Calculate Millimoles With Ease: A Comprehensive Guide

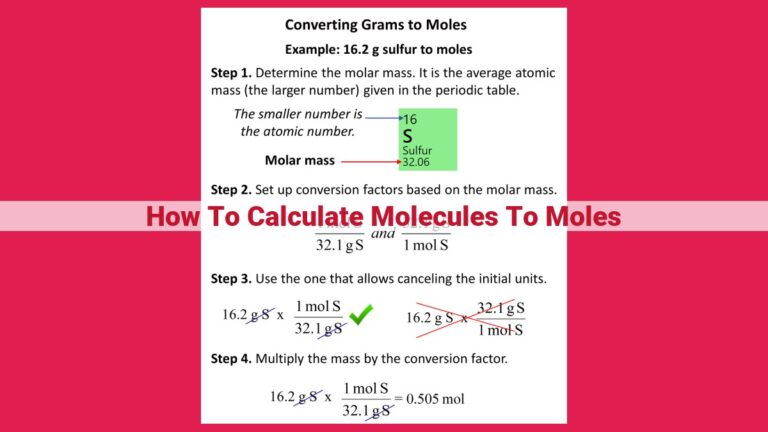
To find millimoles, first determine the mass of the substance in grams and the molar mass. Millimoles are calculated using the formula: millimoles = mass (in grams) / molar mass (in grams per mole). For example, to find the millimoles of NaCl, divide the mass of NaCl (in grams) by the molar mass of NaCl (58.44 g/mol). Millimoles are used in chemistry to determine concentrations, quantities, and reaction stoichiometry.
Define millimoles and explain their significance in chemistry.
Understanding Millimoles: The Cornerstone of Chemistry
In the vast tapestry of chemistry, millimoles serve as the fundamental building blocks that facilitate our understanding of chemical interactions. They represent the quantity of a substance in terms of the number of moles, providing insights into the molecular makeup of matter.
The Significance of Millimoles in Chemistry
Millimoles play a crucial role in chemistry due to their versatility and applicability. They allow scientists to:
- Determine the concentration of solutions, which is essential for understanding chemical reactions and their rate of occurrence.
- Calculate the quantity of reactants and products involved in chemical reactions, ensuring accurate stoichiometry.
- Determine the molar mass of substances, which provides information about their molecular weight and chemical composition.
- Understand the behavior of substances in various chemical and biological processes.
By comprehending the significance of millimoles, we unlock the gateway to unraveling the mysteries of chemical interactions and unlocking the secrets held within the molecular world.
How to Find Millimoles: A Comprehensive Guide
When it comes to understanding chemical reactions and concentrations, millimoles play a crucial role. In this blog post, we’ll dive into the world of millimoles and guide you through a step-by-step process of calculating them.
Understanding Millimoles
Millimoles are units of measurement that express the amount of substance. They’re closely related to moles, which represent the number of atoms or molecules in a given sample. However, millimoles are a smaller unit, with 1 millimole (mmol) equaling 0.001 moles.
In chemistry, millimoles are particularly useful for measuring concentrations. The concentration of a solution indicates how much of a substance is dissolved in a solvent. It’s typically expressed in units of moles per liter (M) or millimoles per liter (mM).
Calculating Millimoles
To calculate millimoles, we need two key pieces of information:
- Mass of Substance: The mass of the substance you’re interested in, usually measured in grams.
- Molar Mass: The mass of one mole of the substance, expressed in grams per mole.
Once you have these two values, you can use the following formula:
Millimoles = Mass of Substance (g) / Molar Mass (g/mol)
Determining Mass of Substance
The mass of a substance can be measured using a variety of techniques, such as weighing with a balance or measuring volume and density. If the substance is in a liquid or gas form, you’ll need to convert its volume or weight to grams.
Finding Molar Mass
The molar mass of a substance is a characteristic property that can be found in reference books or online databases. It represents the mass of one mole of that substance. Molar mass is typically expressed in grams per mole (g/mol).
Steps to Find Millimoles
Now that we have all the necessary information, let’s go through the steps to calculate millimoles:
- Convert the mass of substance to grams, if necessary.
- Find the molar mass of the substance.
- Substitute the mass of substance and molar mass into the formula:
Millimoles = Mass of Substance (g) / Molar Mass (g/mol)
Example Calculation
Let’s say we want to calculate the millimoles of sodium chloride (NaCl) in 10 grams of NaCl. The molar mass of NaCl is 58.44 g/mol.
