Beryllium: Alkaline Earth Metal With Unique Electron Configuration And Chemical Properties
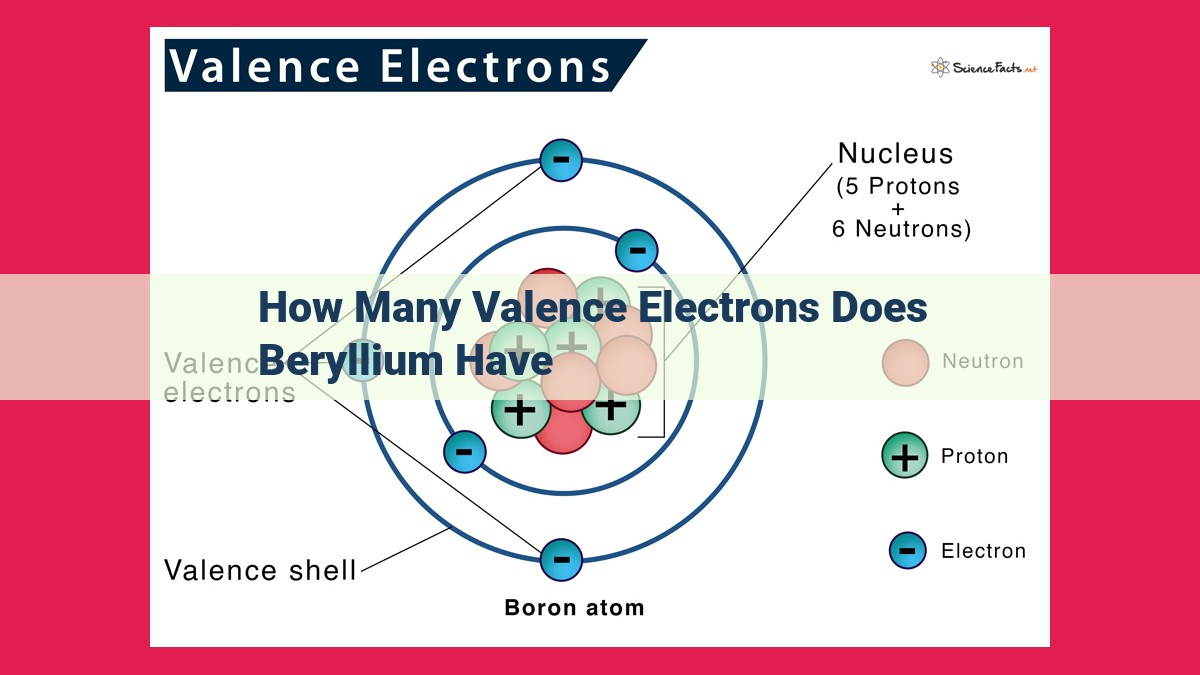
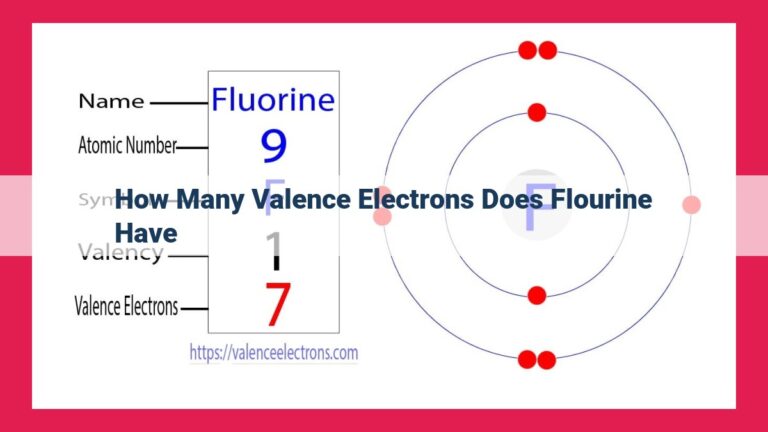
Beryllium, an alkaline earth metal in group 2, possesses four electrons. Its electronic configuration (1s² 2s²) indicates two valence electrons in the outermost energy level. Valence electrons play a crucial role in chemical bonding, determining beryllium’s ability to form compounds and its chemical reactivity.
Unveiling the Significance of Valence Electrons
Get ready to embark on a captivating journey into the realm of valence electrons, the fundamental building blocks of chemical interactions. We’ll unravel the mysteries surrounding atomic orbitals and electron configuration, and explore how these interplay to determine the unique properties and reactivity of elements like beryllium. So, buckle up and let’s dive right in!
