Convert Joules To Electron Volts (Ev) And Vice Versa: A Guide For Particle And Atomic Physics
To convert joules to electron volts (eV), multiply the joule value by the conversion factor 6.242 x 10^18. The formula is: eV = joules x (6.242 x 10^18 eV/J). Conversely, to convert eV to joules, divide the eV value by the same conversion factor. This conversion is commonly used in particle physics and atomic physics, where energies are often expressed in eV.
Understanding Units of Energy
- Define joules and electron volts as units of energy.
- Explain the significance of these units in their respective fields.
Understanding Units of Energy: Joules and Electron Volts
In the vast expanse of science, energy reigns supreme as the fundamental player. To measure and comprehend this enigmatic quantity, scientists have devised a lexicon of units, each tailored to a specific domain. Among these units, two stand out: the joule and the electron volt.
The joule (J), named after the esteemed physicist James Prescott Joule, is the SI unit of energy. It is defined as the energy transferred or work done when a force of one newton (N) is applied over a distance of one meter (m). Joules are widely used in fields such as physics and engineering to quantify various energy forms, including mechanical, electrical, and thermal.
On the other hand, the electron volt (eV) is an energy unit specifically employed in the context of atomic and subatomic physics. One electron volt represents the energy gained or lost by an electron when it moves through a potential difference of one volt. This unit is particularly useful when dealing with phenomena involving electron interactions, such as in the study of quantum mechanics and particle physics.
Conversion Factors: The Bridge Between Units
- Introduce the conversion factors between joules and electron volts.
- Provide the exact numerical values of these factors.
Conversion Factors: The Bridge Between Units
When dealing with the vast world of energy, scientists and engineers encounter a myriad of units, each measuring a different aspect of this fundamental quantity. Two prominent units are joules and electron volts (eV). Understanding the conversion factors between these units is crucial for bridging the gap between different fields of study and practical applications.
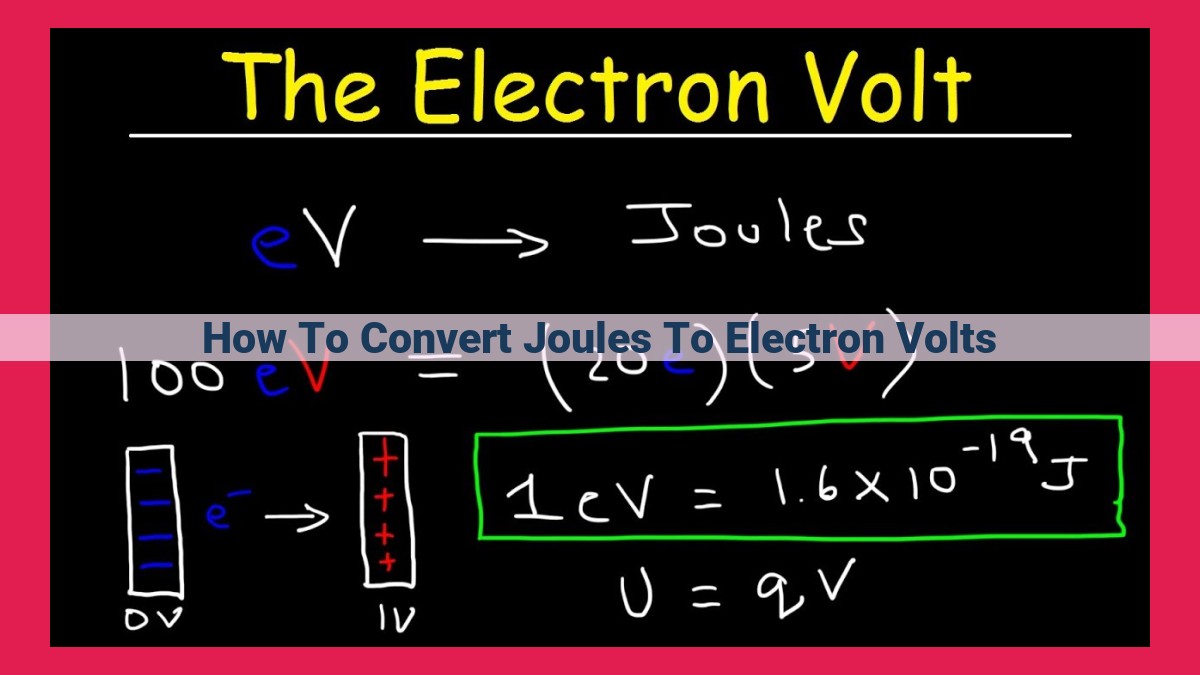
The conversion factor between joules and electron volts is a numerical value that allows us to translate energy values expressed in one unit to the other. The exact numerical value of the conversion factor is 1 electron volt = 1.602176634 × 10^-19 joules.
