Lambdoid Suture: Crucial Joint In Skull Anatomy, Growth, And Medical Diagnosis
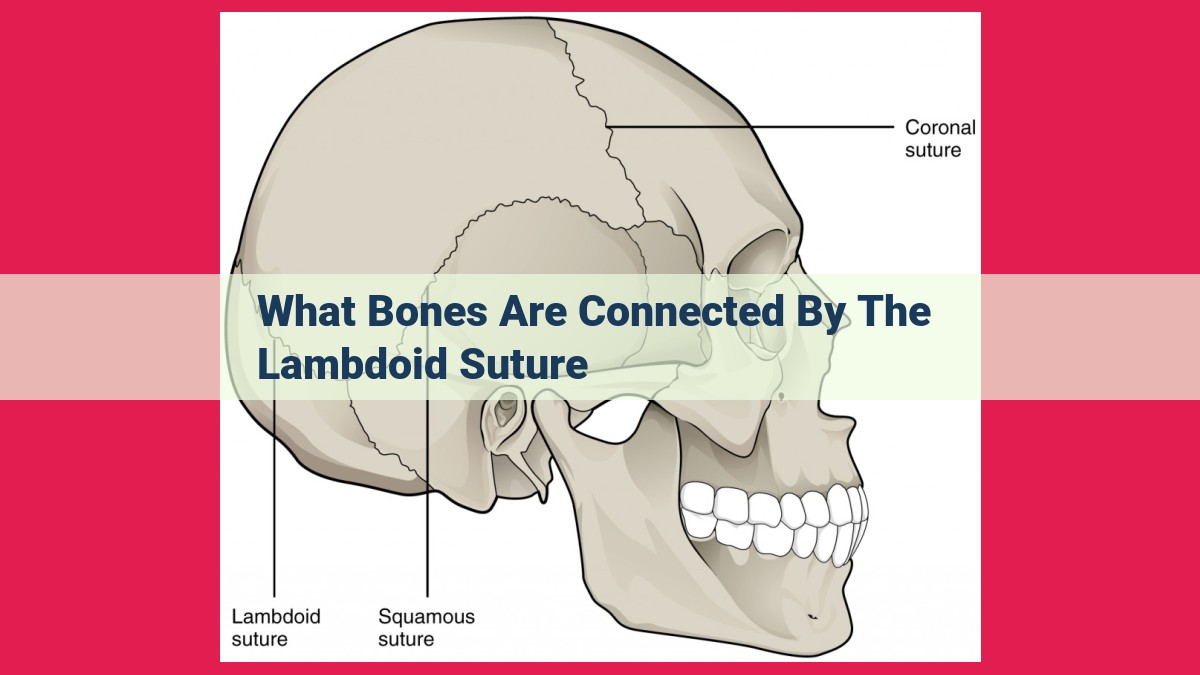
The lambdoid suture, a serrated joint located at the junction of the occipital and parietal bones, plays a pivotal role in skull anatomy. The occipital bone forms the back and part of the base of the skull, while the two symmetrical parietal bones form the cranial vault. The serrated shape of the lambdoid suture allows for slight movement and accommodates skull expansion during growth. Its unique characteristics distinguish it from other skull joints. Clinically, the lambdoid suture aids in diagnosing and treating conditions like craniosynostosis, contributing to proper skull development and head shape assessment.
- Provide an overview of the lambdoid suture, its location, and its significance in the human skull.
The human skull is a remarkable structure, providing protection and support for our delicate brain. Among the many intricate joints that hold the skull together is the lambdoid suture, a fascinating boundary that plays a vital role in our skull’s anatomy and growth. This suture, named for its resemblance to the Greek letter lambda, is located at the back of the skull, connecting the occipital bone at the base with the two parietal bones that form the upper sides of the skull.
The lambdoid suture is a serrated joint, meaning that its edges are jagged, allowing for slight movement and adjustment as the skull grows and develops. This flexibility is crucial for accommodating changes in the brain and skull during infancy and childhood, ensuring that the skull can expand and reshape as needed. The lambdoid suture also contributes to the skull’s unique shape, giving it a more rounded appearance than it would have with straight sutures.
The lambdoid suture is more than just a physical boundary; it also has clinical significance. By studying this suture, medical professionals can gain insights into various skull-related conditions. For example, premature fusion of the lambdoid suture can lead to craniosynostosis, a condition where the skull bones fuse prematurely, potentially affecting the shape of the head. Understanding the lambdoid suture can also aid in the diagnosis and treatment of skull fractures, as it can provide valuable information about the extent of the injury.