Millimoles = 10 g / 58.44 g/mol = 0.171 mmol
Applications of Millimole Calculations
Millimole calculations are essential in various fields, including chemistry, biology, and medicine. They’re used to:
- Determine the concentration of solutions
- Calculate the quantities of reactants and products in chemical reactions
- Understand the stoichiometry of reactions
- Analyze biochemical processes in living organisms
How to Find Millimoles: A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding Millimoles
In the world of chemistry, understanding millimoles is crucial. They represent the amount of substance present in a sample, allowing chemists to quantify and compare chemical reactions. To calculate millimoles, we need to delve into the realm of moles, concentration, and molarity.
Calculating Millimoles
The fundamental formula for calculating millimoles is:
Millimoles (mmol) = Mass (g) / Molar Mass (g/mol)
Two key factors are involved in this formula: the mass of the substance and its molar mass. Molar mass is the mass of one mole of the substance and is expressed in grams per mole (g/mol).
Determining Mass of Substance
Mass can be expressed in various units, including weight, volume, and density. For millimole calculations, we typically use grams. If you have a mass measurement in a different unit, you’ll need to convert it to grams using appropriate conversion factors.
Finding Molar Mass
Molar mass is a characteristic property of each substance. It can be found in reference tables or calculated from the molecular weight of the substance. Molecular weight is the sum of the atomic weights of all the atoms in a molecule.
Steps to Find Millimoles
- Determine the mass of the substance in grams.
- Find the molar mass of the substance in grams per mole.
- Substitute the values into the formula: Millimoles (mmol) = Mass (g) / Molar Mass (g/mol).
- Calculate the millimoles present in the sample.
Example Calculation
Let’s say we have 25 grams of sodium chloride (NaCl). What is the number of millimoles of NaCl present?
- Molar mass of NaCl: 58.44 g/mol
- Substitution: Millimoles = 25 g / 58.44 g/mol
- Result: 0.428 mmol of NaCl
Applications of Millimole Calculations
Millimole calculations are instrumental in various fields, including chemistry, biology, and medicine. They are used to:
- Determine the concentration of substances in solutions.
- Calculate quantities of reactants and products in chemical reactions.
- Understand the stoichiometry of biochemical pathways.
- Make dilutions and calibrations in laboratory settings.
Understanding Millimoles and Their Importance
In the realm of chemistry, millimoles (mmol) are like the puzzle pieces that help us quantify and understand the behavior of substances. They provide insights into the numbers of molecules or ions present, which is crucial for various chemical processes and applications.
Calculating Millimoles: A Journey to the Molecular World
To determine the millimoles of a substance, you need two essential factors: the mass of the substance (measured in grams) and its molar mass (expressed in grams per mole).
Mass of the Substance:
The mass can be measured using a balance. Different units of mass exist, such as kilograms (kg) or milligrams (mg). If the mass is not in grams, convert it using the appropriate conversion factors.
Molar Mass:
The molar mass represents the mass of one mole of a substance. It is determined by adding the atomic masses of all the atoms in the molecular formula. For example, the molar mass of sodium chloride (NaCl) is 58.44 g/mol, as it consists of one sodium atom (atomic mass 22.99 g/mol) and one chlorine atom (atomic mass 35.45 g/mol).
Steps to Find Millimoles
Once you have the mass and molar mass, you can calculate the millimoles using the following formula:
Millimoles (mmol) = Mass (grams) / Molar Mass (grams per mole)
For instance, if you have 10 grams of glucose (C6H12O6), the molar mass of which is 180.16 g/mol, the millimoles would be calculated as:
mmol = 10 g / 180.16 g/mol = **55.51 mmol**
Applications of Millimole Calculations
Millimole calculations find widespread use in various scientific fields, including chemistry, biology, and medicine. They help determine concentrations (molarity, molality), quantities of substances, and reaction stoichiometry. In chemistry, millimoles are essential for balancing chemical equations and predicting product formation. In biology, they enable the quantification of biomolecules such as proteins and enzymes. In medicine, they aid in dosage calculations and understanding drug interactions.
Determining Mass of Substance: Unveiling the Secret Behind Millimole Calculations
When embarking on the quest to determine millimoles, unraveling the concept of mass is crucial. Mass represents the “heaviness” or quantity of matter an object possesses. While often mistaken for weight, mass remains constant regardless of location or gravitational force.