Demystifying Atomic Orbitals and Electron Configuration
Imagine atoms as miniature solar systems, with a nucleus at the center and electrons orbiting around it. These electrons reside in specific energy levels, known as atomic orbitals. Each atomic orbital can hold a maximum of two electrons. The arrangement of electrons in these orbitals is called the electron configuration, which provides a fingerprint-like signature for each element.
The Crucial Role of Valence Electrons in Chemical Bonding
Now, let’s focus on valence electrons, the electrons that reside in the outermost atomic orbital. These electrons are the key players in chemical bonding, the process that holds atoms together to form molecules and compounds. Valence electrons can be shared, donated, or accepted, resulting in a myriad of chemical bonds. They determine an element’s reactivity, which is its tendency to form chemical bonds with other elements.
Stay tuned in our next installment, where we’ll delve into the fascinating characteristics of beryllium and discover how its valence electrons shape its unique properties and behavior.
Beryllium: Unveiling the Secrets of Valence Electrons and Metallurgical Marvels
In the realm of chemistry, valence electrons hold the key to understanding the behavior and reactivity of elements. Our focus today is on beryllium, an enigmatic alkaline earth metal with captivating characteristics and technological significance.
Beryllium: A Member of the Group 2 Family
Beryllium belongs to group 2 of the periodic table, sharing the company of metals such as magnesium, calcium, and strontium. As an alkaline earth metal, beryllium exhibits properties of high reactivity and rapid oxidation when exposed to air or water.
Metallurgical Properties and Uses
Beryllium’s metallurgical properties make it a valuable material in various industries. Its lightness and rigidity make it an ideal choice for aerospace applications, where weight reduction is crucial. Additionally, beryllium’s high melting point and high thermal conductivity make it suitable for use in nuclear reactors and high-performance electronics.
One remarkable application of beryllium is in the production of copper-beryllium (CuBe) alloys. CuBe alloys are known for their _exceptional strength, wear resistance, and non-sparking properties. These unique characteristics make CuBe alloys indispensable in industries such as shipbuilding, mining, and electronics.
Valence Electrons in Beryllium
Atomic orbitals and electron configuration play a crucial role in understanding the chemical behavior of elements. Beryllium’s electronic configuration, 1s² 2s², reveals that it has two valence electrons in the outermost energy level. These valence electrons are the gateway to chemical bonding, allowing beryllium to interact with other elements and form compounds.
The two valence electrons of beryllium participate in chemical reactions, determining its reactivity and compound formation abilities. By understanding the fundamental role of valence electrons in beryllium, we gain valuable insights into its chemical properties and versatility.
Valence Electrons in Beryllium: A Journey into Chemical Bonding
In the realm of chemistry, electrons dance around atoms, playing a crucial role in shaping their behavior. Among these electrons, valence electrons take center stage, influencing the chemical destiny of elements. Let’s embark on a microscopic adventure to unravel the fascinating world of valence electrons in beryllium, an enigmatic alkaline earth metal.
Electronic Configuration: A Blueprint of Electron Arrangement
Every element possesses a unique blueprint for its electron configuration, which dictates how its electrons are distributed among atomic orbitals. Beryllium, a member of group 2 in the periodic table, boasts an electron configuration of 1s² 2s². This arrangement reveals the presence of two electrons in the first energy level (1s orbital) and two electrons in the second energy level (2s orbital).
Valence Electrons: The Gateway to Bonding
Valence electrons, residing in the outermost energy level, hold the key to an element’s chemical interactions. In beryllium’s case, its two valence electrons reside in the 2s orbital. These electrons are eager to participate in chemical bonding, forming partnerships with other atoms to achieve stability.
Significance of Valence Electrons in Beryllium Chemistry
The presence of two valence electrons in beryllium has a profound impact on its chemical behavior. These electrons determine beryllium’s ability to form compounds and dictate its chemical reactivity. Beryllium readily forms ionic bonds by transferring its two valence electrons to more electronegative atoms, leading to the formation of compounds such as beryllium oxide (BeO).
Moreover, the number of valence electrons influences beryllium’s chemical reactivity. Elements with a low number of valence electrons tend to be more reactive as they can easily form bonds to achieve a stable configuration. Beryllium’s two valence electrons make it a moderately reactive metal, capable of reacting with various elements to form diverse compounds.
In summary, valence electrons play a pivotal role in the chemistry of beryllium. The presence of two valence electrons in the 2s orbital determines beryllium’s bonding behavior, chemical reactivity, and ability to form compounds. Understanding valence electrons is essential for comprehending the intricate world of chemical interactions.