Unlocking The Foundations Of Matter: Atoms, Molecules, And Subatomic Particles
Matter is composed of atoms, the fundamental units of elements. Each element is unique, containing atoms with a set number of protons. Atoms combine to form compounds through chemical bonding. Molecules are formed when atoms unite in specific arrangements. Subatomic particles, such as protons, neutrons, and electrons, reside within atoms. Understanding these building blocks provides a foundation for exploring the properties and interactions of matter.
The Quest for the Fundamental: Exploring the Building Blocks of Matter
Throughout human history, we have been captivated by the quest to understand the very essence of existence, from the vastness of the cosmos to the minute workings of the physical world around us. At the heart of this quest lies the exploration of the fundamental building blocks of matter, a journey that has shaped our understanding of the universe we inhabit.
Unveiling the Atom: The Heart of Matter
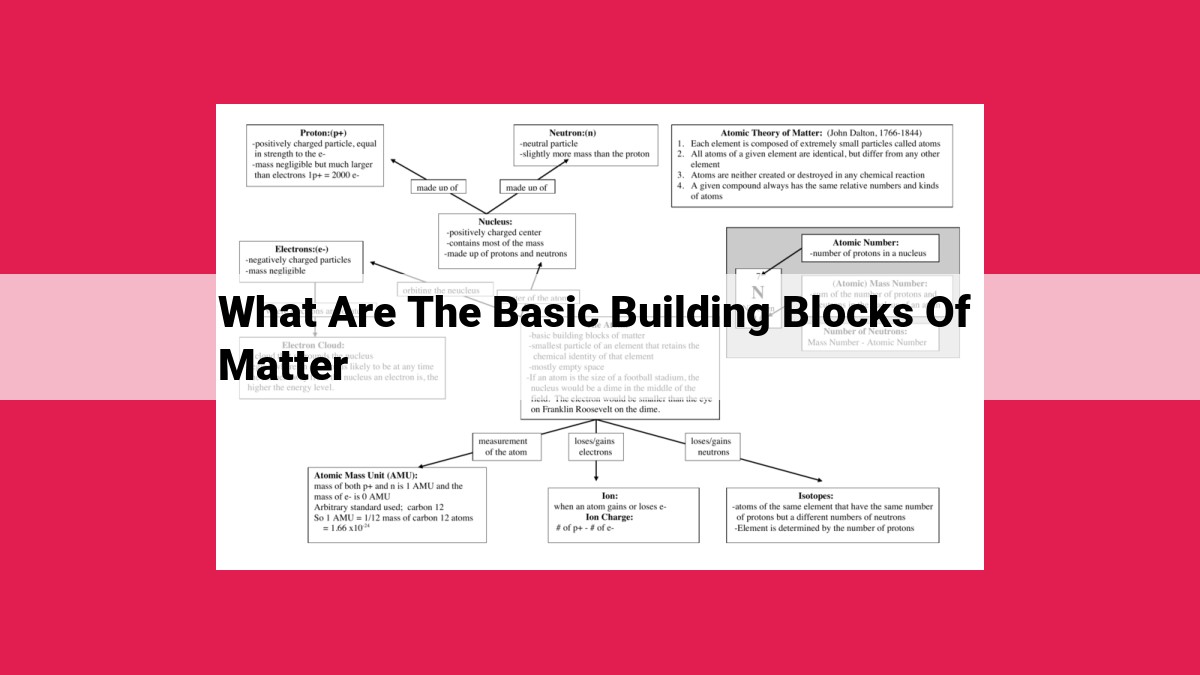
At the core of all matter lies the atom, the indivisible unit that forms the basis of all substances. Composed of a dense nucleus containing protons and neutrons, and surrounded by a cloud of whirling electrons, atoms are the smallest building blocks of matter that retain the chemical properties of an element.
Elements: The Purest Expressions
When matter consists solely of atoms of the same type, it is known as an element. Elements form the foundation of the periodic table and serve as the raw materials for all substances in the universe. From the lightest element, hydrogen, to the heaviest, oganesson, elements exhibit a diverse array of properties that give rise to the myriad forms of matter we encounter.
Compounds: When Elements Dance
When atoms of different elements combine, they form compounds. Unlike elements, compounds have distinct properties that differ from their constituent elements. Chemical bonding, the force that binds atoms together, plays a crucial role in shaping the structure and properties of compounds, allowing for an infinite variety of substances.
Molecules: Where Matter Unites
In many cases, atoms group together to form molecules, the smallest units of a compound that can exist independently. Molecules are the workhorses of chemistry, participating in countless reactions that drive the processes of life and shape the world around us. From the oxygen we breathe to the water we drink, molecules are the essential building blocks of the biological world.