The realm of mass measurement encompasses various units, each catering to specific scenarios. Grams (g) stands as the fundamental unit in the metric system, commonly used for precise measurements. Volume, on the other hand, quantifies the amount of space occupied by a substance, typically expressed in milliliters (mL) or liters (L). Finally, density measures the compactness of a substance, indicating how much mass it packs into a given volume, often denoted in grams per cubic centimeter (g/cm³).
In our millimole calculation journey, converting mass to grams may arise as a necessity. This conversion ensures uniformity in units, allowing for seamless integration with the molar mass value. By meticulously following these steps, you can confidently embark on the path to millimole mastery.
Explain how to convert mass to grams if necessary.
How to Find Millimoles: A Step-by-Step Guide
Understanding Millimoles
Millimoles (mmol) are a unit of measurement commonly used in chemistry to quantify the amount of a substance present in a solution. They represent thousandths of a mole, which is the standard unit for measuring the amount of a substance. Millimoles are particularly useful for measuring small amounts of substances, making them essential in various scientific fields.
Calculating Millimoles
The formula for calculating millimoles is:
Millimoles (mmol) = Mass of substance (g) / Molar mass (g/mol)
The mass of the substance is typically measured in grams (g), while the molar mass is a constant value that represents the mass of one mole of the substance.
Determining Mass of Substance
The mass of a substance can be measured using various units, including weight, volume, and density. However, for millimole calculations, the mass must be expressed in grams (g). If the mass is given in other units, it needs to be converted to grams. Conversions can be done using unit conversion formulas or reference tables.
Finding Molar Mass
Molar mass is the mass of one mole of a substance. It is typically expressed in grams per mole (g/mol). The molar mass of a substance can be obtained from the periodic table (for elements) or from reference materials (for compounds).
Steps to Find Millimoles
- Determine the mass of the substance in grams.
- Find the molar mass of the substance in grams per mole.
- Divide the mass by the molar mass.
- The result will be the number of millimoles.
Example Calculation
Suppose you have 25 grams of sodium chloride (NaCl). The molar mass of NaCl is 58.44 g/mol. To calculate the number of millimoles:
Millimoles (mmol) = 25 g / 58.44 g/mol = 0.428 mmol
Therefore, there are 0.428 mmol of NaCl in 25 grams of the substance.
Applications of Millimole Calculations
Millimole calculations are widely used in various fields, including:
- Chemistry: Determining concentrations of solutions, calculating reaction stoichiometry, and analyzing chemical reactions.
- Biology: Measuring concentrations of биологические molecules, such as proteins and nucleic acids.
- Medicine: Calculating drug dosages, determining electrolyte balance, and assessing kidney function.
How to Find Millimoles: A Comprehensive Guide
In the realm of chemistry, the concept of millimoles plays a pivotal role in understanding the composition and behavior of substances. Whether you’re a seasoned scientist or a curious learner, comprehending how to find millimoles is essential for unlocking the secrets of the molecular world.
What are Millimoles?
- Millimoles (mmol) are a unit of measurement used to quantify the amount of a substance present in a chemical sample.
- They represent a specific number of particles (usually molecules, atoms, or ions) present in a solution or mixture.
Understanding Related Concepts
- Moles: A mole is the SI unit for the amount of substance, representing approximately 6.022 × 10^23 particles.
- Concentration: The concentration of a solution refers to the amount of solute dissolved in a specific volume of solvent.
- Molarity: Molarity is a unit of concentration that expresses the number of moles of solute per liter of solution.
Calculating Millimoles
The formula for calculating millimoles is:
Millimoles (mmol) = Mass (g) / Molar Mass (g/mol)
Determining Mass of Substance
- Mass is typically measured in grams (g).
- If the mass is given in other units, such as kilograms or milligrams, it must be converted to grams.
Finding Molar Mass
- Molar mass is the mass of one mole of a substance.
- It is expressed in grams per mole (g/mol).
- Molar mass values can be obtained from reference tables or by calculating them using the molecular weight of the substance.
Steps to Find Millimoles
- Convert the mass of the substance to grams (if necessary).
- Determine the molar mass of the substance.
- Apply the formula: Millimoles = Mass / Molar Mass
Example Calculation
Let’s calculate the number of millimoles in 10 grams of sodium chloride (NaCl).
