Calculate Direct Labor Cost: A Guide To Time Tracking And Rate Setting
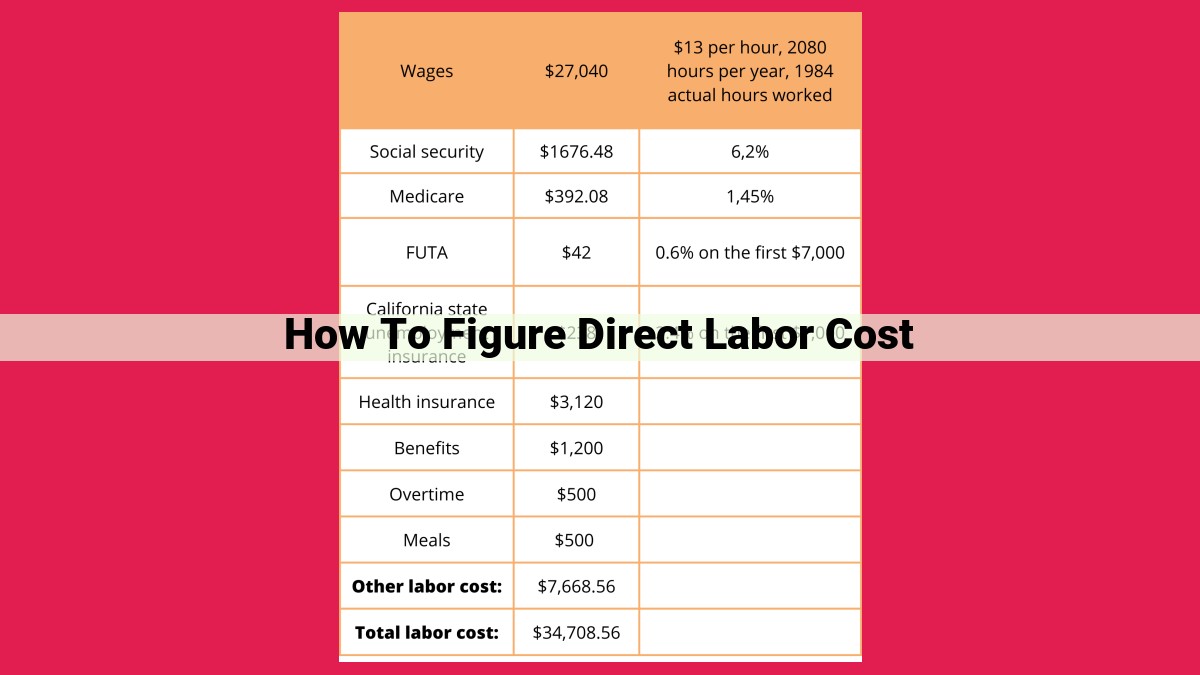
To determine direct labor cost, calculate the labor rate based on market conditions and employee experience. Track actual hours worked using time cards or payroll records. Multiply the direct labor rate by hours worked, considering overtime premium pay and employee benefits. The sum of all these costs represents the total direct labor cost, essential for accurate cost accounting and budgeting.
Calculating the Direct Labor Rate: The Key to Accurate Costing
In the intricate world of business finance, pinpointing the true cost of labor is crucial. Direct labor rate plays a pivotal role in this equation, serving as the foundation for calculating the total compensation paid to employees for their direct involvement in production processes.
Determining the direct labor rate is a multi-faceted task that begins with a thorough assessment of the labor market conditions. This includes researching industry benchmarks, analyzing regional trends, and considering the supply and demand dynamics for skilled workers. The ultimate goal is to establish a competitive wage that attracts and retains a skilled workforce while balancing the company’s financial constraints.
In addition to market conditions, industry benchmarks provide valuable insights. By comparing wages with similar businesses in the same industry, companies can gauge their competitiveness and make informed decisions about their labor rate. The worker’s experience and skills are also important considerations. Experienced workers with specialized skills typically command higher wages, while entry-level employees with less experience may be compensated at a lower rate.
Identifying Actual Hours Worked: A Vital Step in Accurately Calculating Direct Labor Costs
Calculating direct labor costs is essential for businesses to accurately determine their production expenses. Actual hours worked play a crucial role in this calculation, providing a true reflection of the time spent by employees on production tasks.
Time Cards:
- Time cards remain a popular and reliable method for tracking employee hours. Employees fill out physical or electronic time cards, noting their start and end times, as well as any breaks taken.
Payroll Records:
- Payroll records also provide valuable information on actual hours worked. These records are generated by payroll systems and typically include employee time entries. They offer a centralized and easily accessible source of data.
Observation Techniques:
- Observation techniques, such as employee time studies, can be useful in certain situations. Observers monitor employees’ activities and record the time spent on specific tasks. This method can provide detailed and accurate data, but it can also be time-consuming and resource-intensive.
Ensuring Accuracy:
Regardless of the method used, it is crucial to accurately track employee hours to ensure reliable cost calculations. Employers should implement clear and consistent policies for recording hours worked, including guidelines for meal breaks, downtime, and overtime.
Technology:
In the digital age, technology offers a range of solutions for tracking employee hours. Time tracking software, mobile apps, and GPS systems can automate the process, improve accuracy, and reduce the risk of errors.
Collaboration:
Effective communication and collaboration between managers and employees are also essential for accurate hour tracking. Managers should set clear expectations, provide training, and monitor employee time entries regularly. Employees should understand the importance of accurate hour reporting and be encouraged to report any discrepancies promptly.
Identifying actual hours worked is a foundational step in calculating direct labor costs. By utilizing appropriate methods, ensuring accuracy, and fostering collaboration, businesses can obtain the reliable data necessary for accurate cost management and decision-making.
