Discover Derived Characters: Unveiling Evolutionary Relationships And Classification
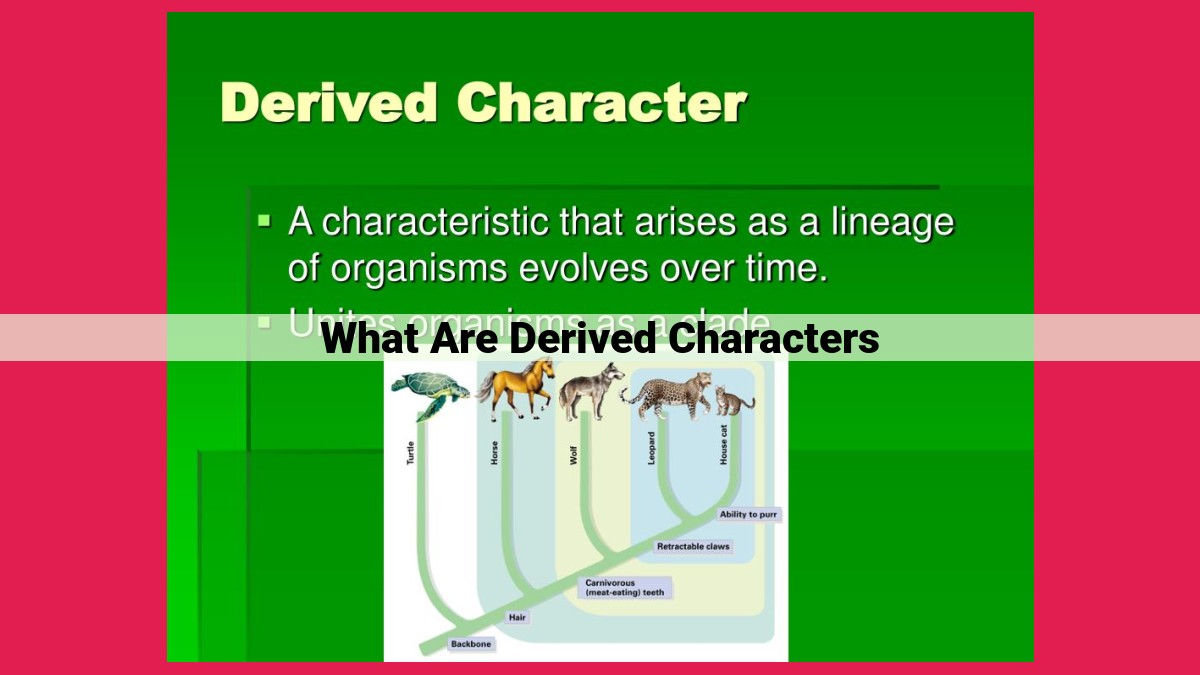
Derived characters are traits that evolved in a lineage after it diverged from its ancestors. They distinguish a group of organisms from their ancestors and are shared by all descendants of the ancestor in which they first arose. Derived characters provide evidence of evolutionary relationships, helping scientists trace evolutionary history and classify organisms. They also indicate evolutionary processes, such as adaptation and speciation. While essential for phylogenetic reconstruction, it’s important to consider ancestral characters and other evidence to avoid misinterpretations based solely on derived characters.
- Definition of derived characters and their significance in understanding evolutionary history
In the realm of evolutionary science, derived characters hold immense significance, akin to breadcrumbs leading us through the labyrinth of life’s past. These characters, traits or features acquired during the course of evolution, serve as vital clues in unraveling the intricate tapestry of our shared ancestry.
Defining Derived Characters
Derived characters are traits that distinguish a group of organisms from their ancestors. They represent novel adaptations that have evolved over time, enabling species to adapt to new environments and diversify. Unlike ancestral characters which are inherited from a common ancestor, derived characters are unique to a particular lineage.
Significance of Derived Characters
Derived characters provide indispensable insights into evolutionary history. By comparing the derived characters of different species, scientists can determine their evolutionary relationships. These characters reveal the branching patterns of the tree of life, helping us understand which species share a common ancestor and when they diverged.
Examples of Derived Characters
In birds, feathers are a striking example of a derived character. Feathers are absent in their closest living relatives, the dinosaurs, demonstrating an adaptation that has enabled birds to conquer the skies. Similarly, the absence of fur in whales, a characteristic inherited from their land-dwelling ancestors, is a derived character that reflects their aquatic lifestyle.
Essential Concepts in Understanding Derived Characters
Embarking on the evolutionary journey, we encounter a crucial concept: the derived character. It’s a distinctive trait that distinguishes species from their ancestors and provides valuable insights into their evolutionary history. To grasp the significance of derived characters, let’s explore some related concepts that illuminate their importance.
Ancestral Characters
Imagining our evolutionary tree, we encounter ancestral characters, representing traits inherited from a common ancestor. These ancestral characteristics are shared among species that descended from that ancestor, forming the foundation for understanding evolutionary relationships.
Shared Derived Characters
Delving deeper, we encounter shared derived characters: traits specifically shared by a group of species but not by their ancestors. These shared characteristics indicate a more recent common ancestor for these species, providing valuable insights into their evolutionary history.
