Mastering Amino Acid Memorization: A Comprehensive Guide To Efficient Learning
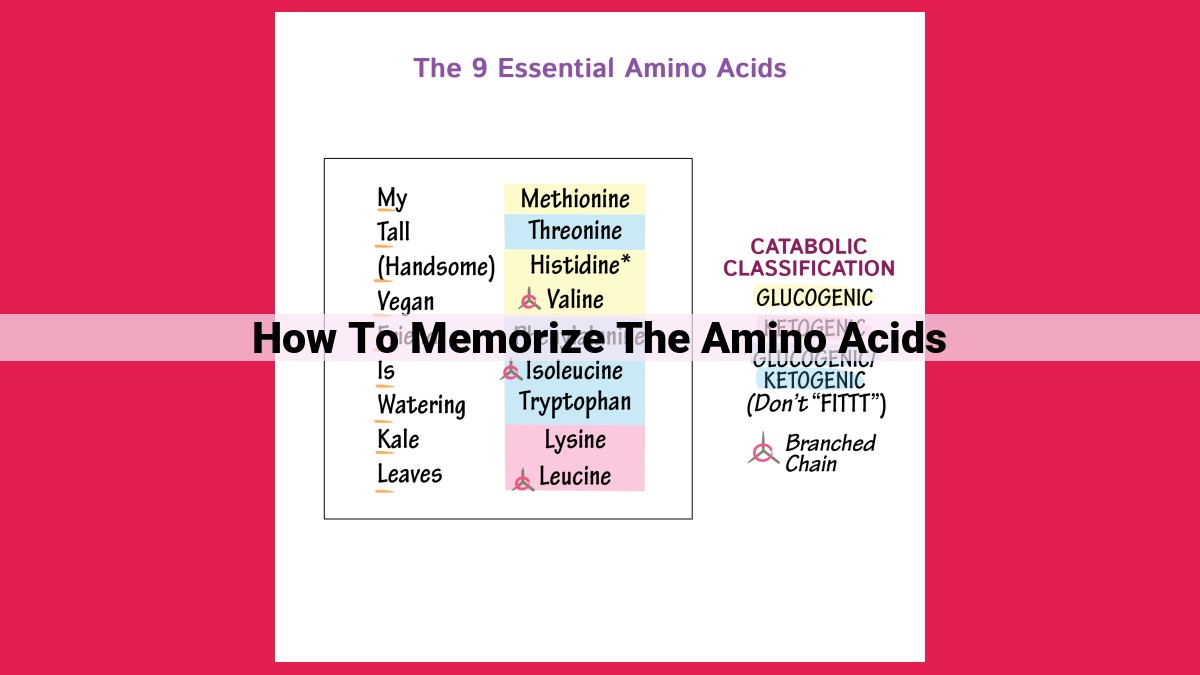
To memorize amino acids effectively, chunk them into groups, use mnemonics like “Never Let Monkeys Eat Bananas” for nonpolar amino acids, and review them regularly using spaced repetition. Actively recall information without references and use visual aids like diagrams. Sensory engagement through songs or rhymes can aid memorization. Connect amino acids to personal experiences or stories to make them meaningful. Engage in group study and quizzes for collaboration. Utilize flashcards to test memory. Writing or drawing amino acids helps improve comprehension. Tailor memorization strategies to your individual learning style for better results.
The Significance of Amino Acid Memorization: A Foundation for Understanding the Symphony of Life
Unveiling the intricate dance of life requires a deep comprehension of the fundamental building blocks that orchestrate its marvelous symphony – amino acids. Each amino acid, a molecular enigma, holds a pivotal role in the tapestry of biological processes, from the construction of proteins to the regulation of cellular functions. Grasping their identity and characteristics is an indispensable endeavor for those seeking to unravel the complexities of life’s enigmatic choreography.
Amino Acids: The Master Architects of Life’s Blueprint
Envision a bustling city, teeming with towering skyscrapers, modest homes, and winding streets – each structure unique, yet intertwined in the intricate tapestry of urban life. So too, amino acids form the cornerstone of biological systems, serving as the building blocks of proteins, the essential machinery that drives cellular processes.
