Atomic Number: Unlocking The Identity And Properties Of Elements

Atomic number, the number of protons in the nucleus, determines an element’s identity. The atomic number of arsenic is 33, indicating that it has 33 protons. As the only positively charged particles in the nucleus, protons play a crucial role in defining an element’s chemical characteristics. Understanding this relationship is fundamental for comprehending the structure and reactivity of elements.
Atomic Number: The Key to Understanding an Element’s Identity
As we delve into the fascinating world of chemistry, understanding the building blocks of matter is crucial. One of the most fundamental concepts is the atomic number, which plays a pivotal role in determining the identity and behavior of every element.
In the heart of every atom lies its nucleus, a dense core packed with positively charged particles called protons. The atomic number of an element is simply the number of protons residing in its nucleus. This number is like a unique fingerprint, distinguishing each element from all others.
Why is the atomic number so significant? Because it directly corresponds to the number of electrons orbiting the nucleus, which in turn governs an element’s chemical properties. For instance, elements with an equal number of protons and electrons exhibit a neutral charge, while those with an imbalance become ions, eagerly reacting with other elements to achieve stability.
Arsenic: A Case in Point
Let’s take arsenic as an example. This metalloid possesses an atomic number of 33. This means that every arsenic atom harbors 33 protons in its nucleus, accompanied by 33 electrons swirling around it. This precise arrangement gives arsenic its distinct chemical signature, making it both toxic and yet essential in various industrial applications.
Protons: The Nucleus’s Positive Force
It’s worth emphasizing that protons are the only positively charged particles within the nucleus. This makes counting protons essential for determining the atomic number. Neutrons, which share the nucleus but lack an electrical charge, do not contribute to the atomic number.
By understanding the close relationship between atomic number and the number of protons in an element’s nucleus, we unlock a key to comprehending the structure and reactivity of all matter around us.
Atomic Number: Unraveling the Essence of Elements
In the realm of chemistry, every element holds a unique identity, and the key to deciphering it lies in understanding atomic number. It’s like a secret code embedded within the heart of every atom, revealing the fundamental blueprint that defines an element’s personality.
The Proton Puzzle
Picture an atom as a tiny universe, with a nucleus at its core. Within this nucleus reside protons, the fearless warriors of the atomic world. Each proton carries a positive charge, akin to a knight’s gleaming shield. And the number of protons in the nucleus, like a royal crest, defines the atomic number of that element.
Atomic Number: The Ultimate Identity Card
The atomic number is the defining characteristic that distinguishes one element from another. It’s the fingerprint that proclaims, “I am this element and no other.” No two elements can share the same atomic number, making it the ultimate identity card in the periodic table.
Chemical Behavior: A Proton-Driven Dance
The number of protons in the nucleus isn’t just a numerical quirk; it has profound implications for an element’s chemical behavior_. Protons orchestrate the dance of _electrons, the tiny particles that orbit the nucleus. Electrons determine an element’s reactivity, dictating how it interacts with other elements to form compounds.
In essence, understanding the atomic number is akin to possessing the master key to the world of elements. It unlocks the secrets of their identity, explains their behavior, and enables us to unravel the intricate tapestry of chemical reactions.
The Heart of the Atom: Uncovering the Number of Positively Charged Particles
Every atom, the fundamental building block of matter, possesses a central core known as the nucleus. Within this nucleus reside the tiniest of particles, protons and neutrons. Protons, the focus of our discussion, carry a positive charge and play a crucial role in determining an element’s identity.