In simpler terms, 1 eV is equivalent to an extremely tiny amount of energy, approximately 1.6 × 10^-19 joules. This minuscule unit is particularly useful in describing the energy of subatomic particles, such as electrons, photons, and atoms. On the other hand, joules are commonly used in macroscopic systems, such as electrical appliances, mechanical work, and thermal energy.
By employing these conversion factors, scientists can seamlessly translate energy values across different scales and contexts. For instance, an electrical engineer designing a circuit may need to convert electron volts of energy stored in a capacitor to joules of energy dissipated as heat. Similarly, a physicist studying nuclear reactions may need to convert electron volts of energy released in a particular reaction to joules of energy in order to calculate its impact.
Formulas: Unlocking the Conversion Secrets
In the realm of energy calculations, understanding the conversion between joules and electron volts is paramount. These units play pivotal roles in their respective fields, enabling scientists and engineers to accurately measure and quantify energy. To facilitate this conversion, we rely on mathematical formulas that bridge the gap between these units.
Formula for Converting Joules to Electron Volts (eV)
1 eV = 1.602176634 × 10^-19 J
This formula tells us that 1 electron volt is equivalent to 1.602176634 × 10^-19 joules. It means that an electron volt represents a much smaller amount of energy compared to a joule.
Formula for Converting Electron Volts to Joules (J)
1 J = 6.241509 × 10^18 eV
Conversely, this formula reveals that 1 joule is equivalent to 6.241509 × 10^18 electron volts. This indicates that a joule represents a significantly larger amount of energy compared to an electron volt.
Using the Formulas in Practice
To convert between joules and electron volts using these formulas, simply plug the known value into the equation and solve for the unknown. For example, to convert 5 joules to electron volts:
5 J × (1 eV / 1.602176634 × 10^-19 J) = 3.116 × 10^19 eV
Similarly, to convert 2 × 10^15 electron volts to joules:
2 × 10^15 eV × (1 J / 6.241509 × 10^18 eV) = 0.3204 J
These formulas are essential tools for scientists and engineers working with energy measurements across various disciplines.
Example Calculations: Putting the Conversion into Practice
To solidify our understanding of the conversion process between joules and electron volts, let’s dive into some practical examples. These step-by-step calculations will illuminate the formulas and provide a clear understanding of how to bridge units seamlessly.
Joules to Electron Volts
Consider a scenario where you have an energy measurement of 50 joules. To convert this value into electron volts, we’ll utilize the conversion factor: 1 electron volt (eV) = 1.602 × 10-19 joules (J).
-
Multiply the joule value by the conversion factor:
50 J × (1 eV / 1.602 × 10<sup>-19</sup> J) -
Calculate the result:
≈ 3.12 × 10<sup>20</sup> eV
Therefore, 50 joules is approximately equivalent to 3.12 × 1020 electron volts.
Electron Volts to Joules
Now, let’s reverse the conversion and convert 2.5 × 1021 electron volts back to joules:
-
Multiply the electron volt value by the conversion factor:
2.5 × 10<sup>21</sup> eV × (1.602 × 10<sup>-19</sup> J / 1 eV) -
Calculate the result:
≈ 4 × 10<sup>2</sup> J
Thus, 2.5 × 1021 electron volts corresponds to approximately 4 × 102 joules.
Applications: Where the Conversions Matter
In the realm of science and engineering, the conversion between joules and electron volts (eV) plays a pivotal role in various fields. Let’s delve into some practical applications where these conversions bridge the gap between different disciplines.
Physics and Quantum Mechanics:
In the realm of quantum mechanics, the eV is the preferred unit for measuring energy of particles. For instance, the energy of an electron in an atom is typically expressed in electron volts. Converting electron volts to joules allows scientists to compare the energy of electrons with other forms of energy, such as the kinetic energy of a moving object.
Materials Science:
Materials scientists utilize eV to describe the energy band gaps of semiconductors and insulators. The energy band gap represents the energy difference between the valence band and the conduction band. Converting eV to joules enables the comparison of energy band gaps with other material properties, such as electrical conductivity.
Biochemistry:
In the field of biochemistry, eV plays a crucial role in understanding the energy metabolism of biological systems. The energy released during cellular respiration, for example, is often expressed in electron volts. Converting eV to joules allows scientists to quantify the efficiency of energy production in living organisms.
