Decigram To Gram Conversion: A Comprehensive Guide For Accurate Measurement
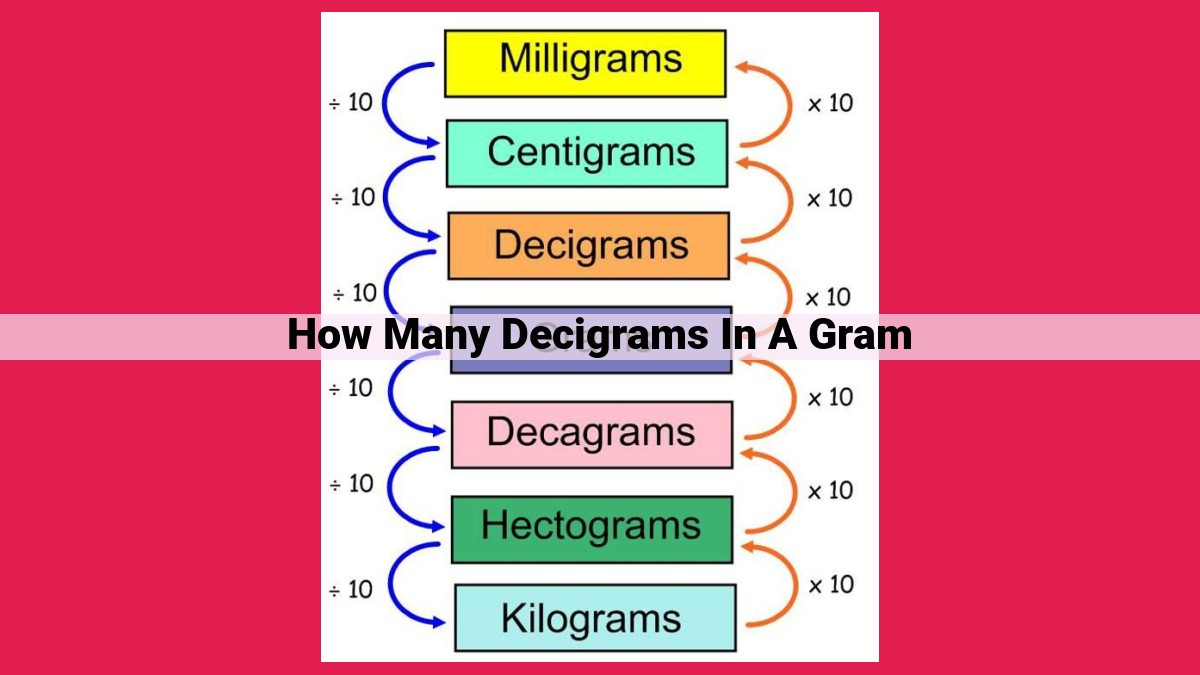
Measuring conversions are crucial in various settings like scientific experiments and everyday life. To convert decigrams (dg) to grams (g), it’s important to understand that the gram is the SI unit of mass and the decigram is defined as 1/10th of a gram. The conversion factor is 1 g = 10 dg. Therefore, to convert decigrams to grams, multiply the decigram value by 0.1 or divide by 10. Conversely, to convert grams to decigrams, multiply by 10. These conversions play a vital role in precise measurement, such as weighing small amounts or calculating quantities in different units in scientific studies.
The Intricacies of Measuring: Delving into the Conversion of Decigrams to Grams
In the realm of scientific exploration, accurate measurement holds paramount importance, underpinning countless discoveries and technological advancements. From calibrating delicate instruments to formulating life-saving medicines, the ability to convert various units of measurement is an indispensable skill. In this article, we will embark on a journey to unravel the intricacies of converting decigrams (dg) to grams (g), shedding light on the significance of this conversion in diverse settings.
Understanding the Essence of Conversion
Imagine you are designing a surgical instrument that requires precise cutting with a blade weighing a mere 10 decigrams. However, your blueprints specify the weight in grams. How do you ensure accuracy without compromising the integrity of the procedure? This is where conversion factors come to our aid. They empower us to translate measurements across different units, ensuring consistency and precision in our calculations.
Understanding the Basics: Weight, Mass, and Metric Units
In the world of measurement, understanding the distinction between weight and mass is crucial. Weight refers to the downward force acting on an object due to gravity, while mass measures the amount of matter an object contains, regardless of its location.
The metric system is a widely accepted system of measurement that includes a set of interrelated units. The gram (g) serves as the SI (International System of Units) unit of mass. It’s commonly used to measure small amounts of substances, such as ingredients in recipes or the weight of a letter.
The decigram (dg) is a smaller unit within the metric system. It is equal to one-tenth of a gram (1 dg = 0.1 g). This unit is often used in scientific experiments and for precise measurement of small quantities, such as the amount of a chemical reagent added to a reaction.
The Conversion Factor: A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding and using conversion factors is essential for precise measurement in various settings. In this section, we’ll delve into the conversion factor for grams (g) and decigrams (dg), which are commonly used units of mass in the metric system.
The conversion factor between grams and decigrams is:
1 gram (g) = 10 decigrams (dg)
This means that 1 gram is equal to 10 decigrams. Conversely, 1 decigram is equal to 0.1 grams.
Example Calculation:
To illustrate the conversion process, let’s say we want to convert 25 decigrams to grams. Using the conversion factor, we can set up the equation:
25 dg * (1 g / 10 dg) = ? g
Simplifying the calculation, we get:
25 dg = 2.5 g
Therefore, 25 decigrams is equivalent to 2.5 grams.
Additional Conversion Factors:
In addition to the gram-to-decigram conversion factor, there are other useful conversion factors in the metric system:
- 1 decigram (dg) = 0.1 grams (g)
- 1 gram (g) = 1000 milligrams (mg)
- 1 milligram (mg) = 0.001 grams (g)
These conversion factors allow us to easily convert between different units of mass and ensure accurate measurements.
Practical Applications of Decigram-to-Gram Conversions
Conversion factors, like the one that connects decigrams to grams, play a critical role in the world of science and everyday life. They enable us to work with different units seamlessly, ensuring accurate and consistent measurements.
In the realm of scientific experiments, conversion factors are indispensable. Imagine a chemist needing to calculate the mass of a substance in grams. They have it measured in decigrams, so they simply multiply the decigram value by 0.1 (or divide by 10) to obtain the gram equivalent. This conversion allows them to compare results across studies that may use different units.
Beyond the laboratory, decigram-to-gram conversions are also essential in various practical scenarios. For instance, suppose a baker wants to precisely weigh small amounts of ingredients in a recipe. They may need to convert a few decigrams of flour to grams for an accurate measurement. Knowing that 1 dg = 0.1 g makes the conversion quick and effortless, ensuring their baking creation turns out as intended.
The versatility of conversion factors extends to other areas as well. In the medical field, converting decigrams to grams helps ensure accurate medication dosing. Similarly, in environmental science, scientists use conversion factors to calculate the mass of pollutants in water samples or soil samples, enabling them to assess environmental impact.
By understanding these conversion factors and how to apply them effectively, we empower ourselves to navigate the world of measurement with greater accuracy and precision. They allow us to ensure consistency across different fields and situations, ultimately contributing to better decision-making and outcomes in science, industry, and everyday life.