Concentric Lamellar Bone: A Comprehensive Guide To Its Structure And Significance
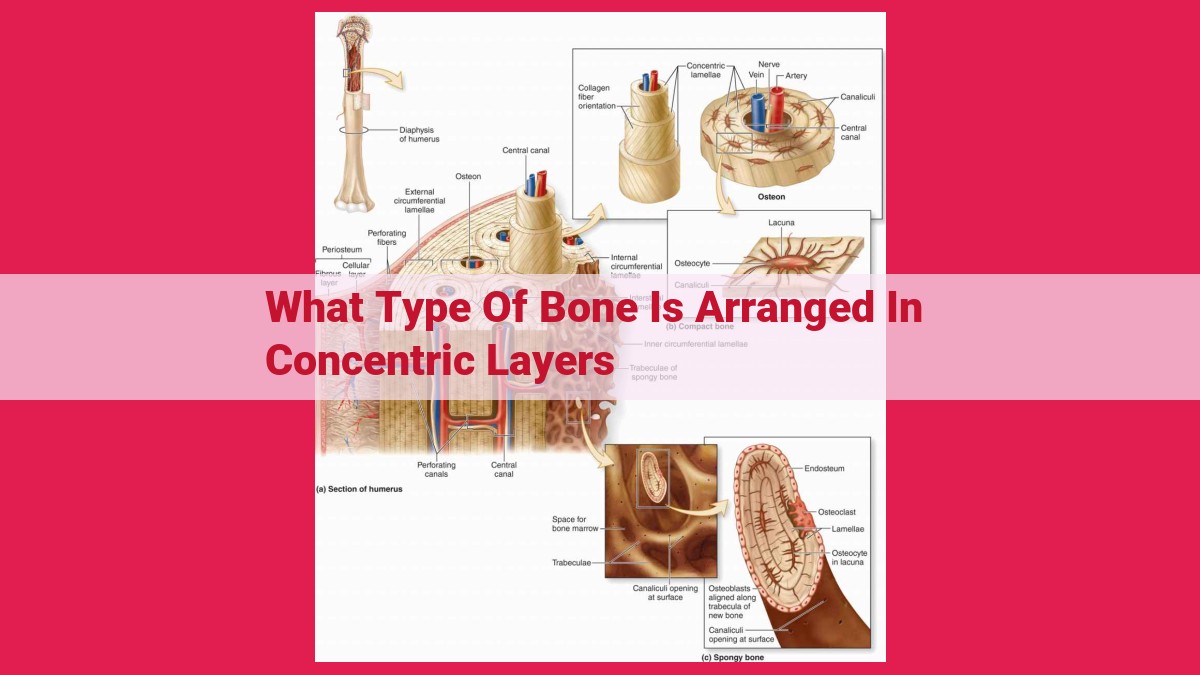
Concentric Lamellar Bone is a type of bone characterized by its arrangement of bone cells and matrix in concentric circles. It is found in the compact bone, which is the dense and solid outer layer of bone that provides strength and rigidity to the skeleton. The concentric arrangement of bone cells and matrix allows for greater resistance to twisting and bending forces, making it well-suited for load-bearing regions.
Concentric Lamellar Bone: The Building Block of Strong and Healthy Bones
At the heart of our skeletal system lies a remarkable tissue called concentric lamellar bone. Imagine it as a symphony of tiny building blocks, meticulously arranged in concentric circles, forming a strong and resilient foundation for our bodies.
Concentric lamellar bone is characterized by its unique layered structure. Like the rings of a tree, bone cells are neatly organized in concentric circles, creating an intricate mosaic. These specialized cells, called osteocytes, are embedded within a mineralized matrix, forming a dense and compact tissue.
Interconnecting channels called canaliculi crisscross through the bone, ensuring efficient communication and nutrient exchange between the osteocytes. These channels provide a lifeline to the living cells within the bone, allowing them to maintain their vital functions.
Concentric lamellar bone is often associated with Haversian bone and compact bone, two other important bone types. Haversian bone is organized into structural units known as osteons, where concentric lamellar bone forms the core. Compact bone, as its name suggests, is dense and solid, providing strength and rigidity to the skeleton.
Haversian Bone: Unraveling the Intricate Architecture of Compact Bone
As we embark on a journey into the fascinating world of bones, let’s delve into the enigmatic structure of Haversian bone, a fundamental component of our sturdy skeletal framework.
Picture an intricate mosaic of concentric circles, each meticulously arranged around a central artery and vein. This mesmerizing pattern, known as an osteon, is the building block of Haversian bone. Within each osteon, bone cells (osteocytes) reside in tiny chambers connected by an intricate network of canals known as canaliculi.
The Haversian canal, the heartbeat of each osteon, provides a vital passage for blood vessels and nerves. While Haversian canals run lengthwise along the bone, Volkmann’s canals intersect them perpendicularly, ensuring the smooth flow of nutrients and waste throughout the bone matrix.
Haversian bone, characterized by its remarkable strength and rigidity, forms the dense outer layer of our bones. This robust structure protects our vital organs, supports our body weight, and enables efficient movement. It stands as a testament to the intricate design of our skeletal system, ensuring our mobility and longevity.
Compact Bone: The Unsung Hero of Bone Strength and Rigidity
Every time you flex your muscles, your bones work tirelessly behind the scenes to support your every move. Among the two main types of bone tissues, compact bone plays a pivotal role in providing strength and rigidity to your skeletal system.
Compact bone, also known as cortical bone, constitutes the dense outer layer of your bones. It’s made up of concentric layers of bone cells and matrix arranged in a tightly packed fashion, creating a solid and impenetrable structure. This unique arrangement gives compact bone its exceptional strength, allowing it to withstand significant forces without bending or breaking.
Compact bone is strategically located in the outermost regions of your bones, forming the shaft of long bones and the outer layer of flat and irregular bones. Its presence ensures the structural integrity of your skeleton, enabling you to move, lift, and carry out your daily activities without compromising bone health.
In addition to its strength, compact bone also plays a vital role in rigidity. It prevents bones from bending or warping under stress, maintaining the shape and alignment of your skeletal system. This property is crucial for supporting your weight, protecting internal organs, and facilitating movement.
So, next time you marvel at the strength and stability of your bones, remember the unsung hero behind it all – compact bone. This dense, intricately structured tissue forms the foundation of your skeletal system, providing the strength and rigidity that allow you to live an active and fulfilling life.