Nuclear Physics:
Nuclear physicists use eV to measure the energy released in nuclear reactions. The binding energy of atomic nuclei, for instance, is typically expressed in eV. Converting eV to joules allows scientists to compare the energy released in nuclear reactions with other forms of energy, such as the energy produced by burning fossil fuels.
Understanding the conversions between joules and eV is indispensable for scientists and engineers working across various disciplines. These conversions provide a common language for describing energy, enabling the comparison and exchange of knowledge across different fields.
Cautions and Considerations When Converting Energy Units
Although converting between joules and electron volts is straightforward, there are a few crucial considerations to keep in mind:
1. Accuracy of Conversion Factors:
It’s essential to use the accurate and up-to-date conversion factors. Using outdated or incorrect conversion factors can lead to erroneous results. Check reputable sources, such as scientific databases or textbooks, to obtain the most recent values.
2. Units and Consistency:
When making unit conversions, it’s crucial to pay close attention to the units of measurement. Ensure that you’re converting between the correct units (joules to electron volts or vice versa). Mixing up units can result in incorrect calculations.
3. Rounding and Precision:
Conversions may sometimes involve rounding or truncating numbers. It’s important to consider the precision required for your calculations. Rounding too much or too little can affect the accuracy of your results.
4. Limitations of Conversion Factors:
Conversion factors are only valid within certain ranges. For example, the conversion between joules and electron volts is based on the assumption that the electron’s rest energy is negligible. This assumption may not hold true in high-energy physics, leading to potential inaccuracies.
5. Context-Dependent Interpretations:
Depending on the specific application, energy units can have context-dependent interpretations. For instance, in thermodynamics, the joule represents macroscopic energy, while in quantum mechanics, the electron volt represents microscopic energy. Understanding the context of your calculations is crucial for interpreting the results correctly.
By adhering to these cautions and considerations, you can ensure the accuracy and reliability of your energy unit conversions.
Navigating the Realm of Energy Units: A Comprehensive Guide to Joules and Electron Volts
In the realm of energy, understanding the units of measurement is crucial for precise communication and accurate calculations. Among the diverse units employed, joules and electron volts stand out as pivotal players in their respective fields. This guide will embark on an enlightening journey, illuminating the significance of these units and providing the necessary tools to navigate the conversion between them.
Unveiling the Essence of Units
Joules, named after the renowned physicist James Prescott Joule, constitute the SI unit of energy. They quantify the work done or energy transferred in various physical processes. On the other hand, electron volts, abbreviated as eV, hold immense significance in the realm of atomic and subatomic physics. They measure the energy of electrons in atomic transitions, providing insights into the behavior of matter at the most fundamental levels.
The Conversion Bridge: Joules and Electron Volts
Interconverting between joules and electron volts is essential for a comprehensive understanding of energy across different scales. The conversion factor between these units acts as a bridge, enabling seamless transitions. One electron volt is numerically equal to 1.602176634 × 10^-19 joules, providing a precise means of converting between the two units.
Mathematical Mastery: The Conversion Formulas
Mathematical formulas provide a systematic approach to energy unit conversions. To convert joules to electron volts, simply divide the energy value in joules by the conversion factor (1.602176634 × 10^-19 joules/eV). Conversely, to convert electron volts to joules, multiply the energy value in electron volts by the conversion factor.
Illustrative Examples: Putting Theory into Practice
Let’s delve into some real-world examples to solidify our understanding. Suppose we have an electron with an energy of 10 eV. To convert this to joules, we divide 10 eV by the conversion factor: (10 eV) / (1.602176634 × 10^-19 joules/eV) = 1.602176634 × 10^-18 joules.
Applications: The Practical Significance
Converting between joules and electron volts transcends theoretical exercises. It finds practical applications in diverse fields, including particle physics, material science, and nuclear chemistry. For instance, in particle accelerators, the energy of charged particles is often expressed in electron volts, while the energy consumption of the accelerators themselves is measured in joules.
Cautions and Considerations: Navigating the Pitfalls
Precision is paramount when dealing with energy unit conversions. Always ensure that the correct conversion factor is used, paying meticulous attention to the units involved. Careless mistakes can lead to inaccurate results and potentially misleading interpretations.
Venturing Beyond: Additional Resources for the Curious
This article provides a solid foundation for understanding joules and electron volts. However, for those seeking to delve deeper, numerous online resources and scientific articles offer comprehensive insights. Links to these resources will be provided for your convenience, encouraging further exploration and a deeper understanding of energy units and conversions.