Comprehensive Guide To Effective Hard Water Softening Methods
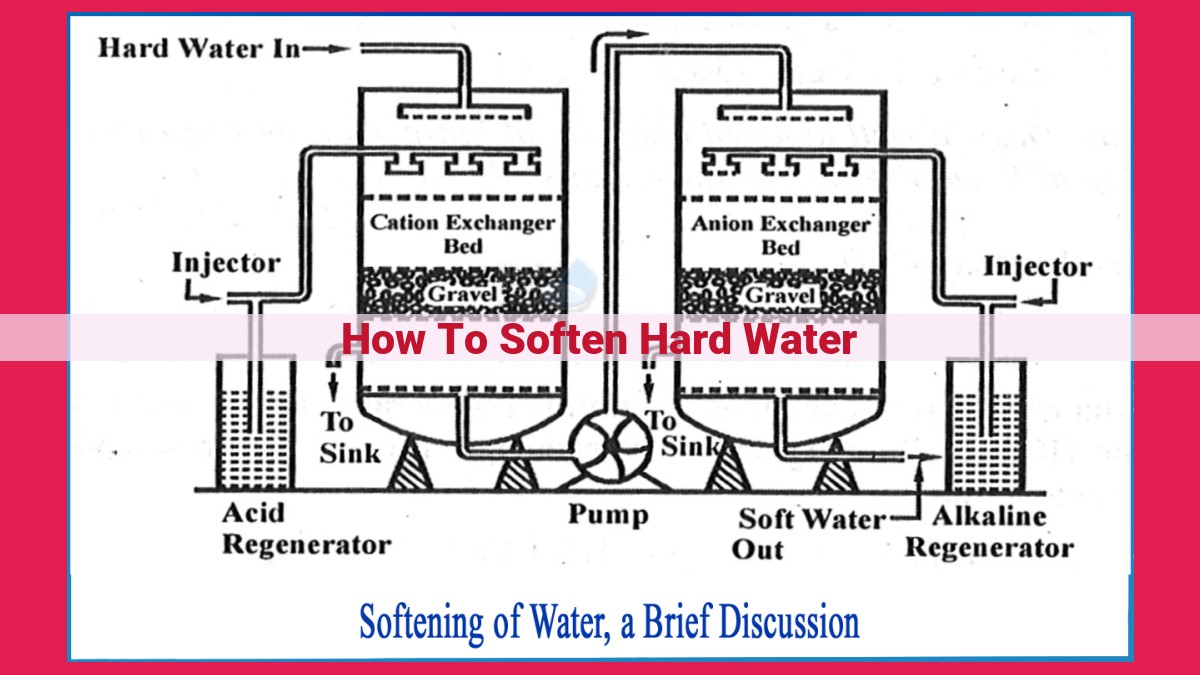
To soften hard water, various methods can be employed. Ion exchange systems remove hardness ions using resins, while reverse osmosis filters out impurities through a membrane. Distillation boils water to create pure H2O. Chemical softening involves using agents to bind hardness ions. Magnetic softening, despite claims, is scientifically ineffective. When choosing a method, consider factors like cost, maintenance, and water usage patterns. Softening hard water reduces scale buildup, improves appliance efficiency, and prolongs plumbing system life.
Understanding Water Hardness: A Comprehensive Guide
Imagine turning on your faucet and being greeted by water that leaves a sticky residue on your hands and causes your clothes to feel rough after laundering. This is the inconvenience of having hard water. Water hardness is a measure of the dissolved minerals, primarily calcium and magnesium ions, present in water. While these minerals are not harmful to health, they can wreak havoc on your home’s plumbing, appliances, and even your personal comfort. That’s why softening hard water is essential for ensuring a hassle-free and comfortable living environment.
The Causes and Effects of Water Hardness
The presence of calcium and magnesium ions in water is what makes it hard. These ions form a mineral buildup called scale that can accumulate in pipes, water heaters, and other appliances, reducing their efficiency and lifespan. Hard water can also leave unsightly stains on fixtures and dishes, and make it difficult to form a lather with soap.