- Molar mass of NaCl = 22.99 g/mol (from reference table)
- Millimoles = 10 g / 22.99 g/mol = 0.435 mmol
Applications of Millimole Calculations
Millimole calculations find widespread use in various fields:
- Chemistry: Determining concentrations, calculating reaction stoichiometry, and analyzing chemical reactions.
- Biology: Quantifying the amount of enzymes or other molecules in biological samples.
- Medicine: Calculating drug dosages and understanding drug pharmacokinetics.
How to Find Millimoles: A Simple Guide for Beginners
Understanding the concept of millimoles is crucial for navigating the world of chemistry and related disciplines. In this blog post, we’ll embark on a step-by-step journey to help you comprehend and calculate millimoles with ease.
What are Millimoles?
Millimoles (mmol) represent a convenient way of expressing the amount of substance. They are closely linked to moles, which measure the amount of a substance in terms of Avogadro’s number (6.022 x 10^23 particles). One millimole is one-thousandth of a mole.
Millimoles are often used to calculate concentration, which measures the amount of a substance dissolved in a specific volume.
Understanding Molar Mass
To calculate millimoles, we need to understand molar mass, which is the mass of one mole of a substance expressed in grams per mole (g/mol). The molar mass of a compound is the sum of the atomic masses of all its constituent atoms.
For instance, the molar mass of water (H2O) is 18 g/mol, which means that 1 mole of water weighs 18 grams.
Calculating Millimoles: A Step-by-Step Guide
Now that we have a grasp of millimoles and molar mass, let’s delve into the steps of calculating millimoles:
-
Determine the mass of the substance. This can be measured in grams, kilograms, or any other unit of mass.
-
Convert the mass to grams if necessary. Most molar mass values are given in g/mol, so it’s important to ensure that your mass value is also in grams.
-
Find the molar mass of the substance. You can consult the periodic table or use online resources to find the molar mass of any element or compound.
-
Calculate the millimoles: Divide the mass of the substance by its molar mass. The result will be the number of millimoles present in the sample.
Formula: Millimoles = Mass (g) / Molar Mass (g/mol)
Example Calculation
Let’s say we want to find the number of millimoles in 5 grams of sodium chloride (NaCl).
- Mass = 5 grams
- The molar mass of NaCl is 58.44 g/mol
- Millimoles = 5 grams / 58.44 g/mol
- Millimoles = 0.0855 mmol
Applications of Millimole Calculations
Millimole calculations play a vital role in various fields:
- Chemistry: Determining concentrations, preparing solutions, and calculating reaction stoichiometry.
- Biology: Measuring enzyme activity, analyzing DNA and RNA, and calculating drug dosages.
- Medicine: Calculating electrolyte levels, determining drug dosages, and monitoring kidney function.
Understanding how to find millimoles empowers you to navigate these fields with confidence. So, put these steps into practice, and embrace the world of millimoles!
How to Find Millimoles: A Step-by-Step Guide
Understanding Millimoles
Millimoles, abbreviated as mmol, are a unit of measurement used to quantify the amount of a substance in chemistry. One millimole is equal to one thousandth of a mole, which is the SI unit for the amount of substance. Moles and millimoles are essential concepts for understanding chemical reactions, concentrations, and quantities.
Calculating Millimoles
Determining Mass of Substance
To find millimoles, we need to determine the mass of the substance we’re interested in. Mass can be measured in grams (g), kilograms (kg), or other units. For most calculations, it’s convenient to convert mass to grams.
Finding Molar Mass
The next step is to find the molar mass of the substance. Molar mass is the mass of one mole of a substance, expressed in grams per mole (g/mol). It’s essentially the sum of the atomic masses of all the elements in the compound. Molar mass values can be found in reference tables or calculated from the chemical formula.
Steps to Find Millimoles
Once we have the mass of the substance and its molar mass, we can calculate the millimoles using the following formula:
Millimoles (mmol) = Mass (g) / Molar Mass (g/mol)
Example Calculation
Let’s say we want to find the number of millimoles in 25 grams of sodium chloride (NaCl). The molar mass of NaCl is 58.44 g/mol.
Millimoles (mmol) = 25 g / 58.44 g/mol
= 0.428 mmol
Applications of Millimole Calculations
Millimole calculations are widely used in various fields, including chemistry, biology, and medicine. They’re essential for determining concentrations, quantities, and reaction stoichiometry. For example, in chemistry, millimoles are used to calculate the number of moles of reactants or products in a chemical reaction. In biology, they’re used to express the concentration of substances in solutions and tissues.