Multiplying Direct Labor Rate by Hours Worked to Determine Direct Labor Cost
Calculating the total direct labor cost is a crucial step in understanding the labor expenses involved in producing goods or services. Direct labor refers to employees who are directly involved in the creation of products or services and whose wages can be directly attributed to specific units of production.
One key component of determining the direct labor cost is multiplying the direct labor rate by the hours worked. The direct labor rate is the hourly wage or salary paid to employees for their work. Hours worked represent the number of hours that employees dedicated to direct labor activities during a specific period.
To calculate the total direct labor cost, simply multiply the direct labor rate by the hours worked:
Total Direct Labor Cost = Direct Labor Rate x Hours Worked
For example, if an employee earns a direct labor rate of $15 per hour and works 40 hours per week, the total direct labor cost for that employee for the week would be:
Total Direct Labor Cost = $15 x 40 hours = $600
It’s important to note that overtime pay, if applicable, should be included in the total direct labor cost. Overtime pay is typically calculated at a higher rate than the regular direct labor rate, so it should be considered when determining the total cost of direct labor.
By multiplying the direct labor rate by the hours worked, businesses can accurately determine the direct labor cost associated with producing goods or services. This information is crucial for budgeting, pricing, and evaluating the efficiency of labor operations.
Considering Overtime Premium Pay
In the realm of direct labor costing, overtime premium pay holds significant implications. Overtime refers to hours worked beyond the standard workday or week, typically attracting additional compensation. Understanding overtime regulations and contractual obligations is crucial for accurately calculating direct labor costs.
Navigating Overtime Regulations
The Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA) sets federal overtime regulations, requiring employers to pay overtime at a rate of one and a half times the regular pay rate for all hours worked over 40 in a workweek. However, some states or industries may have specific overtime regulations that differ from FLSA standards.
Reviewing Employment Contracts
Employment contracts frequently outline overtime stipulations, including the hourly rate for overtime pay and the conditions under which overtime is eligible. It’s essential to thoroughly review contracts to ensure compliance with both FLSA and contractual obligations.
Calculating Premium Pay
Once you have a clear understanding of overtime regulations and contractual requirements, calculating overtime premium pay is straightforward. Simply multiply the overtime hours worked by the established overtime pay rate.
Integrating into Direct Labor Costing
The total overtime premium pay is incorporated into the direct labor cost calculation. By factoring in this additional labor cost, you ensure an accurate representation of the total labor expenses associated with a particular production process or project.
By considering overtime premium pay, organizations can maintain compliance with labor laws and regulations, accurately calculate direct labor costs, and make informed decisions regarding overtime utilization and workforce management.
Calculating the Direct Labor Cost: Accounting for Employee Benefits
Calculating the direct labor cost is essential for businesses to accurately determine production costs and profitability. Employee benefits play a significant role in determining the total direct labor cost, as they represent additional expenses associated with labor expenses.
Types of Employee Benefits to Consider:
- Health Insurance: Employers typically contribute a portion of the premiums for health insurance coverage provided to employees and their families.
- Retirement Plans: Contributions to employee retirement plans, such as 401(k) matches or defined benefit plans, represent a significant cost for many businesses.
- Paid Time Off: Paid time off, including vacation days, sick leave, and holidays, is another employee benefit that adds to the direct labor cost.
Methods for Calculating Employee Benefits Costs:
Percentage-Based Method:
- Calculate the percentage of total wages that is allocated towards employee benefits.
- This percentage can be determined by examining historical data or industry benchmarks.
Fixed-Cost Method:
- Assign a fixed cost per employee or hour worked to cover employee benefits.
- This method simplifies the calculation but may not accurately reflect actual costs.
Integration with Payroll System:
- Many payroll systems can automatically calculate employee benefits based on predefined formulas or employee-specific information.
- This approach eliminates the need for manual calculations and ensures accuracy.
Impact on Direct Labor Cost:
The cost of employee benefits should be added to the direct labor rate and multiplied by the hours worked to determine the total direct labor cost.
Importance of Accurate Calculation:
Accurate calculation of direct labor cost, including employee benefits, is crucial because it affects:
- Product costing
- Profitability analysis
- Budgeting and forecasting
- Financial reporting
Determining the Total Direct Labor Cost
In the intricate tapestry of manufacturing, direct labor costs play a crucial role in determining profitability. To accurately calculate these costs, it is essential to encompass all associated expenses, not just the direct labor rate and hours worked.
Once you have a clear understanding of these fundamental elements, it’s time to consolidate all direct labor costs into a single comprehensive figure. This final step involves meticulously summing up the rate, hours worked, overtime pay, and employee benefits.
-
Hourly Rate: This is the agreed-upon compensation for each hour of labor performed. It should reflect industry benchmarks, labor market conditions, worker experience, and skills.
-
Hours Worked: Accurately tracking employee hours is paramount. Time cards, payroll records, and observation techniques can be utilized to ensure precision.
-
Overtime Premium Pay: Overtime regulations and contracts must be carefully reviewed. Any additional compensation for hours worked beyond the standard must be included in the calculation.
-
Employee Benefits: Health insurance, retirement plans, and paid time off all contribute to employee compensation. These costs can be factored in as a percentage or fixed cost.
By meticulously summing up these components, you arrive at the Total Direct Labor Cost. This aggregate figure represents the true cost of labor, including not only the base wages but also the additional expenses associated with employee compensation. This information is not only crucial for cost accounting but also for budgeting, pricing decisions, and performance analysis. By gaining a precise understanding of direct labor costs, manufacturers can make informed decisions and optimize their operations for greater profitability.