The Importance of Water Softening
Softening hard water involves removing or reducing the concentration of these dissolved minerals. This process offers numerous benefits, including:
- Reduced Scale Buildup: Soft water prevents the formation of scale in pipes and appliances, ensuring optimal performance and longevity.
- Soap and Detergent Efficiency: Soft water allows soap and detergents to work more effectively, reducing the amount needed for laundry and cleaning, saving you money and reducing chemical waste.
- Improved Fixture Appearance: Eliminating scale buildup prevents stains on fixtures and surfaces, maintaining their aesthetics and ease of cleaning.
- Increased Comfort: Softened water feels smoother on skin and hair, and reduces the need for harsh soaps and conditioners.
Causes and Effects of Water Hardness
Water hardness refers to the presence of dissolved minerals, primarily calcium and magnesium ions, in water. These minerals can have significant effects on household appliances, plumbing systems, and even our health.
Calcium and Magnesium Ions
- Calcium and magnesium are essential minerals for human health, but their presence in water can cause problems.
- In very low concentrations, these ions are harmless, but as their concentration increases, they start to form scale.
Scale Formation
- Scale is a hard, crusty deposit that forms when calcium and magnesium ions react with other minerals in water and combine with carbonates and bicarbonates.
- This scale can build up inside water heaters, pipes, and fixtures, reducing their efficiency and causing premature failure.
Consequences of Scale
- Scale buildup in water heaters can reduce their heating capacity and lead to higher energy bills.
- In pipes, scale buildup can restrict water flow, causing low water pressure and even blockages.
- Scale can also clog showerheads, faucets, and other fixtures, making them less effective and more difficult to clean.
Measuring Water Hardness
- Water hardness is typically measured in parts per million (ppm) of calcium carbonate.
- There are various methods for measuring water hardness, including:
- Using a test kit
- Sending water samples to a laboratory for analysis
- Contacting your local water utility company
Understanding the causes and effects of water hardness is crucial for homeowners and businesses alike. By measuring water hardness and choosing the appropriate water softening method, you can protect your appliances, plumbing systems, and enjoy softer, more enjoyable water.
Ion Exchange: A Reliable Solution for Hard Water Woes
If you’re tired of battling with the unwelcome effects of hard water, like limescale buildup and cloudy laundry, ion exchange water softening might just be your knight in shining armor.
How Ion Exchange Works:
Imagine a team of tiny superheroes called ion exchange resins, armed with a special power: the ability to swap one type of ion for another. In the case of water softening, these superheroes target the pesky calcium and magnesium ions that make your water hard. They latch onto these ions and release sodium ions in return, effectively removing the hardness ions from the water.
Benefits of Ion Exchange Systems:
- Effective scale prevention: By eliminating calcium and magnesium ions, ion exchange systems prevent scale from forming on your pipes, water heater, and appliances, ensuring their longevity.
- Improved lather and cleaning: Soft water enhances the performance of detergents and soaps, making your laundry brighter and your dishes cleaner with less effort.
- Lower energy consumption: Scale buildup can reduce the efficiency of water heaters and dishwashers. By removing scale, ion exchange systems help these appliances run more efficiently, saving you energy costs.
- Healthier skin and hair: Hard water can irritate skin and cause hair dryness. Soft water, on the other hand, is gentler on your skin and hair, leaving you feeling refreshed and revitalized.
Limitations of Ion Exchange Systems:
While ion exchange systems are highly effective, they do have some limitations:
- Sodium addition: They add sodium ions to the water during the ion exchange process. For people on low-sodium diets, it’s important to consider the sodium intake associated with softened water.
- Maintenance: Ion exchange systems require regular regeneration with salt to keep the resins charged. This involves adding salt to the system and flushing it out to remove the accumulated hardness ions.
Related Concepts:
- Reverse Osmosis: A more comprehensive water purification process that removes not only hardness ions but also other impurities through a semi-permeable membrane.
- Chemical Softening: A method that uses chemical reactions to bind hardness ions, forming insoluble particles that can be filtered out.
Reverse Osmosis Water Softening: A Pristine Water Odyssey
In the realm of water purification, reverse osmosis reigns supreme as a champion against water hardness. This remarkable process transforms hard water into a crystalline haven, devoid of pesky impurities.
