Hyaline Cartilage: Essential Joint Support, Shock Absorption, And Body Weight Bearing
Hyaline cartilage, a type of cartilage found in joints and other structures, provides essential support and shock absorption. Composed of chondrocytes and collagen fibers, its unique structure enables it to withstand compressive forces while maintaining its shape. This cartilage acts as a cushion between bones, reducing friction and protecting them from damage. It also supports the weight of the body, providing stability and preventing excessive movement.
Cartilage: The Essential Building Block of Your Body’s Movement
Invisible to the eye, yet crucial to our daily movements, cartilage is an extraordinary tissue that plays a pivotal role in our body’s ability to move and function. Imagine a symphony, where each instrument contributes a unique harmony; cartilage is the maestro that orchestrates this symphony of motion. It lines our joints, serving as a shock absorber, preventing our bones from grinding against each other with every step we take. It shapes our ears and nose, giving them their distinctive form. It even supports our intervertebral discs, allowing us to bend, twist, and reach without discomfort.
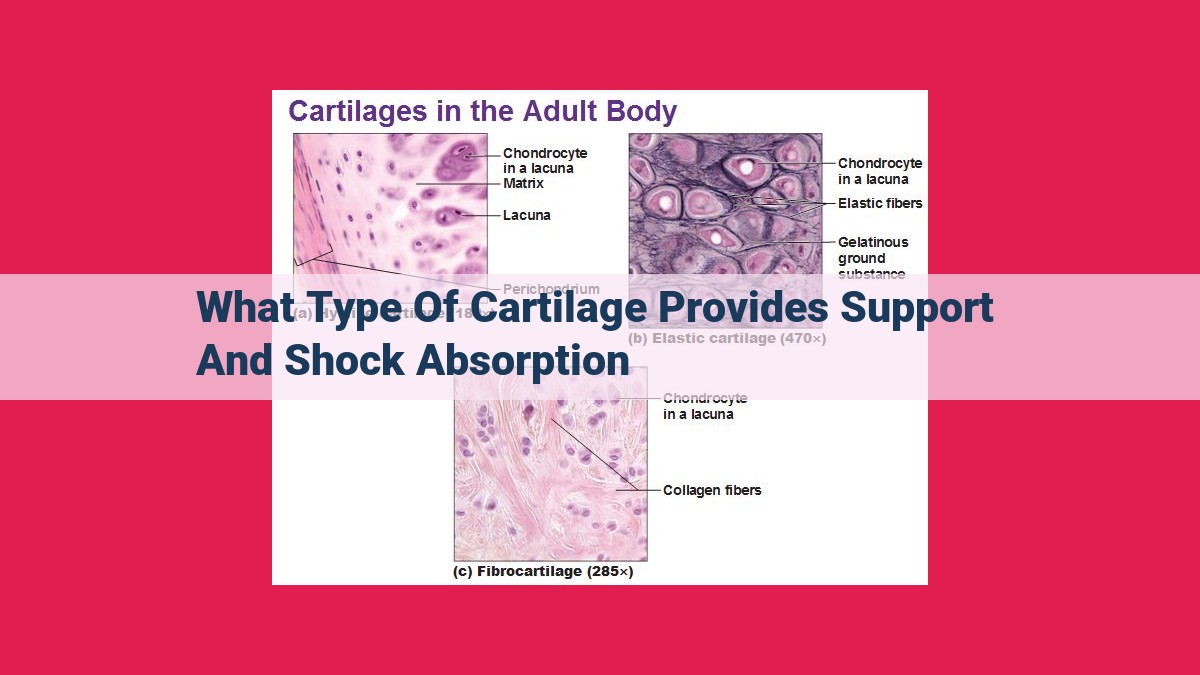
Cartilage is a resilient and versatile tissue that exists in three distinct forms: hyaline, elastic, and fibrocartilage. Each type possesses unique characteristics, tailored to specific functions within the body.
Types of Cartilage: Building Blocks of Flexibility and Support
In the intricate tapestry of our bodies, cartilage plays a pivotal role in maintaining our structural integrity and mobility. There are three primary types of cartilage, each with unique characteristics and functions: hyaline, elastic, and fibrocartilage.
Hyaline Cartilage: The Shock Absorber
Hyaline cartilage, the most prevalent type, is renowned for its glassy, smooth surface. This marvel of nature lines the joints, providing a frictionless buffer between bones and acting as a shock absorber. Its chondrocytes–specialized cells–are embedded in a dense network of collagen fibers, providing both support and cushioning.
Elastic Cartilage: The Bending Specialist
Elastic cartilage is a master of flexibility, allowing us to move with grace. Found in structures like the epiglottis and external ear, its resilience enables the bending and recoiling necessary for vital functions like swallowing and sound perception. Its secret lies in the presence of elastic fibers, which grant it flexibility and the ability to withstand repeated bending without losing shape.
