Line Voltage Heating: Efficient And Cost-Effective Home Heating Solution With Considerations
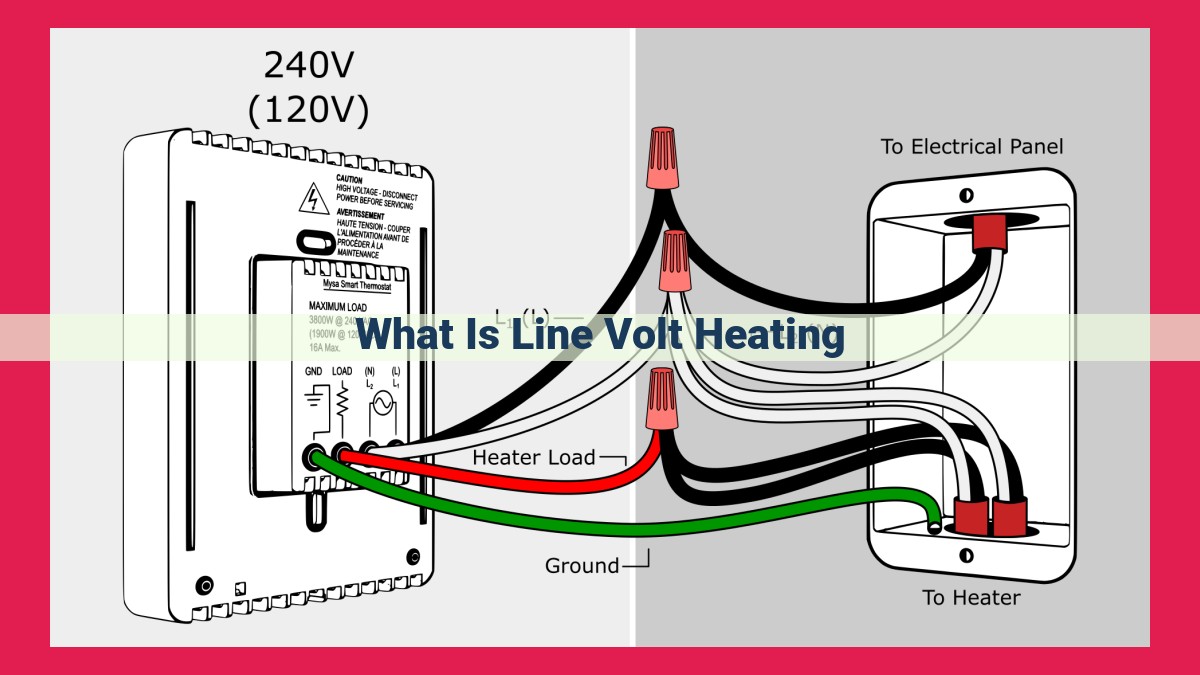
Line voltage heating, a type of electrical resistance heating, utilizes the standard 120 or 240 volts of household electricity to directly power heating elements. Its advantages include high efficiency, rapid heating, and low operating costs. However, it involves higher upfront costs, professional installation, and overheating risks due to the high voltage and current involved. Line voltage heating systems are commonly used in baseboards, radiant heat panels, and heat pumps, and require proper wiring and electrical considerations to ensure safe and efficient operation.
- Explain the concept of line voltage heating and its role in electrical resistance heating.
Line Voltage Heating: An In-Depth Guide to Electrical Resistance Heating
Electricity finds its way into countless aspects of our daily lives, and one of its more essential roles is in heating our homes and businesses. Line voltage heating is a popular and efficient method of electrical resistance heating that offers several advantages and applications. In this blog post, we’ll take a comprehensive look at line voltage heating, exploring its benefits, drawbacks, applications, wiring considerations, and safety concerns.
Line voltage heating, also known as direct-wire heating, involves the use of electrical current to directly heat conductive elements. When electricity flows through these elements, resistance is encountered, causing them to generate heat. This heat is then transferred to the surrounding environment, providing warmth and comfort. Line voltage heating systems are commonly used in various applications, including baseboards, radiant heat panels, and heat pumps, thanks to their efficiency, durability, and rapid heating capabilities.
Advantages of Line Voltage Heating: Efficient, Cost-Effective, and Speedy Warmth
Line voltage heating systems offer a myriad of benefits that make them an attractive choice for homeowners seeking efficient, cost-effective heating solutions.
High Efficiency: Line voltage heating systems operate at high voltages, which minimizes power loss and enhances energy efficiency. These systems convert electricity into heat with remarkable efficiency, resulting in reduced energy consumption and lower utility bills.
Low Operating Costs: The high efficiency of line voltage heating translates into lower operating costs, making them an economical option in the long run. The reduced energy consumption means you can enjoy a warm and comfortable home without breaking the bank.
Rapid Heating: Unlike other heating systems that take time to warm up, line voltage heating systems deliver rapid heating thanks to their high voltage. These systems can quickly raise the temperature in a room, providing instant warmth and comfort on demand.