The Science Behind Reverse Osmosis:
Reverse osmosis is a technological marvel that mimics the natural process of water filtration through a semipermeable membrane. This membrane acts as a selective gatekeeper, allowing pure water molecules to pass through while trapping dissolved solids, including hardness-causing ions.
Embracing Purity and Clarity:
Reverse osmosis excels in removing hardness ions, delivering crystal-clear water that is soft to the touch. Its effectiveness extends to other impurities, including bacteria, viruses, pesticides, and heavy metals, leaving you with water as pure as the driven snow.
Advantages of Reverse Osmosis Water Softeners:
- Exceptional water purity and clarity
- Effective removal of hardness ions and other contaminants
- Versatile applications for drinking, cooking, and cleaning
Drawbacks to Consider:
- Higher cost compared to other softening methods
- Slower water flow rate due to the filtering process
- Wastewater production during the purification process
Exploring Related Concepts:
Ion Exchange: A complementary method that uses charged resins to swap hardness ions for sodium ions.
Distillation: A process that boils water and condenses the purified steam, leaving behind impurities.
Choosing Reverse Osmosis for Your Needs:
If water purity is your paramount concern and cost is a secondary consideration, reverse osmosis emerges as the unrivaled choice. Its exceptional performance ensures pristine water for your home, enhancing the taste of your beverages, safeguarding your appliances from scale buildup, and promoting healthier skin and hair.
Distillation Water Softening: A Thorough Purification Process
In the realm of water softening methods, distillation stands out as one of the most effective and purest ways to eliminate hardness minerals. Unlike other methods that merely exchange ions or mask impurities, distillation removes them altogether, producing demineralized water that is safe and free of unwanted substances.
The Distillation Process: A Journey of Purification
Distillation mimics the natural water cycle, where water evaporates, leaving behind its impurities. In a distillation system, hard water is vaporized at a high temperature. As the water vapor rises, it condenses on a cool surface, forming pure water that is collected and stored. This process effectively removes all contaminants, including calcium, magnesium, and other hardness-causing ions.
Unveiling the Benefits of Distillation for Hard Water
For homes plagued by hard water, distillation offers a comprehensive solution that transforms the quality of water in every faucet. With distilled water, you can bid farewell to scale buildup in your appliances, plumbing, and faucets. No more worries about reduced water flow, corrosion, or the unappetizing taste of hard water. Additionally, distilled water is ideal for sensitive skin, providing a gentle touch that leaves your skin feeling refreshed and revitalized.
Delving into the Suitability of Distillation Systems
While distillation is a highly effective water softening method, it’s important to consider its suitability for your specific needs and budget. Distillation systems tend to be costlier than other methods and require regular maintenance, including filter replacements. Additionally, the process of distillation can be time-consuming compared to other methods.
Related Concepts: Exploring Ion Exchange and Reverse Osmosis
Distillation shares similarities with ion exchange and reverse osmosis water softeners in terms of their ability to remove hardness minerals. However, distillation distinguishes itself by producing pure, demineralized water, while ion exchange systems exchange hardness ions and reverse osmosis systems use a semipermeable membrane for filtration. Understanding these differences will help you make an informed decision when choosing the right water softening method for your home.
Chemical Water Softening: A Path to Pure Water
Hard water, with its stubborn minerals, can wreak havoc on your pipes, appliances, and even your skin. Enter chemical water softening, a scientifically proven method to tame this water beast.
How It Works: A Chemical Bonding Adventure
Chemical water softening agents, like sodium carbonate or trisodium phosphate, magically bind with the calcium and magnesium ions that cause water hardness. These ions are then transformed into insoluble compounds, which peacefully settle at the bottom of your water tank.
Common Chemical Softening Agents
- Sodium Carbonate: A natural and eco-friendly option, sodium carbonate softens water gently.
- Trisodium Phosphate: A stronger agent, trisodium phosphate rapidly eliminates hardness ions.
- Lime Soda Ash: A cost-effective choice, lime soda ash reduces water hardness but may require additional filtration to remove sludge.