How to Find Millimoles: A Step-by-Step Guide
Are you a budding chemist struggling to grasp the concept of millimoles? Fear not, dear reader, for this comprehensive guide will unveil the mysteries of millimoles, empowering you to navigate the complexities of chemistry with confidence!
Understanding Millimoles, the Building Blocks of Chemistry
Millimoles are like the microscopic building blocks of chemistry. They play a pivotal role in understanding the concentration of chemical solutions, the amount of reactants required for a reaction, and more. To truly fathom their significance, let’s delve into the world of moles and molarity. A mole represents a specific quantity of a substance, akin to a pack of 60 eggs. Molarity, on the other hand, expresses how many moles of a substance are present in a liter of solution.
Calculating Millimoles: Unlocking the Formula
To calculate millimoles, we’ll employ a simple formula:
Millimoles = Mass (in grams) / Molar Mass (in grams per mole)
Molar Mass, the unique fingerprint of a substance, tells us the mass of one mole of that substance. It’s like a name tag, identifying each substance by its atomic weight.
Determining the Mass of Substance: Units Unraveled
Before we can determine millimoles, we need to know the mass of the substance. Remember, mass is the amount of matter in an object, while weight is the force of gravity acting on it. To ensure accuracy, we’ll convert the mass to grams, the standard unit for mass in chemistry.
Finding Molar Mass: Unveiling the Essence of Substances
Next, we’ll need to find the molar mass of the substance. This value is like the “molecular weight” of a substance, expressed in grams per mole. We can consult periodic tables or databases to find this essential piece of information.
Steps to Find Millimoles: A Guided Journey
Now, let’s put it all together with these easy steps:
- Determine the mass of the substance in grams.
- Find the molar mass of the substance in grams per mole.
- Plug these values into the formula: Millimoles = Mass (in grams) / Molar Mass (in grams per mole).
- Calculate the millimoles.
Example Calculation: Making it Real
Let’s say we have 25 grams of sodium chloride (NaCl). Its molar mass is 58.44 grams per mole. Using our formula, we can calculate the millimoles of NaCl:
Millimoles of NaCl = 25 grams / 58.44 grams per mole
Millimoles of NaCl = 0.427 millimoles
Now, you’ve successfully determined the millimoles of NaCl!
Applications of Millimole Calculations: A Powerful Tool
Millimole calculations are indispensable in various scientific disciplines:
- Chemistry: Determining concentrations, calculating reaction stoichiometry, and analyzing titration results.
- Biology: Measuring enzyme activity, quantifying drug dosages, and understanding cell metabolism.
- Medicine: Determining blood glucose levels, electrolyte concentrations, and drug dosages.
How to Find Millimoles: A Step-by-Step Guide for the Chemistry Novice
Understanding Millimoles
In the fascinating world of chemistry, millimoles play a crucial role. They are a unit of measurement that helps us quantify the amount of a substance present. Just as we use millimeters to measure small distances, millimoles are used to measure minuscule quantities of matter.
Millimoles are closely related to another important concept in chemistry, moles. A mole is defined as the amount of a substance that contains exactly 6.022 × 10^23 particles (atoms, molecules, ions, etc.). Millimoles are simply one-thousandth of a mole.
Calculating Millimoles
To calculate millimoles, we need to know two things: the mass of the substance and its molar mass. Molar mass is a measure of the mass of one mole of a substance. It is typically expressed in grams per mole (g/mol).
The formula for calculating millimoles is:
Millimoles = Mass of substance (in grams) / Molar mass (in g/mol)
Determining Mass of Substance
The mass of a substance can be measured in various units, such as grams, kilograms, or pounds. For our calculations, we’ll need to convert the mass to grams if necessary.
For example, if we have a sample of sugar weighing 100 pounds, we would need to convert it to grams using the conversion factor 1 pound = 453.592 grams:
Mass of sugar in grams = 100 pounds × 453.592 grams/pound = 45,359.2 grams
Finding Molar Mass
The molar mass of a substance can be obtained from the periodic table or a reference book. It is simply the sum of the atomic masses of all the atoms in the molecule.
For instance, the molar mass of sodium chloride (NaCl) is 58.44 g/mol. This is because sodium has an atomic mass of 22.99 g/mol and chlorine has an atomic mass of 35.45 g/mol.
Steps to Find Millimoles
Now that we have the mass of the substance and its molar mass, we can follow these steps to find the millimoles:
- Convert the mass to grams if necessary.
