Calculate Cumulative Percentage With Ease: A Comprehensive Guide
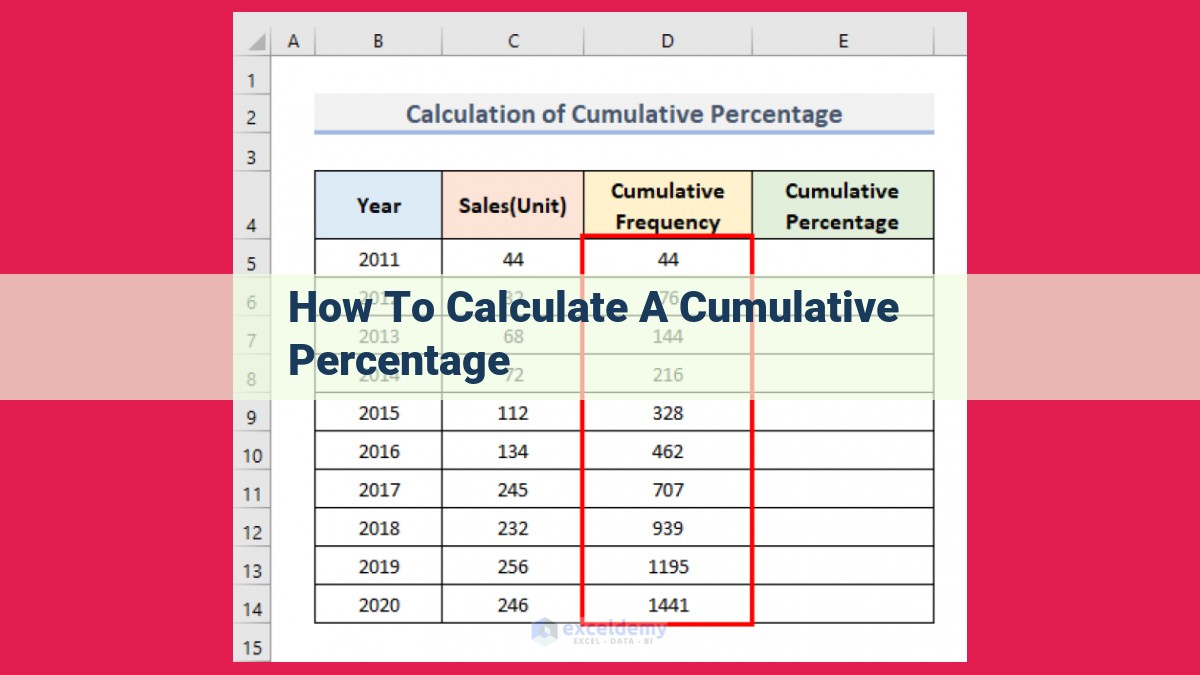
To calculate a cumulative percentage, determine the current position, start point, and total range. The cumulative percentage formula is ((Current Position – Start Point) / Total Range) * 100. Identify the start and end points of the range and the current position to be measured. Define the total range as the distance or interval between the start and end points. Use the formula to calculate the cumulative percentage, which represents the progress made as a fraction of the total range. A cumulative percentage helps track progress towards a goal or measure the accumulation of values over time.
Understanding Cumulative Percentage: A Comprehensive Guide
Cumulative percentages, unlike regular percentages, provide a running total of the percentage completed over a range of values. They are commonly used in various fields, such as statistics, finance, and progress tracking.
The concept of a cumulative distribution function (CDF) is crucial in understanding cumulative percentages. A CDF is a function that provides the probability of a random variable taking a value less than or equal to a specified value. By using a CDF, we can calculate the cumulative percentage up to any given point.
Calculating Cumulative Percentage: A Simplified Guide
Imagine you’re tracking the progress of a marathon runner. You want to know what percentage of the race they’ve completed so far. That’s where cumulative percentage comes into play.
To calculate the cumulative percentage, we use the formula:
((_Current Position_ - _Start Point_) / _Total Range_)
Let’s break down the variables:
- Current Position: The current point or value for which you want to calculate the percentage.
- Start Point: The initial value or starting point of the range.
- Total Range: The total distance or interval over which the percentage is calculated.
So, the cumulative percentage tells you what portion of the total range has been covered, expressed as a percentage.