In summary, the lambdoid suture is a crucial joint in the human skull, playing a vital role in its anatomy, development, and clinical significance. Its unique shape and function make it an essential component of our skeletal system, ensuring the proper growth and protection of our brains.
Bones Intertwined: Exploring the Lambdoid Suture’s Connective Network
In the intricate tapestry of the human skull, the lambdoid suture stands as a crucial juncture, seamlessly linking the keystone bones that shape our cranial structure. This serrated seam, nestled at the skull’s posterior, plays a pivotal role in our physical development and serves as a diagnostic aid for various medical conditions.
The Occipital Bone: The Foundation of our Cranial Fortress
At the base of the skull, where the spinal cord enters our sanctuary of thought, rests the occipital bone. Like a sturdy bastion, it forms the back and a portion of the skull’s base, providing a solid foundation for our cognitive fortress. This bone, with its unmistakable contours, houses vital structures like the foramen magnum, through which our spinal cord passes, and the condyles that articulate with the vertebrae of our neck.
Parietal Bones: The Symmetrical Guardians of Our Cranial Vault
Atop the occipital bone, forming the bulk of our cranial vault, lie the parietal bones. These two symmetrical plates, mirroring each other across the skull’s midline, play a crucial role in protecting our delicate brain tissue. Their smooth outer surfaces act as a shield against external forces, while their inner surfaces provide a secure haven for the brain’s intricate circuitry.
The Lambdoid Suture: A Pivotal Joint in Your Cranial Symphony
The Lambdoid Suture: A Masterpiece of Interwoven Bones
Deep within the intricate framework of our skulls, there lies a suture that plays an undeniably pivotal role in its development and seamless functioning. Unveiling the lambdoid suture is akin to unraveling a hidden treasure, a masterpiece of interwoven bones that serves as a testament to the body’s remarkable design.
Nestled at the skull’s posterior, the lambdoid suture gracefully unites two formidable bones: the occipital and parietal. The occipital, a formidable bone at the base of the skull, safeguards the delicate structures of the brainstem. Its symmetrical counterparts, the parietal bones, form the cranial vault’s protective roof.
An Articulate Joint: Symphony of Movement and Adaptability
Unlike other immovable skull joints, the lambdoid suture possesses a unique serrated design, a symphony of interlocking ridges and grooves. This ingenious configuration permits subtle cranial movements, accommodating our dynamic growth and adapting to the skull’s ever-changing contours.
Distinctive Traits: A Landmark in the Cranial Mosaic
The lambdoid suture stands out from its osseous counterparts, exhibiting a distinct anatomy that sets it apart. Its zigzagged pattern, resembling a series of interconnected “V” shapes, allows for greater flexibility and resilience. This intricate design not only facilitates skull expansion but also serves as a landmark for neurosurgeons and forensic anthropologists.
Clinical Significance of the Lambdoid Suture: Unraveling Its Medical Importance
Beyond its anatomical intricacies, the lambdoid suture holds immense clinical significance in the diagnosis and treatment of various medical conditions.
Craniosynostosis: A Case of Premature Fusion
One of the primary clinical roles of the lambdoid suture lies in the diagnosis and management of craniosynostosis, a condition characterized by the premature fusion of one or more skull sutures. When the lambdoid suture is affected, it can lead to lambdoid synostosis, resulting in an elongated and narrow skull shape. Early detection and surgical intervention are crucial to correct the shape and prevent potential developmental issues.
Assessing Skull Fractures: A Guiding Landmark
The lambdoid suture also plays a pivotal role in assessing skull fractures. Its unique serrated edge and location make it a valuable landmark for medical professionals to identify the type and extent of skull fractures. By examining the displacement and alignment of suture edges, doctors can diagnose fractures and determine the appropriate treatment plan.
Guiding Head Shape Correction: A Path to Optimal Development
Understanding the lambdoid suture’s anatomy and function is essential in addressing head shape abnormalities. Certain conditions, such as plagiocephaly (flat head syndrome), can result from external pressures affecting the developing skull. By manipulating the lambdoid suture’s mobility, medical professionals can guide the skull back into a more symmetrical shape, ensuring proper brain development and overall well-being.