Proteins, nature’s molecular maestros, orchestrate a symphony of vital functions, from catalyzing biochemical reactions to ferrying substances across cellular membranes. Their ability to fulfill these diverse roles stems from the precise arrangement of amino acids, each contributing its unique properties to the overall protein structure and function.
Delving into the Molecular Alphabet of Life
Just as the letters of the alphabet combine to form words and sentences, amino acids assemble in specific sequences to create proteins. Understanding these sequences is crucial, for they determine the protein’s structure and, ultimately, its function.
memorizing the 20 standard amino acids, the building blocks of proteins, is a daunting task for many students. However, various techniques and strategies can make this process more manageable and effective.
One effective method is chunking, which involves breaking down the 20 amino acids into smaller groups based on their properties, such as their polarity or side chain characteristics. This can make them easier to remember and recall.
Mnemonics and acronyms are also helpful for memorizing amino acids. For example, the acronym “HARK” can be used to remember the four hydrophobic amino acids (histidine, alanine, arginine, and lysine).
Spaced repetition is another effective technique for memorizing amino acids. This involves reviewing the amino acids at increasing intervals, which helps to strengthen memories and improve long-term retention.
Active recall is also important for memorizing amino acids. This involves trying to recall the amino acids without looking at your notes. This forces you to think about the information and helps to improve your memory.
Chunking: Divide and Conquer the Amino Acid Landscape
Imagine yourself as a biochemist navigating the complex world of amino acids, the building blocks of life. The sheer number and diversity of these molecules can seem overwhelming, making it challenging to grasp the intricacies of biological processes.
But fear not! Chunking, a strategy as effective as a mighty divide-and-conquer general, comes to your rescue. By breaking down the vast army of amino acids into smaller, more manageable groups based on common characteristics, you can conquer memorization with newfound ease.
This brilliant strategy is not a mere suggestion; it’s a scientifically proven method. Research has consistently shown that chunking is a highly efficient approach to enhancing memory and comprehension. One study even found that participants who chunked information into groups of three or four items recalled significantly more than those who attempted to memorize the same information as a single, overwhelming whole.
So, how do you divide and conquer the amino acid landscape? Start by understanding their key properties:
- Polarity: Group amino acids based on their ability to dissolve in water (polar) or oil (nonpolar).
- Charge: Identify amino acids that are positively charged (basic), negatively charged (acidic), or neutral.
- Side chain structure: Categorize amino acids based on the structure of their side chains, which can be aliphatic (nonpolar), aromatic (nonpolar), hydroxylated (polar), or sulfhydryl (polar).
Chunking amino acids based on these properties not only makes them easier to memorize, but it also helps you understand the functional roles they play in biological systems. By comprehending the relationships between structure and function, you’ll gain a deeper understanding of biochemistry and be well-equipped to tackle even the most complex biological processes.
Mnemonics and Acronyms: Unlock the Secrets of Amino Acids
In the realm of biology, amino acids hold the key to understanding the intricate tapestry of life. Their mastery unlocks the secrets of proteins, the building blocks of cells. Yet, memorizing these essential molecules can be a daunting task. Enter the world of mnemonics and acronyms, where creativity and fun collide to make learning a breeze.
Let’s dive into some clever mnemonics that will help you remember amino acids like a pro:
-
Polar Pals: Asparagine, Glutamine, Serine, and Threonine are all polar, making them the perfect friends.
-
Aromatic Accomplices: Phenylalanine, Tyrosine, and Tryptophan boast aromatic rings, like a trio of fragrant companions.
-
Basic Buddies: Histidine, Lysine, and Arginine are all basic, sharing a cheerful disposition.
-
Acidic Attitude: Aspartic acid and Glutamic acid have a sour demeanor, thanks to their acidic nature.
Acronyms are another powerful tool in the memorization toolbox:
-
PONFADE: Proline, Ornithine, Nitrogen, Phenylalanine, Alanine, Asparagine, Aspartic Acid, Glutamic Acid
-
EAGLE: Extracellular, Alanine, Glycine, Leucine, and Glutamic acid
By harnessing the power of mnemonics and acronyms, you can transform amino acid memorization from a chore into a delightful game. Embrace these tricks and witness your knowledge soar.