Convergent Characters
However, not all shared traits indicate a close relationship. Convergent characters arise when unrelated species independently evolve similar traits due to adaptation to similar environmental pressures. Understanding the difference between convergent characters and shared derived characters is crucial to accurately infer evolutionary relationships.
Identifying Derived Characters: Unraveling Evolutionary Tales
In the realm of evolution, derived characters play a crucial role in illuminating the intricate tapestry of life’s history. These characters are the telltale signs of how organisms have diverged from their common ancestors, providing valuable evidence for tracing their evolutionary journeys.
Scientists employ meticulous methods and criteria to identify these insightful traits. One approach is outgroup comparison. By comparing a target organism to a closely related but more primitive species known as an outgroup, researchers can pinpoint the characters unique to the target species. These unique features are likely to be derived, having evolved after the two species diverged.
Another valuable tool is parsimony. This principle assumes that the most economical evolutionary explanation is the most likely. When comparing multiple species, scientists seek the simplest scenario that explains the observed character differences. The characters that fit this scenario are considered to be derived.
Examining embryological development can also shed light on derived characters. Structures that appear later in ontogeny (individual development) than in phylogeny (evolutionary history) are often derived. This suggests that these structures have evolved more recently.
By combining these methods, scientists can unravel the complex web of evolutionary relationships between organisms. Derived characters serve as crucial stepping stones, guiding researchers towards a deeper understanding of the history of life and the remarkable diversity that surrounds us.
The Role of Derived Characters in Unraveling Evolutionary History
Derived characters, those traits that have evolved from ancestral forms, play a pivotal role in comprehending the intricate tapestry of life’s history. Like breadcrumbs left behind on an evolutionary trail, they guide scientists in tracing the paths of ancient lineages and reconstructing the grand narrative of our planet’s biodiversity.
Evidence of Evolutionary Processes
Derived characters serve as tangible witnesses to the dynamic nature of evolution. They embody the genetic changes that have shaped species over time, providing concrete evidence of the relentless drive toward adaptation and diversification. By comparing derived characters across different organisms, scientists can infer the evolutionary processes that have given rise to their distinct forms and functions.
Tracing Evolutionary History and Identifying Closely Related Organisms
Derived characters are indispensable for mapping the branches of the evolutionary tree. Traits that are shared by different species, yet absent in their common ancestor, indicate a shared evolutionary history. These shared derived characters illuminate the splitting points between lineages, allowing scientists to reconstruct the branching patterns that have shaped the diversity of life on Earth. Furthermore, derived characters aid in identifying closely related organisms, providing insights into their genetic heritage and evolutionary affinities.
Practical Applications of Derived Characters
In the realm of evolutionary biology, derived characters hold immense significance, not only in unraveling the intricate tapestry of evolutionary history but also in aiding practical applications such as phylogenetic reconstruction and organism classification.
Phylogenetic reconstruction, a cornerstone of evolutionary science, seeks to depict the evolutionary relationships among organisms. Derived characters serve as invaluable tools in this endeavor, providing crucial evidence for constructing phylogenetic trees. These trees illustrate the branching patterns of evolutionary lineages, revealing the common ancestry and evolutionary history of different species. By comparing shared derived characters among organisms, scientists can infer their taxonomic relatedness and reconstruct the evolutionary pathways that have shaped their present-day diversity.
Taxonomists harness the power of derived characters to classify organisms into taxonomic groups. These characters act as diagnostic features, enabling researchers to differentiate between species and higher taxonomic ranks. For instance, the presence of feathers in birds, a derived character not found in their closest relatives, defines the avian group. Similarly, the possession of mammary glands is a derived character that distinguishes mammals from other vertebrates. By identifying and analyzing derived characters, taxonomists gain insights into the evolutionary history and relationships among diverse organisms.
Limitations and Considerations in Using Derived Characters
In unraveling the evolutionary history of organisms, derived characters play a crucial role. However, it’s essential to recognize their potential limitations and the need for a holistic approach to evolutionary inferences.
One challenge lies in the possibility of homoplasy, where similar traits arise independently in different lineages. This can lead to the misinterpretation of shared derived characters, especially in the absence of supporting evidence. To mitigate this, scientists employ rigorous criteria to establish true homology, considering factors such as developmental patterns and genetic evidence.
Furthermore, an overemphasis on derived characters can obscure ancestral relationships. While derived characters provide evidence of change over time, they only tell part of the story. Ancestral characters, representing primitive traits, are equally valuable in tracing evolutionary pathways and understanding the origins of shared characteristics. A balanced consideration of both ancestral and derived characters allows for a more comprehensive understanding of evolutionary history.
Additionally, it’s important to note that evolutionary patterns can be complex. Some derived characters may be more conserved than others, leading to variations in their informativeness. Moreover, relying solely on derived characters can overlook other types of evidence, such as fossil records, molecular data, and ecological adaptations. By integrating multiple lines of evidence, scientists gain a fuller picture of evolutionary processes and relationships.