Optimized Title:unraveling The Elemental Symphony Of Fire: Fuel, Oxygen, Heat, And Combustion
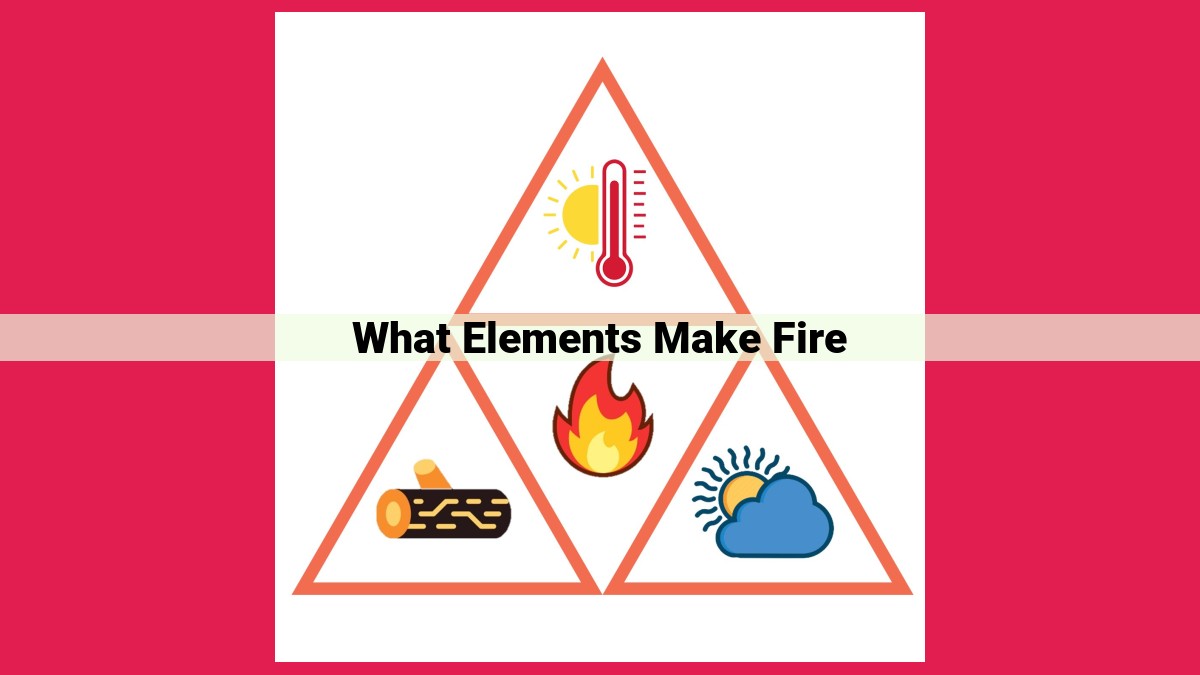
Fire, a captivating natural phenomenon, arises from a harmonious interplay of essential elements:
- Fuel, as the energy source,
- Oxygen, the vital gas that drives reactions,
- Heat, the catalyst that triggers chemical transformations.
- These elements combine through a chemical reaction, releasing heat and light.
- Combustion, a process delicately balanced by the fire triangle, underpins numerous applications that shape our everyday lives.
Fuel: The Foundation of Fire
In the realm of combustion, where flames dance and heat is unleashed, fuel stands as the cornerstone element fueling this fiery spectacle. As the lifeblood of fire, it serves as the energy source, providing the necessary sustenance for the chemical reaction that sets the world ablaze.
From the depths of the earth emerge fossil fuels, such as coal, gas, and oil, which have reigned supreme for centuries as the primary sources of energy. Their carbon-rich composition fuels combustion, unleashing vast amounts of heat to power industries and warm homes. However, the finite nature of these resources and their impact on the environment raise concerns, prompting a search for cleaner, more sustainable alternatives.
Biofuels, derived from renewable plant-based sources like sugarcane and corn, offer a more eco-friendly option. Their organic composition makes them less polluting than fossil fuels, while their ability to be replenished ensures a more sustainable future for combustion.
Renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind power, present another promising avenue for fuel. By harnessing the sun’s rays or the power of the wind, these technologies generate electricity without the need for combustion, paving the way for a cleaner, greener future.
As we continue to explore and innovate, the fuel landscape is constantly evolving, pushing the boundaries of what combustion can achieve. From the depths of the earth to the heights of the atmosphere, fuel remains the indispensable foundation upon which the transformative power of fire rests.
Oxygen: The Vital Gas for Combustion
In the intricate tapestry of combustion, oxygen plays an indispensable role. This colorless, odorless gas is the breath of life for aerobic organisms, fueling their cellular processes and sustaining the planet’s ecosystems.
Respiration’s Essential Ally
For aerobic respiration, oxygen is the sine qua non for converting glucose into energy. In the presence of this vital gas, our bodies break down complex carbohydrates into smaller molecules, releasing the energy stored within. This process powers our every movement, thought, and heartbeat.