Spaced Repetition: Optimize Your Amino Acid Recall
The Art of Reinforcement
Memorizing amino acids can be a daunting task, but spaced repetition offers a powerful solution. This technique involves reviewing the material at progressively increasing intervals, reinforcing the information in your memory and making it stick.
Why Spaced Repetition Works
When you first encounter new information, it’s stored in your short-term memory. However, if you don’t review it regularly, it gradually fades away. Spaced repetition prevents this forgetting curve by reminding you of the information at strategic intervals.
How to Implement Spaced Repetition
Start by reviewing the amino acids you’re trying to memorize immediately after you learn them. Then, review them again after a few hours. As you progress, gradually increase the time between reviews. For example, you might review them:
- Day 1: Immediately, 4 hours later, 12 hours later
- Day 2: 24 hours later, 48 hours later
- Day 3: 72 hours later, 96 hours later
- Week 1: 1 week later
- Month 1: 1 month later
Benefits of Spaced Repetition
Incorporating spaced repetition into your study routine has several key benefits:
- Enhances long-term retention: By repeatedly reviewing the material, you strengthen the neural connections in your brain, making the information more permanent.
- Reduces study time: Spaced repetition makes it easier to remember the material, which means you’ll need less time to review it later.
- Improves comprehension: Each time you review the amino acids, you have the opportunity to deepen your understanding and make connections between different concepts.
Spaced repetition is an essential technique for memorizing amino acids effectively. By reviewing the material at increasing intervals, you can reinforce the information in your memory and make it stick for the long term. Whether you’re a student, researcher, or healthcare professional, implementing spaced repetition will greatly enhance your ability to recall and use amino acid knowledge.
Active Recall: Test Yourself to Master Amino Acid Memorization
In the pursuit of biological understanding, mastering amino acids is essential. However, memorizing these building blocks can be daunting. But fear not, my friend! Active recall is your secret weapon, a powerful technique to cement amino acids into your memory.
What’s Active Recall?
It’s simply the act of testing yourself without peeking at your notes. It forces your brain to work harder, retrieving information from its depths. Unlike passive reading, active recall engages your critical thinking and problem-solving skills.
How to Practice Active Recall for Amino Acids
-
Create Flashcards: Write down an amino acid’s name on one side, and its properties (e.g., structure, charge) on the other. Test yourself by flipping the card and trying to recall the missing information.
-
Self-Quizzes: Set aside time to quiz yourself, without any notes or textbooks. Focus on specific groups of amino acids, or even random selections. Challenge yourself to recall their names, abbreviations, and properties.
-
Teach Someone Else: One of the best ways to test your understanding is to explain it to someone else. Try to teach a friend, family member, or even a stuffed animal about amino acids. If you can convey the information clearly, you’re on the right track.
-
Drawing and Writing: Sketching amino acid structures or writing out their properties not only reinforces their images in your mind but also activates different parts of your brain.
Benefits of Active Recall
-
Improved Retention: Studies have shown that active recall significantly improves long-term memory. It prevents information from slipping away into the abyss of forgotten knowledge.
-
Critical Thinking: By actively retrieving information, you engage higher-order thinking skills. You learn to analyze, synthesize, and apply your knowledge, not just memorize facts.
-
Preparation for Exams: Active recall is the ultimate exam preparation strategy. It forces you to confront gaps in your understanding and ensures that you’re truly mastering the material.
So, buckle up and challenge yourself with active recall. It’s the key to unlocking the mysteries of amino acids and empowering yourself with unforgettable knowledge.
Visual Aids: See the Structure
Visual aids can be incredibly effective in helping you understand the structure and characteristics of amino acids. Diagrams, charts, and images can make complex concepts more accessible and help you retain information better.