- Divide the mass of the substance by its molar mass.
Example Calculation
Let’s say we have a sample of sugar with a mass of 100 grams. We want to find the number of millimoles of sugar present. The molar mass of sugar (C₁₂H₂₂O₁₁) is 342.30 g/mol.
Millimoles of sugar = 100 grams / 342.30 g/mol = **0.292 millimoles**
Applications of Millimole Calculations
Millimole calculations are essential in various fields, including chemistry, biology, and medicine. They are used to:
- Determine the concentration of solutions
- Calculate the quantity of reactants and products in chemical reactions
- Analyze the stoichiometry of reactions, which helps us predict the amounts of reactants and products required or produced.
By understanding how to find millimoles, we open the door to a deeper exploration of the world of chemistry.
How to Find Millimoles: A Comprehensive Guide for Beginners
Embark on a journey into the fascinating realm of chemistry as we delve into the concept of millimoles, a fundamental unit for measuring the quantity of substances. Join us as we unveil the secrets of calculating millimoles, with a step-by-step guide designed for clarity and understanding.
Understanding Millimoles
Millimoles are a convenient unit for expressing the amount of a substance based on its molecular weight. One millimole is equal to one-thousandth of a mole, the SI unit for measuring the amount of a substance. Understanding millimoles is crucial for various fields, including chemistry, biology, and medicine.
Calculating Millimoles
To determine the millimoles of a substance, we use the following formula:
Millimoles = mass of substance (grams) / molar mass (grams per mole)
Determining Mass of Substance
The mass of a substance can be expressed in various units such as grams (g), milligrams (mg), or kilograms (kg) or even volume (mL) or density (g/mL). If the mass is not given in grams, it must be converted to grams using the appropriate conversion factor.
Finding Molar Mass
The molar mass of a substance is the mass of one mole of that substance, expressed in grams per mole (g/mol). The molar mass of an element is equal to its atomic weight, while the molar mass of a compound is the sum of the atomic weights of its constituent elements.
Steps to Find Millimoles
1. Determine the mass of the substance: Convert the mass to grams if necessary.
2. Find the molar mass of the substance: Use the periodic table or other reference materials to obtain the molar mass.
3. Apply the millimole formula: Divide the mass of the substance by its molar mass.
Example Calculation
Let’s say we want to find the millimoles of sodium chloride (NaCl) in 25 grams of the substance.
- Mass of substance: 25 grams
- Molar mass of NaCl: 58.44 g/mol (22.99 g/mol for Na + 35.45 g/mol for Cl)
- Millimoles of NaCl: 25 g / 58.44 g/mol = 0.428 millimoles
Applications of Millimole Calculations
Millimole calculations are widely used in various scientific fields:
- Chemistry: Determining concentrations of solutions, calculating quantities of reactants and products in reactions.
- Biology: Expressing concentrations of enzymes, hormones, and other biological substances.
- Medicine: Determining drug dosages, analyzing blood samples, and understanding metabolic processes.
Mastering millimole calculations is a cornerstone of scientific understanding. By following the steps outlined in this guide, you can confidently navigate the world of chemistry and related fields, empowering yourself with the knowledge to tackle complex problems and make informed decisions.
How to Find Millimoles: A Step-by-Step Guide
Understanding Millimoles
In the realm of chemistry, millimoles (mmol) play a crucial role. They represent the amount of a substance in terms of thousandths of a mole, offering a convenient unit of measurement for quantifying small quantities of matter.
Calculating Millimoles
To embark on the journey of finding millimoles, we invoke the mathematical formula:
Millimoles = (Mass of Substance in Grams) / Molar Mass
**Mass of Substance:** This refers to the mass of the substance we’re interested in, expressed in grams.
**Molar Mass:** A property of the substance, representing the mass of one mole of that substance (typically in grams per mole).
Determining Mass of Substance
Mass, often expressed in grams, can also be given in other units such as weight (kilograms or pounds) or volume (liters or milliliters). Conversions: are necessary if the mass is not provided in grams.
Finding Molar Mass
**Molar Mass:** is the total mass of all the atoms in a molecule or formula unit. It’s usually expressed in grams per mole (g/mol). For elements, molar mass is simply the atomic mass. For compounds, it’s the sum of the atomic masses of all the constituent elements.
Steps to Find Millimoles
With the mass of substance and molar mass in hand, we can embark on the step-by-step calculation:
- Convert the mass to grams if necessary.