Subatomic World: A Universe Within
Delving deeper into the realm of atoms, we encounter subatomic particles, the tiny denizens of the atomic nucleus. Protons, neutrons, and electrons, with their unique charges and properties, weave together the tapestry of matter. Understanding the interplay of these particles is key to unlocking the secrets of the atom and unraveling the mysteries of the physical world.
The Atom: Unraveling the Heart of Matter
Embarking on a journey into the microscopic realm, we encounter the atom, the fundamental building block of all matter. The atom is a marvel of nature, an intricate dance of subatomic particles that holds the key to understanding the very fabric of our universe.
At its core, the atom is a miniature universe. Each atom is composed of three essential components: the protons, neutrons, and electrons. Protons reside in the nucleus, the central part of the atom, and carry a positive electric charge. Neutrons, also found in the nucleus, possess no electrical charge. Orbiting around the nucleus at astonishing speeds are electrons, with their negative electric charge.
Protons and neutrons determine the unique identity of an atom, defining its atomic number and atomic mass. The atomic number represents the number of protons in the nucleus, while the atomic mass reflects the combined number of protons and neutrons. Together, these properties define the element to which the atom belongs.
Electrons, on the other hand, are responsible for the atom’s interactions with its surroundings. They dance within the electron shells, energy levels encircling the nucleus. Electrons participate in chemical reactions, forming bonds with other atoms to create molecules and compounds.
The arrangement of protons, neutrons, and electrons within the atom is a precise symphony of forces. The positive charge of protons attracts the negative charge of electrons, creating a delicate equilibrium that holds the atom together. This intricate balance is essential for the atom’s stability and determines its chemical behavior.
Understanding the atom is the cornerstone of chemistry and other scientific disciplines. It provides a gateway into the fascinating world of matter, paving the way for advancements in materials science, nuclear physics, and beyond. By unraveling the secrets of the atom, we gain a deeper appreciation for the fundamental building blocks of our existence.
Elements: The Purest Foundations of Matter
In the tapestry of matter that weaves our universe, there lie fundamental building blocks that hold the secrets to its very existence. These building blocks are known as elements, the purest forms of matter, like the vibrant hues of an artist’s palette. Each element is unique, defined by its own distinctive atomic makeup.
An element is a pure substance that cannot be broken down into simpler components by chemical means. It consists of atoms, the smallest units of matter that retain the characteristics of the element. Atoms of a particular element share an identical number of protons, the positively charged particles at its core. This atomic fingerprint distinguishes one element from another.
For instance, take hydrogen, the lightest and most abundant element in the cosmos. Every hydrogen atom carries a single proton, giving it its unique identity. Similarly, gold, the element prized for its radiance and malleability, is characterized by 79 protons in its atomic nucleus.
The purity of elements is essential for understanding the fundamental nature of matter. By studying elements, scientists can unravel the secrets of their atomic structures and predict their chemical behavior. This knowledge has led to countless technological advancements, from the creation of modern materials to the development of life-saving medicines.
As we delve deeper into the realm of elements, we uncover a vast array of properties that shape the world around us. The transition metals, such as iron and copper, possess remarkable strength and conductivity, making them indispensable for construction and electronics. Noble gases, like helium and neon, are renowned for their chemical inertness, finding applications in everything from balloons to lasers.
The purity of elements not only provides a foundation for understanding matter but also serves as a reminder of the interconnectedness of our universe. From the stars that illuminate the night sky to the minerals that form the very ground beneath our feet, elements are the building blocks upon which all life depends. Embracing the fundamental nature of elements is a gateway to unlocking the mysteries of our cosmos.
Compounds: The Fusion of Elements
In the grand tapestry of matter, where atoms dance and elements hold sway, compounds emerge as the enigmatic alchemists, transforming the properties of their constituent elements into something extraordinary. A compound is a distinct substance composed of two or more different elements chemically bonded together. This unique union gives birth to a new entity with properties that defy the limitations of its individual components.
Unlike elements, which consist solely of atoms of the same type, compounds venture beyond this simplicity. They are the result of a harmonious dance between different elements, their atoms yearning to forge bonds that create something entirely distinct. Chemical bonding is the catalyst of this transformation, the invisible force that holds atoms together and orchestrates their properties.
Among the myriad of chemical bonds, one stands out – the ionic bond. Here, atoms transfer electrons to each other, creating a magnetic attraction that binds them together. The result is a salt, a crystalline compound that often dissolves in water. Salt, the backbone of our culinary world, is a testament to the transformative power of ionic bonding.
Another prevalent bond type is the covalent bond, where atoms share electrons. This shared electron cloud, like a molecular glue, holds atoms in a covalent bond together. Covalent compounds often appear as liquids or gases at room temperature, their properties shaped by the specific elements involved.
Compounds are the building blocks of our physical world. They weave together the fabric of life, forming the molecules of proteins, carbohydrates, and the very air we breathe. From the sweet taste of sugar to the pungent aroma of garlic, the diverse properties of compounds reflect the boundless possibilities that arise when elements unite.