Diagrams provide a clear representation of the arrangement of atoms and bonds within an amino acid. By visualizing the structure, you can gain a deeper understanding of its functionality. For instance, a diagram of the amino acid glycine will show you that it has a central carbon atom bonded to an amino group, a carboxyl group, a hydrogen atom, and a side chain consisting of a single hydrogen atom.
Charts can be useful for comparing the properties of different amino acids. A table summarizing the polarity, charge, and side chain characteristics of the 20 common amino acids can make it easier for you to identify similarities and differences among them. This can be particularly helpful when it comes to understanding their role in protein structure and function.
Images, such as photographs or illustrations, can provide a tangible representation of amino acids. Seeing an image of the amino acid serine, for example, can help you visualize its structure and appreciate its unique characteristics.
By incorporating visual aids into your amino acid memorization strategy, you can enhance your understanding and retention. Whether it’s a diagram of a single amino acid, a chart comparing multiple amino acids, or an image that illustrates their role in a protein, visual aids can be invaluable tools for mastering this complex topic.
Sound and Music: Engage Your Senses to Master Amino Acids
Learning is not just confined to textbooks and lectures. Sometimes, the most effective way to grasp complex concepts is to engage your senses. When it comes to memorizing amino acids, sound and music can be incredibly powerful tools.
Rhymes, songs, and other auditory cues can create a memorable experience that sticks with you. By associating amino acids with catchy tunes or witty rhymes, you make them easier to recall. For instance, the rhyme “Serine, threonine, asparagine, and glutamine” can help you remember the polar, uncharged amino acids.
Beyond rhymes, exploring songs specifically designed for amino acid memorization can be highly beneficial. These songs often incorporate repetition and melodies that make it easier to learn and retain information. By listening to such songs regularly, you can turn the memorization process into an enjoyable and engaging activity.
In addition to songs, other auditory cues like podcasts or audiobooks can also be effective. Listening to experts or students discussing amino acids can provide a different perspective and reinforce your understanding. Furthermore, audiobooks can be a convenient way to learn while multitasking, such as during your commute or workout.
By incorporating sound and music into your memorization strategy, you not only enhance your learning but also make it a more enjoyable and memorable experience.
Association and Stories: Personalize Learning
Subheading: Craft a Memorable Narrative
In the realm of amino acid memorization, mere rote memorization falls short. To truly master these building blocks of life, infuse your learning with a touch of creativity. Associate amino acids with personal experiences that resonate with you. Whether it’s a peculiar nickname or an amusing anecdote, weave a narrative that transforms these scientific entities into characters in a vibrant storyline.
Subheading: Engage Your Imagination
Allow your imagination to soar as you paint vivid mental images. Visualize amino acids as your favorite superheroes or whimsical creatures. Assign each a unique personality or backstory that makes them stand out in your memory. By creating a memorable tapestry of stories, you’ll not only enhance your understanding but also make the memorization process a delight.
Subheading: Apply to Real-World Scenarios
Take your amino acid adventures beyond the confines of textbooks and into the wide world. Connect their properties to everyday objects or relate them to current events. For instance, imagine the aromatic amino acids as the sweet scent of freshly baked bread or the pungent odor of a ripe banana. Such associations bridge the gap between the academic and the practical, making your knowledge both meaningful and unforgettable.
Subheading: Foster a Personal Connection
Treat amino acids as more than just abstract symbols. Personalize your studies by assigning them roles in your daily life. Designate glycine as your morning alarm, a reminder to start the day with a positive attitude. Or envision arginine as a superhero protecting you from day-to-day stresses. By infusing amino acids with a touch of your individuality, you’ll create a deep connection that aids in their recall.
Group Study: Collaborate and Quiz
Engage in Collaborative Discussions
Joining forces with fellow students in group discussions sparks a dynamic exchange of ideas. Engage in active listening as your peers share their perspectives, expanding your knowledge base. Participate eagerly, posing thoughtful questions and contributing insightful comments. These discussions create a rich learning environment, where diverse perspectives merge, igniting a deeper understanding of amino acids.
Challenge Yourself with Quizzes
Collaborate with your group to design interactive quizzes. Test each other’s knowledge through challenging questions, covering essential concepts and structures of amino acids. Provide constructive feedback, highlighting areas where further study is needed. Quizzes not only assess comprehension but also reinforce learning, solidifying the information in your memory.