Fibrocartilage: The Strong and Silent Type
Fibrocartilage is the epitome of strength and durability. Its abundance of collagen fibers endows it with exceptional toughness, making it the ideal choice for high-stress areas. It plays a crucial role in the intervertebral discs, providing cushioning and support for our spines, and in the menisci of our knees, protecting these vital structures from wear and tear.
Hyaline Cartilage: The Silent Supporter of Our Joints
Hyaline cartilage, like a silent guardian, plays a crucial role in our joint health. It silently cushions and supports our weight-bearing joints, providing the shock absorption we need for everyday activities.
Imagine hyaline cartilage as a delicate mesh of collagen fibers interwoven with chondrocytes, its specialized cells. These cells reside within small chambers called lacunae, dotted throughout the cartilage.
The unique structure of hyaline cartilage endows it with remarkable elasticity and resilience. It deforms under pressure and springs back when the force is released, making it an ideal shock absorber for our knee and hip joints.
At the articular surfaces of joints, hyaline cartilage covers the ends of bones, preventing direct bone-on-bone contact. This smooth, slippery surface allows for frictionless movement, enabling us to move with ease.
Additionally, hyaline cartilage distributes weight evenly, ensuring that the load is not concentrated on a single area of the joint. This equal weight distribution minimizes wear and tear, prolonging joint longevity.
Implications of Cartilage Damage
Despite its resilience, hyaline cartilage can be damaged through trauma, injury, or degenerative conditions. Cartilage damage can lead to pain, stiffness, and impaired joint function.
Preserving Joint Health
Maintaining healthy joints is essential for a pain-free, active life. Protecting cartilage is one of the keys to preserving joint health.
- Maintaining a healthy weight reduces stress on joints.
- Regular exercise strengthens supporting muscles and improves joint stability.
- Avoiding excessive joint use prevents overuse injuries.
- Seeking prompt medical attention for joint pain allows for early diagnosis and treatment.
By understanding the importance of hyaline cartilage and adopting protective measures, we can safeguard our joints and enjoy a lifetime of mobility.
Elastic Cartilage: The Flexible and Resilient Pillar
Cartilage, a resilient connective tissue, plays a crucial role in our body’s structural support and movement. Among the three main types of cartilage, elastic cartilage stands out for its unique flexibility and resilience.
Structure and Composition:
Unlike its stiff cousin, hyaline cartilage, elastic cartilage owes its flexibility to an intricate network of elastic fibers. These fibers, interwoven with collagen fibers, allow elastic cartilage to stretch and recoil, making it the perfect choice for structures that require both support and flexibility.
Function and Location:
This remarkable cartilage type resides in areas where flexibility and resilience are paramount. It graces the epiglottis, a small flap that prevents food from entering the windpipe during swallowing. Its presence in the external ear, where it forms the ear’s framework, allows us to wiggle our ears and hear sound waves.
In addition to these high-profile roles, elastic cartilage provides support and cushioning in other areas, including the larynx, trachea, and bronchi. Its elasticity enables these structures to withstand the constant movement and vibration associated with breathing and speaking.
Elastic cartilage is a vital component of our body’s intricate architecture, providing flexibility where necessary and ensuring the smooth functioning of essential organs. Its unique composition allows us to indulge in activities like singing, dancing, and even simply breathing without worrying about our cartilaginous structures giving way. Preserving the health of our elastic cartilage is vital for maintaining our overall mobility and well-being.
Fibrocartilage: The Unsung Hero of Structural Support
Amongst the three main cartilage types, fibrocartilage stands out as the silent guardian of high-stress zones within your body. Unlike its hyaline and elastic counterparts, fibrocartilage boasts a unique composition that sets it apart.
Imagine a dense network of collagen fibers, interwoven like a tapestry of strength. This intricate arrangement grants fibrocartilage an exceptional resilience that rivals even its more celebrated peers. But its true calling doesn’t lie in flexibility or cushioning; it’s in providing unwavering support to areas that bear the brunt of your daily wear and tear.
Take the intervertebral discs, those shock absorbers between your vertebrae. Without fibrocartilage’s robust nature, every step you took would be a jolting assault on your delicate spine. Similarly, the menisci within your knees rely on fibrocartilage to withstand the crushing forces generated by your every stride.
Every time you squat, jump, or engage in strenuous activity, fibrocartilage silently comes to the rescue. It absorbs and distributes force, protecting bones and surrounding tissues from damage. It’s the unsung hero that allows you to move freely, effortlessly, and without discomfort.
So, next time you appreciate the seamless motion of your body, spare a thought for fibrocartilage, the silent guardian that empowers your every move. It’s the unseen force that keeps you going, day after day, without a care in the world.