Molecules: The Union of Atoms
In the realm of chemistry, the dance between atoms unfolds, giving rise to the marvelous symphony of matter. Molecules, the fundamental players in this cosmic ballet, emerge as intricate unions of atoms, their properties harmoniously intertwined.
The Genesis of Molecules
Molecules are born when atoms, those indivisible building blocks of matter, join forces through chemical bonding. This enchanting process involves the sharing or transfer of electrons, resulting in the formation of covalent bonds and ionic bonds, respectively. These interatomic bonds serve as the invisible threads that seamlessly stitch atoms together, giving birth to a boundless array of molecular forms.
The Symphony of Properties
The properties of molecules, like the notes in a symphony, are a testament to the unique arrangement of their constituent atoms. Each molecule, shaped by its atomic blueprint, possesses distinct physical and chemical characteristics. Boiling point, freezing point, solubility, reactivity, and countless other properties dance to the tune of molecular composition.
For instance, water, a molecule of unrivaled importance, owes its life-giving properties to the harmonious union of two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom. This seemingly simple arrangement grants water its polarity, enabling it to dissolve a multitude of substances and become the universal solvent of life.
The Essence of Life
Molecules, the epitome of unity and diversity, orchestrate the symphony of life itself. Proteins, the workhorses of cells, are complex molecules responsible for catalyzing chemical reactions, transporting nutrients, and providing structural support. Nucleic acids, the architects of genetic information, hold the blueprint of life within their molecular chains.
A Tapestry of Matter
From the simplest molecule to the most complex, these atomic unions weave the fabric of our universe. Molecules give rise to the matter we see, touch, and experience every day. The air we breathe, the food we eat, the water we drink—all are composed of molecules, each playing its part in the intricate tapestry of our existence.
In conclusion, molecules, as the very essence of matter, stand as a testament to the power of unity. Through their unique atomic compositions and intricate bonds, they give rise to the myriad properties that shape our world. Understanding the nature of molecules is the key to unlocking the secrets of the physical and biological realms.
Subatomic Particles: Delving into the Atom’s Core
Within the realm of the atom, a world of unseen wonders unfolds. Here, at the heart of matter, tiny subatomic particles play a pivotal role in shaping the very essence of our universe. Embark on a journey of discovery as we unravel the enigmatic secrets of these fundamental building blocks.
Protons: The Positively Charged Nucleus
Imagine a tiny, densely packed sphere at the center of the atom, brimming with positive charges. These are protons, the heavyweight champions of the atomic nucleus. Their unyielding presence defines the atomic number of an element, which ultimately determines its chemical identity.
Neutrons: The Neutral Interpreters
Nestled alongside the protons, neutrons act as the conciliators of the atomic nucleus. Neutral in charge, they balance the positive influence of protons, maintaining the atom’s stability. Together, protons and neutrons form the nucleus, the dense heart of the atom.
Electrons: The Whirlwind Dance
Surrounding the nucleus like a swarm of celestial bodies, electrons dance in constant motion. These minuscule particles carry a negative electrical charge. Their perpetual dance around the nucleus defines the electron cloud, an ethereal aura that governs the atom’s chemical behavior and shapes the properties of matter.
The Symbiotic Harmony
Each subatomic particle plays a unique role in the symphony of the atom. Protons determine identity, neutrons provide stability, and electrons dictate chemistry. Together, these fundamental building blocks form the foundation of all matter, from the breath we take to the stars that shimmer in the night sky.
The Symphony of Matter: A Tapestry of Elements, Atoms, and Molecules
The microscopic world that exists beyond our naked eyes holds the key to understanding the very foundation of our universe. It is a symphony of particles, each playing a distinct role in the creation of the matter that surrounds us.
Atoms, the fundamental building blocks of matter, are composed of a nucleus containing protons and neutrons, surrounded by a cloud of electrons. These subatomic particles interact through electromagnetic forces to form a stable structure. Each element, such as hydrogen, oxygen, and carbon, is defined by the unique number of protons in its nucleus.
When atoms combine, they form compounds. The chemical bonds between atoms determine the properties of the compound. For instance, water (H2O) is composed of two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom, making it a molecule with unique characteristics.
Molecules are the building blocks of larger structures. They can be simple, like water, or complex, like proteins. The interactions between molecules govern the behavior of matter in its various states, from solid to liquid to gas.
This hierarchy of matter forms a tapestry of interconnectedness. Atoms create elements, which combine to form compounds. Compounds, in turn, form molecules. Each layer builds upon the previous one, creating a complex and dynamic universe.
Understanding this symphony of matter is fundamental to our comprehension of the world around us. It unlocks the secrets of chemistry, biology, and physics, enabling us to explore the wonders of the microscopic realm and appreciate the interconnectedness of all things.