Harness the Power of Collaboration
Foster a spirit of collaborative learning, where you actively engage in solving problems and sharing knowledge with your peers. Discuss complex concepts, exploring different viewpoints and approaches. Brainstorm creative strategies to memorize amino acids, drawing upon the collective wisdom of the group. Together, you can overcome obstacles and achieve academic success.
Flashcards: A Powerful Tool for Reinforcing Amino Acid Knowledge
Flashcards, those ubiquitous study aids, aren’t just for memorizing vocabulary anymore. They can also be a game-changer for understanding the complexities of amino acids.
Imagine you’re trying to grasp the properties of 20 different amino acids. It can feel like navigating a maze. But with flashcards, you can divide and conquer, breaking down these complex molecules into manageable chunks.
Each flashcard becomes a concise summary of an amino acid’s key characteristics: its name, structure, polarity, and so on. By testing your memory with these flashcards, you’re not just memorizing data; you’re reinforcing concepts and building a deep understanding.
Moreover, flashcards allow you to personalize your learning experience. Jot down any associations or personal anecdotes that you find helpful in remembering specific amino acids. This active engagement makes the memorization process more meaningful and less like rote memorization.
So, next time you’re struggling to decipher the amino acid alphabet, reach for a deck of flashcards. They’re not just a tool for memorization; they’re a pathway to mastery.
Writing and Drawing: Enhance Comprehension
Transforming amino acid memorization from a daunting task to an engaging experience, writing and drawing emerge as powerful tools to enhance comprehension and retention. By physically writing out the names, structures, and properties of amino acids, you engage your cognitive processing and muscle memory. This multisensory approach creates stronger connections in your brain, solidifying the information in your long-term memory.
Drawing structural diagrams of amino acids is particularly effective. Sketching out the backbone, side chains, and other key features helps you visualize the molecular structures, fostering a deeper understanding of their three-dimensional properties. By labeling each atom and functional group, you reinforce the names and characteristics of the amino acids, turning abstract concepts into tangible representations.
Furthermore, creating colorful charts and tables can organize the information in a way that makes it easy to recall. Color-coding amino acids based on their properties, such as polarity or structure, helps you associate them with specific categories, making it easier to retrieve the information when needed.
In conclusion, incorporating writing and drawing into your amino acid memorization strategy is an innovative and multifaceted approach that enhances comprehension, facilitates retention, and fosters a deeper understanding of the building blocks of life. Embrace these techniques and unlock a world of effortless amino acid mastery.
Personalization and Adaptation: Tailor to Your Style
Embrace Your Uniqueness
Just as amino acids come in diverse structures and properties, learning styles vary among individuals. It’s crucial to recognize that there’s no one-size-fits-all approach to memorizing amino acids. Embrace your unique strengths and preferences and tailor the strategies to suit your individual learning style.
Sensory Symphony
Engage your senses by utilizing auditory, visual, and kinesthetic cues. If you’re an auditory learner, create rhymes, songs, or listen to podcasts that cover amino acids. Visual learners may find diagrams, charts, or images helpful. For kinesthetic learners, actively handle flashcards or draw structures of amino acids to enhance comprehension.
Imagination and Storytelling
Don’t just memorize facts; personalize the learning experience. Associate amino acids with personal memories, anecdotes, or imaginative scenarios. Create stories that weave together the properties and functions of amino acids. This engaging and meaningful approach will make memorization effortless.
Collaboration and Quizzing
Share your knowledge and learn from others. Join study groups, engage in quizzes, and discuss amino acids with your peers. This collaborative environment foster understanding and provides new perspectives. Quizzes help test your knowledge and identify areas for improvement.
Writing and Drawing for Comprehension
Actively engage with the material by writing or drawing amino acids and their properties. This repetitive process reinforces concepts and improves recall. Write poems, summaries, or even create your own flashcards. By engaging multiple senses, you’ll strengthen your understanding and make memorization more enjoyable.