- Divide the mass in grams by the molar mass.
- Report the result in millimoles.
Example Calculation
Let’s calculate the millimoles in 10 grams of glucose (_C₆H₁₂O₆_).
- Molar mass of glucose: 180.16 g/mol
- Millimoles of glucose = 10 g / 180.16 g/mol
- Millimoles of glucose = ≈0.0555 mmol
Applications of Millimole Calculations
Millimole calculations have wide-ranging applications in various scientific fields:
- Chemistry: Determining concentrations, dilution factors, and reaction stoichiometry.
- Biology: Quantifying enzyme activity, substrate concentrations, and cellular metabolism.
- Medicine: Calculating drug dosages, electrolyte levels, and blood glucose concentrations.
How to Find Millimoles: A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding the concept of millimoles is crucial in chemistry, biology, and medicine. It allows us to quantify the amount of a substance present, which is essential for various calculations and analysis.
In chemistry, millimoles are widely used to determine the concentration of solutions. The concentration, expressed in moles per liter (M), indicates the number of moles of solute present in a liter of solution. By knowing the millimoles of a substance, we can easily calculate its molarity.
Moreover, millimoles play a significant role in chemical reactions. By determining the millimoles of reactants and products, we can calculate the stoichiometry of the reaction and predict the quantities of substances involved. This information is vital for balancing chemical equations and ensuring accurate experimental outcomes.
In biology, millimoles are used to quantify the concentration of substances in biological fluids, such as blood and urine. By measuring the millimoles of specific metabolites, enzymes, or hormones, we can assess metabolic processes, diagnose diseases, and monitor treatment efficacy.
In medicine, millimoles are essential for calculating dosages of medications. Most drugs are prescribed in milligrams, but millimoles allow us to determine the precise amount of active ingredient in a given dose. This information is crucial for ensuring drug efficacy and minimizing side effects.
Additionally, millimoles are used in various other fields, including environmental science, engineering, and manufacturing. They provide a standardized unit for expressing the quantity of substances involved in various processes, enabling accurate measurements and calculations.
In conclusion, understanding how to find millimoles is essential in a wide range of disciplines. By accurately calculating millimoles, we can determine the concentration, stoichiometry, and dosage of substances, leading to more precise analysis, effective treatments, and efficient processes.
How to Find Millimoles: A Comprehensive Guide for Beginners
Understanding Millimoles
Millimoles are a fundamental unit of measurement in chemistry. They represent the amount of a substance, similar to moles, but on a smaller scale. Millimoles are often used when dealing with small quantities or when expressing concentrations.
Calculating Millimoles
To calculate millimoles, you need two pieces of information:
- Mass of the substance: This is the amount of your substance in grams.
- Molar mass: This is the mass of 1 mole of the substance in grams.
Once you have these values, you can use the following formula:
Millimoles = (Mass of substance in grams) / (Molar mass in grams per mole)
Determining the Mass of Substance
The mass of a substance can be found using a variety of methods, depending on its form:
- Solids: Weigh the substance using a scale.
- Liquids: Use a graduated cylinder or pipette to measure the volume and multiply by the liquid’s density.
- Gases: Use a gas flow meter or a displacement method.
Finding the Molar Mass
The molar mass of a substance is the sum of the atomic masses of the elements that make it up. It can be found in:
- Periodic table: For elements
- Compound formulas: For compounds
For example, the molar mass of sodium chloride (NaCl) is the sum of the atomic masses of sodium (22.99 g/mol) and chlorine (35.45 g/mol), which is 58.44 g/mol.
Applications of Millimole Calculations
Millimole calculations are essential in various fields:
- Chemistry: To determine concentrations and reaction stoichiometry
- Biology: To study enzyme activity and cellular processes
- Medicine: To calculate drug dosages and analyze blood tests
Determining Concentrations
Concentration is the amount of a substance dissolved in a solvent. It can be expressed as:
- Millimoles per liter (mM): For aqueous solutions
- Millimoles per kilogram (mmol/kg): For non-aqueous solutions
Millimole concentration can be calculated using the following formula:
Concentration (mM) = Millimoles / Volume of solution in liters
Quantities
Millimoles can be used to express the quantity of a substance, especially when working with small amounts.
Reaction Stoichiometry
In chemical reactions, millimoles provide a basis for balancing equations and calculating the amount of reactants and products involved.