Understanding Boron’s Valence Electrons: Key To Its Chemical Reactivity
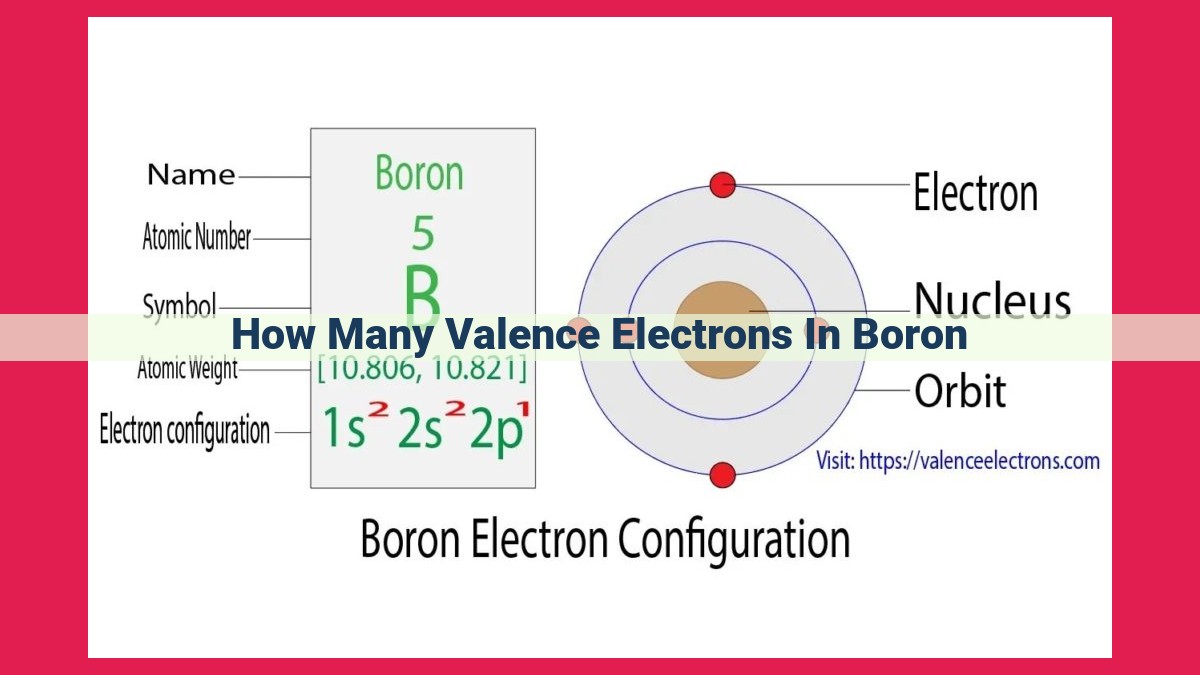
Boron, a chemical element with atomic number 5, possesses three valence electrons. These valence electrons occupy the outermost energy level, designated as 2p¹, and are responsible for boron’s ability to participate in chemical bonding. By understanding the valence electron count of boron, we gain insights into its chemical reactivity and behavior.
- Briefly introduce boron as a chemical element and its atomic number.
- Highlight the importance of understanding its valence electrons.
Boron: An Intriguing Element with Versatile Valence Electrons
Let’s delve into the fascinating world of chemistry and explore an element that plays a pivotal role in shaping the molecular bonds around us: boron. With an atomic number of 5, boron is a lightweight element that holds a unique position in the periodic table. Its valence electrons, the outermost electrons in its atomic structure, are key players in determining its chemical behavior and reactivity.
Understanding Valence Electrons
Electrons are tiny subatomic particles that orbit the atomic nucleus. The electrons closest to the nucleus, called core electrons, are tightly bound and have little influence on the chemical properties of an element. However, the electrons in the outermost shell, known as valence electrons, are the ones that participate in chemical bonding and determine an element’s reactivity.
Boron’s Valence Electrons
Boron has three valence electrons. This is a crucial piece of information because it dictates how boron interacts with other atoms. Valence electrons are like the “social butterflies” of the atomic world, seeking out opportunities to form bonds with other elements to achieve a stable configuration.