For instance, if the marathon runner has covered 10 kilometers and the total race distance is 42 kilometers, the cumulative percentage would be:
((10 km - 0 km) / 42 km) * 100 = 23.8%
This means the runner has completed approximately 23.8% of the race so far.
Understanding cumulative percentage helps you gauge progress, track performance, and set realistic milestones. From tracking sales targets to managing project timelines, this tool empowers you with data-driven insights.
Determining Start and End Points: A Crucial Step in Calculating Cumulative Percentages
In the quest to understand cumulative percentages, identifying the start and end points of the range is of paramount importance. Just as knowing where you’re heading and where you started is essential for calculating progress, determining these boundaries is crucial for accurate cumulative percentage calculations.
Think of a progress bar on your computer. It has a lower bound (the starting point) and an upper bound (the ending point). The length of the bar represents the total range. By pinpointing the current position within this range, you can calculate the cumulative percentage of progress made.
So, how do you identify these boundaries? Let’s explore two scenarios:
Initial Values (Lower Bounds)
Example 1: Measuring Academic Performance
Suppose you’re tracking your performance in a math class. The first test serves as your initial value or lower bound. It establishes a starting point from which progress can be measured.
Final Values (Upper Bounds)
Example 2: Estimating Project Completion
Now, let’s consider a software development project. The target release date becomes the final value or upper bound. This endpoint defines the ultimate goal and provides a reference point for calculating how far along you are.
Determining start and end points gives a clear framework for understanding the cumulative percentage. Without these boundaries, progress remains ambiguous, and percentages become meaningless. So, remember to carefully set your coordinates before embarking on cumulative percentage calculations.
Identifying Current Position: The Key to Calculating Cumulative Percentage
In the realm of cumulative percentages, the current position holds an esteemed place. It represents the progress you’ve made towards your goal, be it completing a task, achieving a milestone, or fulfilling a dream.
Determining your present location along the journey is vital for accurate calculation. Imagine you’re on a road trip, driving from California to New York. You start at mile 0 in Los Angeles. After 1,000 miles, you reach Denver, Colorado. To determine your cumulative percentage, you need to know your current position (1,000 miles), the start point (0 miles), and the total range (3,000 miles, the distance from Los Angeles to New York).
The same principle applies in countless scenarios. Whether you’re tracking the completion of a project, your progress in a race, or your savings towards a house, your current position is the crucial reference point. Remember, it’s the value that reflects how far you’ve come and how close you are to reaching your destination.
Calculating Cumulative Percentage: The Ultimate Guide
Cumulative percentages play a crucial role in measuring progress, comparing data, and making informed decisions. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the concept of cumulative percentage and provide step-by-step instructions for calculating it.
Understanding Cumulative Percentage
A cumulative percentage represents the proportion of a total range that has been completed up to a certain point. It is different from a regular percentage, which calculates the proportion of a part to the whole. To understand cumulative percentages, we must first grasp the concept of a cumulative distribution function (CDF). A CDF plots the probability of a random variable taking a value less than or equal to a given value. It is essentially a graphical representation of the cumulative percentage.
Calculating Cumulative Percentage
The formula for calculating cumulative percentage is:
Cumulative Percentage = ((Current Position - Start Point) / Total Range) * 100
Variables:
- Current Position: The point at which the cumulative percentage is being calculated.
- Start Point: The initial point from which the cumulative percentage is measured.
- Total Range: The total distance or interval over which the cumulative percentage is being calculated.
Determining Start and End Points
Identifying the start and end points is critical for accurate calculation. The start point represents the lower bound (0%) and the end point represents the upper bound (100%). For example, measuring progress on a project could have a start point of “project initiation” and an end point of “project completion.”
Identifying Current Position
The current position is the point for which the cumulative percentage is being calculated. It represents the progress made or the value attained. For instance, if a sales team has reached 50% of its monthly target, the current position would be 50%.
Defining Total Range
The total range is the entire distance or interval over which the cumulative percentage is calculated. It is critical to define the total range accurately to ensure a meaningful calculation. For example, when calculating the cumulative percentage of a road trip, the total range could be the total distance from the starting point to the destination.
Measuring Distances or Intervals:
- Miles or Kilometers: For measuring distances on roads or distances between cities.
- Time: For measuring durations, such as the cumulative percentage of a marathon or a project timeline.
- Units: For measuring quantities, such as the cumulative percentage of inventory sold or production output.