Henry Moseley: Revolutionizing The Periodic Table With Atomic Number Theory
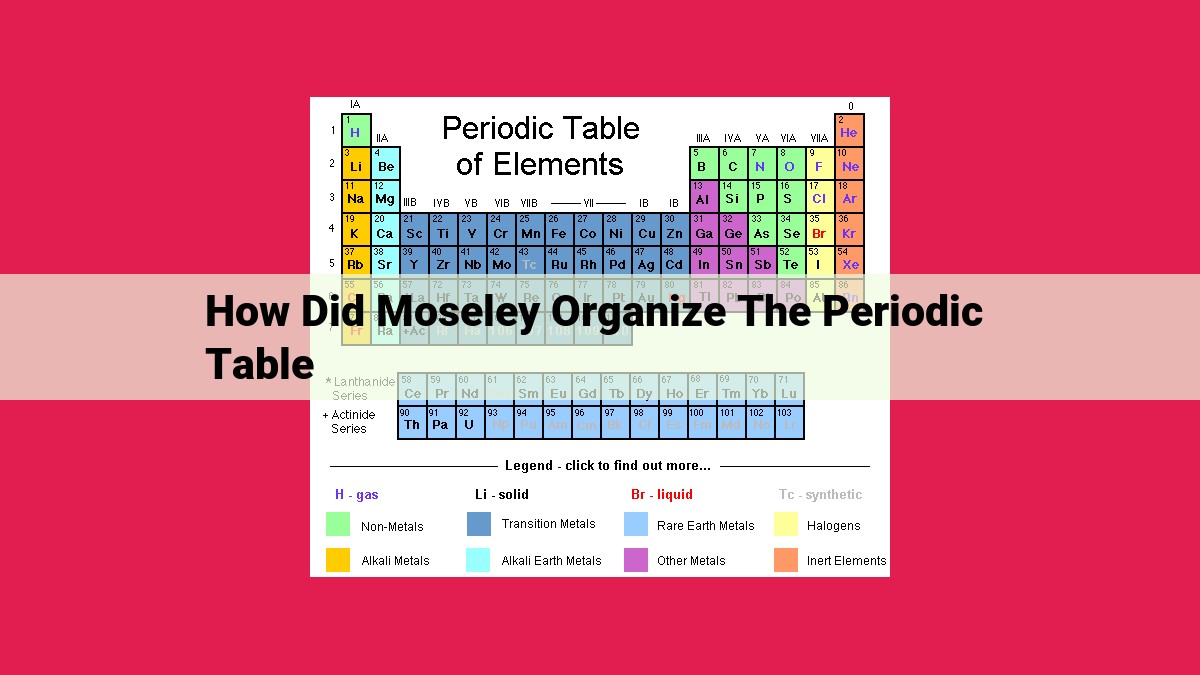
In his groundbreaking work, Moseley revolutionized the periodic table by organizing elements based on their atomic number, which he determined through X-ray spectroscopy. This approach superseded the previous method of relying on atomic mass, leading to a more accurate and consistent ordering of elements. Moseley’s discovery established atomic number as the fundamental property for organizing the periodic table, enabling scientists to better understand the structure and properties of atoms and elements.
The Atomic Number: A Fundamental Building Block
Every atom, the tiniest building block of matter, possesses a unique characteristic known as its atomic number. This number represents the number of protons, the positively charged subatomic particles, residing in the atom’s nucleus. Protons, along with electrons, the negatively charged particles orbiting the nucleus, determine an element’s overall electrical neutrality and its chemical properties.
Equally crucial is the atomic mass of an element, which reflects the mass of its protons and neutrons, the uncharged particles also found in the nucleus. Atomic mass plays a pivotal role in determining the weight of matter. The heavier an element, the greater its atomic mass. Understanding these fundamental concepts is crucial for comprehending the nature of matter and the diverse elements that compose our universe.
The Periodicity of the Periodic Table: Unraveling the Secrets of Elemental Order
In the fascinating realm of chemistry, the periodic table stands as a testament to the intricate symphony of nature’s building blocks. With its rows and columns, it offers a captivating glimpse into the hidden order that governs the elements.