Importance of Understanding Boron’s Valence Electrons
Comprehending the number and arrangement of boron’s valence electrons is essential for understanding its chemical properties. Boron’s valence electrons play a significant role in:
- Determining the types of chemical bonds it can form
- Predicting its reactivity with other elements
- Uncovering its potential applications in various fields
Boron Atomic Number and Atomic Structure
In the vast tapestry of chemical elements, boron, a metalloid with an atomic number of 5, holds a unique position. To grasp its chemical behavior, we must delve into its atomic structure, the foundation of its existence.
The atomic number of an element defines its identity. It represents the number of protons residing in the nucleus, the heart of the atom. Electrons, with their opposing charge, orbit the nucleus, balancing the protonic charge. In the case of boron, its atomic number indicates the presence of 5 protons and 5 electrons.
These electrons are not mere spectators; they actively participate in chemical bonding, the process that unites atoms to form molecules. The electrons involved in bonding are known as valence electrons. Boron, with its three valence electrons, possesses a unique potential for forming chemical bonds. Its valence electrons occupy the outermost energy level, the 2p orbital, poised to engage in interactions with other atoms.
Valence Electrons: The Invisible Force Behind Chemical Bonding
In the vast realm of chemistry, elements engage in a fascinating dance, forming bonds that create the molecules and substances that make up our world. At the heart of this dance lies a crucial concept: valence electrons. These electrons, like the keys to a lock, determine the chemical behavior and reactivity of elements.
One such element is boron, a lightweight metalloid that plays a vital role in various industrial and medicinal applications. To understand boron’s chemical properties, it’s essential to unravel the mystery of its valence electrons.
What are Valence Electrons?
Imagine atoms as tiny worlds, each with a nucleus at the center and electrons orbiting around it. Valence electrons are the outermost electrons in an atom’s electron cloud, farthest from the nucleus. These electrons are not tightly bound to the nucleus, making them highly reactive and eager to engage with other atoms.
Boron’s Unique Trio
Boron, with an atomic number of 5, has a total of five electrons. Three of these electrons occupy the outermost shell, making them valence electrons. Boron’s valence electron configuration is 2s²2p¹, with one electron in the 2p orbital and two in the 2s.
The Significance of Valence Electrons
Valence electrons are the key players in chemical bonding. They determine the number and type of bonds an element can form. In the case of boron, its three valence electrons allow it to form bonds with other elements. For example, boron can bond with three hydrogen atoms to form borane (BH3) or with three fluorine atoms to form boron trifluoride (BF3).
Understanding the concept of valence electrons is fundamental to comprehending the chemical properties and reactivity of elements. Boron, with its three valence electrons, exemplifies the crucial role valence electrons play in shaping the molecular world around us. By unraveling the mystery of valence electrons, we unlock the secrets of chemical bonding and gain valuable insights into the intricate tapestry of our universe.
**Electron Configuration: Unveiling Boron’s Chemical Secrets**
Understanding Boron’s Electron Arrangement
In the realm of chemistry, understanding the intricacies of an element’s electron configuration is crucial in unraveling its chemical behavior. For boron, an element with atomic number 5, deciphering its electron arrangement holds the key to comprehending its unique properties and reactivity.
Electron Configuration: A Blueprint of Electron Distribution
Imagine the electron configuration of an atom as a blueprint that meticulously describes the spatial arrangement of its electrons. Each electron occupies a specific orbital, akin to an apartment in a high-rise building. These orbitals are labeled according to their energy level (principal quantum number, n) and shape (angular momentum quantum number, l).
Boron’s Electron Configuration: A Trio of Valence Electrons
Delving into boron’s electron configuration, we find a concise notation: 1s²2s²2p¹. This compact string of numbers and letters unveils the distribution of boron’s five electrons in its orbitals.
- 1s²: Two electrons reside in the first energy level (n = 1) in an orbital with an s shape (l = 0).
- 2s²: Two more electrons occupy the second energy level (n = 2) in an s-shaped orbital.
- 2p¹: The final electron finds its home in the second energy level again, but in a p-shaped orbital (l = 1).
The Significance of Boron’s Valence Electron: A Gateway to Reactivity
Of particular interest is boron’s 2p¹ electron. This lone electron, situated in the outermost energy level, is known as a valence electron. Valence electrons play a pivotal role in chemical reactions, acting as the gateway through which boron interacts with other atoms.
Unveiling boron’s electron configuration is akin to unearthing the blueprint for its chemical behavior. By understanding the arrangement of its valence electrons, we gain insights into boron’s reactivity and versatility in forming compounds. This knowledge serves as a cornerstone for further exploration into the fascinating world of boron chemistry.