Disadvantages of Line Voltage Heating: The Costs and Cautions
While line voltage heating offers benefits, it also poses certain drawbacks that potential users should be aware of before making a decision.
High Upfront Costs:
- Installing a line voltage heating system can be expensive, especially for larger spaces.
- The materials, labor, and professional expertise required can add up quickly.
- Compared to other heating options, line voltage systems may require a more substantial investment upfront.
Professional Installation Required:
- Due to the high voltage involved, line voltage heating systems must be installed by qualified electricians.
- DIY enthusiasts should not attempt to install these systems on their own to avoid electrical hazards and potential safety risks.
- The costs of professional installation can further increase the initial expenses of the system.
Overheating Concerns:
- Line voltage heating systems can generate significant heat, posing a risk of overheating.
- Inadequate ventilation or improper installation can lead to excessive temperatures, which can damage the system and surrounding materials.
- Special safety features, such as thermal cutouts, are often incorporated into line voltage heaters to prevent overheating, but homeowners should still take precautions to ensure safe operation.
Applications of Line Voltage Heating: Versatility and Efficiency
Line voltage heating systems offer a diverse range of applications, catering to various heating needs. Their versatility makes them suitable for both residential and commercial spaces.
Baseboards: Discreet Warmth at Floor Level
Line voltage baseboards are sleek and unobtrusive, blending seamlessly into the lower perimeter of walls. They emit gentle radiant heat that rises from the floor, creating a comfortable and even temperature distribution.
Radiant Heat Panels: Ceiling-Mounted Comfort
Mounted on ceilings, radiant heat panels emit infrared rays that penetrate objects, providing targeted warmth to occupants. These panels are energy-efficient and create a cozy ambiance in any room.
Heat Pumps: Energy-Saving Solutions
Line voltage heat pumps are a sustainable and cost-effective heating option. They extract heat from outdoor air and transfer it indoors, reducing energy consumption while providing comfortable temperatures.
Specialized Applications
Beyond these common applications, line voltage heating systems also serve specialized purposes. For instance, they are used in greenhouses to maintain optimal growth conditions, in agricultural buildings to prevent livestock freezing, and in industrial facilities to provide localized heating for equipment and workspaces.
Wiring and Electrical Considerations for Line Voltage Heating Systems
When it comes to installing line voltage heating systems, meticulous attention to electrical requirements and wiring specifications is paramount. These systems operate directly on the household electrical supply, typically utilizing either 120 volts or 240 volts. Ensure your electrical service can accommodate the high voltage and amperage demands of line voltage heating.
Proper wiring is essential for the safe and efficient operation of these systems. Professional installation is highly recommended, as improperly wired systems can pose electrical hazards, including fires. Dedicated circuits, equipped with appropriate breakers or fuses, are necessary to prevent overloading and overheating.
Consider the wire gauge (thickness) required for your system. Thicker gauge wire, indicated by a lower numerical value, can handle higher amperage. Consult an electrician to determine the appropriate wire gauge based on the system’s wattage and circuit length.
Grounding is crucial for electrical safety. Connect all components, including the heating elements, control panel, and thermostat, to a proper grounding system. This provides a path for excess current to safely dissipate, reducing the risk of electrical shocks or fires.
Conduit, a protective pipe encasing the wires, is often used in line voltage heating systems, especially when running wires through walls or ceilings. Conduit safeguards the wires from physical damage and potential exposure to moisture, further enhancing safety.
Remember, line voltage heating systems operate at high voltage. Always follow electrical codes and manufacturer’s instructions precisely. Engage a qualified electrician for installation and maintenance to ensure the system’s safe and optimal performance.
Safety Concerns and Mitigation in Line Voltage Heating Systems
Maintaining a warm and comfortable home with line voltage heating is undoubtedly appealing, but it’s crucial to be aware of the potential safety hazards associated with these systems. Electrical hazards, overheating, and fires are some of the concerns that need to be addressed to ensure a safe indoor environment.
Electrical Hazards:
Line voltage heating systems operate at high voltages, posing a significant risk of electrical shock. Always ensure that qualified electricians handle the installation and maintenance of these systems. Additionally, regular inspections of wiring and components are essential to detect any potential electrical faults.
Overheating:
Overheating is another common issue with line voltage heating systems. If the system is not properly installed or maintained, it can lead to excessive heat buildup, which can damage the system and pose a fire hazard. To prevent overheating, ensure that there is adequate ventilation around the heating unit and that it is not obstructed by furniture or other objects.
Fires:
In rare cases, line voltage heating systems can cause fires. Faulty wiring, loose connections, or overheating can create arcs or sparks, which can ignite flammable materials nearby. To mitigate this risk, always use approved electrical components and ensure that the system is properly grounded. Additionally, keep flammable materials away from heating units and consider installing smoke detectors in the vicinity.
By understanding these safety concerns and implementing appropriate mitigation measures, you can enjoy the benefits of line voltage heating while ensuring the safety of your home and family. Regular maintenance, proper installation, and adherence to safety guidelines will help prevent potential hazards and create a cozy and secure indoor environment.