Photosynthesis’s Catalyst
Oxygen is equally crucial for photosynthesis, the lifeblood of our planet’s plant life. Through this process, plants harness sunlight to convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose and release oxygen as a byproduct. This not only provides the planet with sustenance but also replenishes the Earth’s atmosphere with the oxygen we rely on.
Oxidation’s Energetic Reaction
Beyond its role in respiration and photosynthesis, oxygen is also central to the process of oxidation. When elements combine with oxygen, their atoms undergo a chemical reaction called oxidation, releasing energy. This energy is what fuels combustion and provides the intense heat and light associated with fire.
In short, oxygen is the vital gas that makes combustion possible, fueling life, powering ecosystems, and enabling the transformative power of fire. Its importance cannot be overstated, as it plays a fundamental role in the very fabric of our world.
Heat: The Trigger of Combustion
In the symphony of life, fire plays an enchanting melody, captivating us with its warmth and brilliance. However, beneath the mesmerizing spectacle lies a fascinating interplay of fundamental elements that orchestrate this fiery dance. Among these elements, heat emerges as the enigmatic trigger, igniting the process of combustion.
Defining Heat and Its Role in Molecular Movement
Heat, in essence, is a form of energy that manifests itself as the kinetic energy of molecules. Imagine a realm where molecules are constantly bustling about, a ceaseless dance of microscopic proportions. Heat, like a maestro, increases the tempo of this dance, causing molecules to move faster and collide more frequently. This frenetic motion is the prelude to combustion.
Laws of Thermodynamics
The laws of thermodynamics govern the behavior of heat and its transfer. The First Law of Thermodynamics declares that energy, including heat, cannot be created nor destroyed, only transformed. The Second Law of Thermodynamics asserts that heat always flows from hotter objects to colder ones, seeking a state of equilibrium.
Heat Transfer Mechanisms
Heat spreads its transformative influence through three primary mechanisms:
- Conduction: Heat directly transfers through physical contact. Like a handshake, heat passes from one molecule to another when they collide.
- Convection: In fluids (liquids and gases), heat is carried by the movement of the fluid itself. Hotter molecules rise, creating a convective current that distributes heat throughout the medium.
- Radiation: Heat can also travel through space as electromagnetic waves, akin to the warmth you feel from the sun. These waves radiate outward, heating any object they encounter.
Significance in Combustion
Heat’s role in combustion cannot be overstated. It acts as the ignition catalyst, providing the initial energy required to break the chemical bonds holding fuel molecules together. This triggers a chain reaction, releasing energy in the form of heat and light—the captivating spectacle we know as fire.
Chemical Reaction: The Heart of Combustion
In the realm of fire, chemical reactions play a crucial role, determining the very nature of this captivating phenomenon. Chemistry, the science of matter and its transformations, unravels the intricate dance of atoms and molecules as they bond and break, giving rise to the release of energy that fuels combustion.
Chemical reactions involve the rearrangement of atoms, forming new substances with distinct properties. These reactions occur when bonds between atoms are broken and new bonds are formed. Chemical equations provide a symbolic representation of these reactions, capturing the essence of the transformations taking place.
For example, in the combustion of methane, a common natural gas, the chemical equation:
CH₄ + 2O₂ → CO₂ + 2H₂O + energy
reveals the reaction between methane (CH₄) and oxygen (O₂), resulting in the formation of carbon dioxide (CO₂), water (H₂O), and the release of energy in the form of heat and light. The balanced equation ensures that the number of atoms of each element remains the same on both sides, reflecting the conservation of mass in chemical reactions.
Combustion: The Complete Process
Fire, a captivating phenomenon that has shaped civilizations, is the result of a chemical reaction that releases both heat and light. This process, known as combustion, is a fundamental element in our world, powering countless industries and providing us with warmth and energy.
The key to understanding combustion lies in the fire triangle. This concept illustrates that three essential components must be present for combustion to occur: fuel, oxygen, and heat.
Fuel, the energy source for combustion, can come in various forms, including fossil fuels, biofuels, or renewable energy sources. Oxygen, the life-giving gas, is crucial for aerobic respiration and photosynthesis. Heat, the catalyst for chemical reactions, triggers the breakdown and reformation of bonds between atoms or molecules.
When the fire triangle is complete, a chemical reaction ensues, releasing the stored energy in the fuel as heat and light. This exothermic process is the heart of combustion.
The practical applications of combustion are immense. It fuels our vehicles, generates electricity, and provides warmth for our homes. From industrial processes to everyday cooking, combustion plays a vital role in modern society.
Understanding the nuances of combustion not only enhances our appreciation for the natural world but also empowers us to harness its potential for practical applications. It is a testament to the fundamental principles that govern our universe, shaping our lives in countless ways.