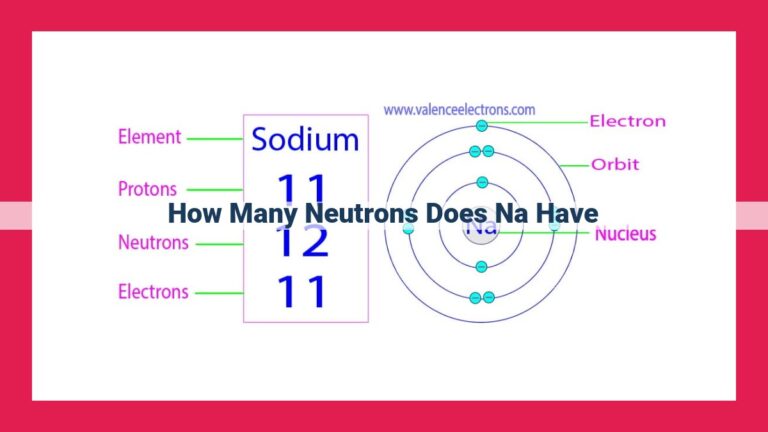
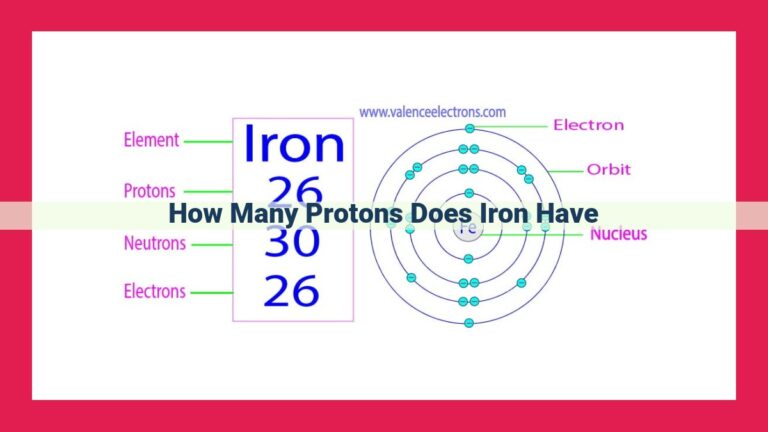
The number of protons in an element’s nucleus is known as its atomic number. This numerical value not only identifies an element but also governs its chemical behavior. For instance, an element with one proton in its nucleus is hydrogen, while an element with 26 protons is iron.
The Direct Correspondence: Atomic Number and Protons
The atomic number of an element serves as a direct indicator of the number of protons within its nucleus. Every element has a unique atomic number, which distinguishes it from all others. This number is a fundamental property that remains constant for a given element.
Protons: The Sole Positively Charged Nuclei Inhabitants
Within the nucleus, protons stand alone as the only positively charged particles. Neutrons, on the other hand, lack an electrical charge and contribute to the nucleus’s mass without influencing its charge. The number of protons in the nucleus, therefore, determines the overall positive charge of the nucleus.
This distinction between protons and neutrons is critical for comprehending atomic structure. The positive charge of the protons counterbalances the negative charge of the electrons that orbit the nucleus, creating a balanced and stable atom.
Understanding the relationship between the atomic number and the number of positively charged particles in the nucleus is essential for grasping the fundamental properties of elements. It lays the foundation for comprehending chemical reactions, as the number of protons influences how an element interacts with other atoms.
Exploring the Atomic Number and the Number of Protons in Arsenic
In the realm of chemistry, understanding the concept of atomic number is akin to unlocking the building blocks of matter. It’s the fundamental property that governs the identity and behavior of every single element in the periodic table. Arsenic, our element of interest, embodies this concept perfectly.
Atomic number, in essence, is the number of protons residing in the nucleus of an atom. These protons hold a special significance because they’re the only positively charged particles in the nucleus, effectively dictating the element’s chemical properties.
Take arsenic, for instance. Its atomic number is 33, which means there are 33 protons nestled within its atomic core. This crucial piece of information unveils the very essence of arsenic, revealing its unique chemical fingerprint.
Delving deeper into this concept, we discover that the number of protons in an atom directly corresponds to its atomic number. This means that arsenic, with its 33 protons, unequivocally identifies it as the 33rd element on the periodic table. It’s a fundamental attribute that sets arsenic apart from every other element, giving it its distinctive chemical characteristics.