Chemical Softening and Its Allies
Ion Exchange: Chemical softening prepares water for ion exchange, a process that removes hardness ions through resin exchange.
Water Hardness: Chemical softening targets and reduces water hardness, creating softer, gentler water for your home.
Benefits of Chemical Water Softening
- Clean Pipes: Say goodbye to scale buildup that clogs and damages your pipes.
- Healthy Appliances: Prevent your appliances from prematurely aging and costly repairs.
- Smoother Skin: Shower in silky-smooth water that hydrates your skin.
Choosing the Right Chemical Agent
The ideal chemical softening agent for your home depends on your water hardness level, budget, and environmental concerns. Consult with a water treatment professional to find the perfect fit.
Chemical water softening is a powerful tool for combating hard water. It protects your home and appliances while enhancing your quality of life. By embracing chemical softening, you unlock a world of softer, purer water.
Magnetic Water Softening: A Scientific Perspective
Water hardness is a prevalent issue affecting homes across the globe, leading to scale buildup in appliances and plumbing fixtures. Magnetic water softeners claim to offer a solution by using magnets to modify water’s properties and prevent scale formation. However, scientific evidence strongly disputes these claims, revealing the inefficacy of magnetic water softeners.
Debunking Magnetic Water Softening Claims
Magnetic water softeners operate on the principle that magnets can alter the molecular structure of water, breaking down calcium and magnesium ions responsible for hardness. However, scientific studies have consistently demonstrated that magnets lack the ability to significantly affect water’s composition. Even powerful magnets fail to alter the chemical bonds between calcium and magnesium ions, rendering them incapable of preventing scale formation.
The Scientific Explanation
The chemical bonds in water molecules are highly stable, requiring substantial energy to break. Magnetic fields, even at very high strengths, are far too weak to overcome these bonds. Therefore, it is scientifically impossible for magnets to alter the molecular structure of water or influence the behavior of calcium and magnesium ions.
Evidence from Rigorous Studies
Numerous independent studies have investigated the effectiveness of magnetic water softeners. The findings consistently indicate no meaningful reduction in scale formation when using magnetic devices. In one such study, water samples treated with magnetic devices exhibited no significant difference in hardness or scale-forming potential compared to untreated samples.
Scientific evidence overwhelmingly refutes the claims made by magnetic water softener manufacturers. Magnets cannot alter the molecular structure of water or prevent scale formation. Investing in magnetic water softeners is a futile endeavor that will not provide any benefit in reducing water hardness. For effective water softening, consider proven methods such as ion exchange, reverse osmosis, or distillation.
Choosing the Right Water Softener: Factors to Consider
Deciding on the best water softener for your home can be a daunting task. With various methods available, each with its own set of advantages and disadvantages, it’s crucial to consider specific factors to make an informed choice.
Cost:
The upfront and ongoing costs of a water softener should be taken into account. Ion exchange systems generally have lower initial costs, while reverse osmosis systems may require higher investments but offer better water quality. Consider the long-term expenses, such as maintenance and filter replacements, for each method.
Maintenance:
Water softeners require regular maintenance to ensure optimal performance. Ion exchange systems necessitate occasional resin bed regeneration using salt, while reverse osmosis systems require regular filter changes. Chemical softeners may require periodic monitoring and chemical replenishment. Determine the level of maintenance you’re comfortable with and choose a system that aligns with your lifestyle.
Environmental Impact:
The environmental impact of water softeners can vary. Ion exchange systems use salt for regeneration, which may contribute to water salinity levels if not disposed of properly. Chemical softeners can introduce chemicals into the water, while reverse osmosis systems may produce wastewater. Consider the environmental impact of each method and choose a system that aligns with your values.
Local Regulations and Water Usage Patterns:
Local regulations may restrict the use of certain water softening methods. For example, distillation systems may not be suitable in areas with water restrictions. Additionally, water usage patterns can influence the choice of softener. If you have a high water usage, a larger system or more frequent regeneration may be necessary.
By carefully considering these factors, you can choose a water softener that meets your specific needs and provides you with soft, pure water for your home. Remember, the benefits of softened water extend to your appliances, plumbing systems, and your overall comfort and satisfaction.