Rows and Periods: A Vertical Tapestry
The periodic table is organized into horizontal rows, known as periods. Each period contains a set number of elements, ranging from 2 in the first period to 8 in the last. As we move down the table, the number of energy levels, or shells, within each atom increases. This progression influences the chemical properties of the elements.
Groups and Families: A Horizontal Hierarchy
The vertical arrangement of the table is complemented by its horizontal organization into groups, also known as families. Elements within the same group share similar chemical characteristics. This is because they have the same number of valence electrons, which are the electrons in the outermost shell.
Discovering the Pattern: A Scientific Eureka Moment
The periodic table as we know it today is the culmination of centuries of scientific inquiry. In the 19th century, Russian chemist Dmitri Mendeleev proposed an early version of the table, arranging elements based on their atomic weight. However, it was the pioneering work of English physicist Henry Moseley in the early 20th century that revolutionized our understanding.
Moseley’s use of X-ray spectroscopy revealed that the atomic number, representing the number of protons in the nucleus, was the fundamental organizing principle of the periodic table. This discovery led to the table’s modern arrangement, where elements are ordered not by weight, but by their increasing atomic number.
A Tale of Chemical Secrets
The periodic table serves as an invaluable tool for chemists and scientists alike. By understanding the periodicity of the elements, we can predict their chemical properties with remarkable accuracy. This knowledge enables us to develop materials with tailored properties, design new drugs, and explore the vast possibilities of the chemical world.
Moseley’s Revolutionary Contribution to the Periodic Table
The development of the periodic table has been a crucial milestone in our understanding of the elements. Mendeleev laid the foundation by organizing elements based on their atomic weights, creating a structure that predicted their chemical properties. However, a major limitation of his table was its reliance on atomic weight, which could not always accurately differentiate between elements.
Enter Henry Moseley, a brilliant English physicist. In the early 20th century, Moseley revolutionized the periodic table using X-ray spectroscopy. This innovative technique allowed him to determine the atomic number of each element, an essential property that refers to the number of protons in its nucleus.
Moseley’s groundbreaking discovery revealed that elements could be organized more accurately based on their atomic number, not just their atomic weight. This fundamental insight led to the restructuring of the periodic table, placing elements in a logical sequence that reflected their true chemical properties.
Moseley’s revolutionary contribution to the periodic table not only corrected Mendeleev’s limitations but also laid the groundwork for modern chemistry. His work allowed scientists to predict and understand the behavior of elements, opening doors to countless advancements in science and technology.
The Significance of the Periodic Table: A Cornerstone of Chemistry
The periodic table, a seemingly simple arrangement of elements, serves as a remarkable tool in our understanding and manipulation of the universe. Its significance lies in its ability to predict the chemical properties of elements and provide a comprehensive framework for organizing and comprehending the natural world.
Predicting Chemical Properties
The periodic table has a remarkable predictive power when it comes to understanding the chemical behavior of elements. By analyzing the position of an element within the table (row and column), scientists can deduce various properties.
The rows (periods) represent the number of energy levels in an atom, while the columns (groups) indicate the number of valence electrons. By knowing these values, chemists can predict, for instance, the oxidation states, valency, and reactivity of an element.
Categorizing and Understanding Elements
The periodic table serves as a powerful tool for categorizing the vast array of elements in the universe. Elements with similar properties are grouped together, allowing scientists to make sense of the seemingly chaotic world of chemistry.
The halogens (Group 17), for example, are highly reactive and form salts with metals, while the noble gases (Group 18) are inert and rarely participate in chemical reactions. This grouping aids in understanding the chemical behavior of different elements.
Moreover, the periodic table has greatly contributed to the discovery and development of new elements. By filling in the gaps in the table, scientists have been able to predict the existence and properties of new elements before their actual discovery.
In conclusion, the periodic table, a masterpiece of scientific exploration and ingenuity, plays a crucial role in advancing our understanding of the natural world. Through its predictive power and ability to categorize elements, it has revolutionized chemistry and serves as an indispensable tool for scientists, students, and anyone seeking to comprehend the intricacies of the universe.