
Constructive feedback, when delivered with a spirit of compassion and growth, serves as a catalyst for improvement. It provides a mirror into our communication, allowing us to identify areas where we can enhance our effectiveness and impact. By embracing feedback as an opportunity to learn and grow, we cultivate a mindset that is open to critique and eager to refine our skills.
Benefits of Providing and Receiving Feedback
Exchanging feedback is a reciprocal process that benefits both the giver and the receiver. For the giver, it offers an opportunity to contribute to others’ development by sharing their observations and insights. Simultaneously, for the receiver, it provides access to valuable information that can be utilized to improve their communication strategies, strengthen relationships, and enhance their overall effectiveness.
The Importance of a Growth Mindset
Embracing a growth mindset is crucial for maximizing the benefits of feedback. A growth mindset recognizes that our abilities are not fixed but rather can be developed through effort and dedication. When we approach feedback with a growth mindset, we view it as an opportunity to identify areas for improvement and take proactive steps to enhance our communication skills.
In Practice: Seeking and Providing Feedback
Actively seek feedback from trusted colleagues, friends, or mentors. Frame your requests in a manner that demonstrates your willingness to learn and embrace constructive criticism. When providing feedback, maintain a respectful and empathetic tone. Focus on specific behaviors or actions, ensuring that your feedback is actionable and relevant. By adhering to these guidelines, you can foster a feedback-rich environment that promotes continuous growth and improvement.
Conflict Management: Resolving Differences Constructively
In the realm of communication, conflicts are inevitable. Like unexpected thunderstorms, they can disrupt otherwise smooth interactions and leave you feeling uneasy. Yet, it’s not the conflicts themselves but how we manage them that truly matters.
There are various types of conflicts that can arise: differences in perspectives, unmet expectations, or clashes of personalities. To navigate these choppy waters effectively, we must first understand the nature of the conflict. Is it a misunderstanding, a clash of values, or a conflict of interests?
Once we’ve identified the conflict’s roots, we can explore strategies for resolving it constructively. Negotiation, mediation, and direct resolution are all tools in our communication toolkit.
Negotiation involves finding a compromise that satisfies both parties. It’s about giving and taking, finding common ground, and understanding the other person’s needs._ Mediation, on the other hand, _involves an impartial third party who facilitates the conversation and helps guide the conflicting parties towards a mutually acceptable solution.
Sometimes, the best approach is direct resolution._ This involves openly addressing the conflict with the other person, _expressing your concerns respectfully, and actively listening to their perspective. By _being honest, transparent, and willing to compromise, you can create a safe space for conflict resolution.
Remember, conflict is not inherently bad. It can be an opportunity for growth, understanding, and strengthening relationships. By embracing conflict management strategies, you can transform conflicts into constructive dialogues that foster better communication and stronger connections.